Abstract
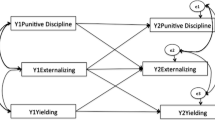
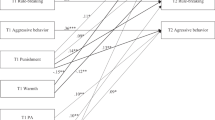
We tested whether individual differences in a component of early conscience mediated relations between parental discipline and externalizing behavior problems in 238 3.5-year-olds. Parents contributed assessments of discipline practices and child moral regulation. Observations of children's behavioral restraint supplemented parental reports. Parents and teachers reported on child externalizing symptoms. Parental induction, warm responsiveness, and less frequent use of physical punishment generally were associated with higher levels of moral regulation and fewer externalizing problems. Moreover, moral regulation partially mediated relationships between discipline and externalizing symptoms, with the clearest case of mediation involving induction. However, relationships were found for boys only. Results support a mediation model wherein inductive and physical discipline may influence the expression of boys' externalizing behavior through effects on conscience. Finally, results suggest that different developmental processes may be associated with early externalizing problems in boys and girls, and confirm that fathers' reports contribute to our understanding of the origins of child externalizing problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1992). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/23 and 1992 profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1997). Guide for the Caregiver-Teacher Report Form for Ages 2-5. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., Edelbrock, C., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Empirically based assessment of the behavioral/emotional problems of 2-and 3-year-old children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 15, 629-650.
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., Rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63, 575-582.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173-1182.
Campbell, S. B. (1995). Behavior problems in preschool children: A review of recent research. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 36, 113-149.
Campbell, S. B., Shaw, D. S., & Gilliom, M. (2000). Early externalizing behavior problems: Toddlers and preschoolers at risk for later maladjustment. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 467-488.
Deater-Deckard, K., & Dodge, K. A. (1997). Externalizing behavior problems and discipline revisited: Nonlinear effects and variation by culture, context, and gender. Psychological Inquiry, 8, 161-175.
DeKlyen, M., Biernbaum, M. A., Speltz, M. L., & Greenberg, M. T. (1998). Fathers and preschool behavior problems. Developmental Psychology, 34, 264-275.
Denham, S. A., Workman, E., Cole, P. M., Weissbrod, C., Kendziora, K. T., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (2000). Prediction of externalizing behavior problems from early to middle childhood: The role of parental socialization and emotion expression. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 23-45.
Dix, T., & Grusec, J. E. (1983). Parental influence techniques: An attributional analysis. Child Development, 54, 645-652.
Dodge, K. A., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (1994). Socialization mediators of the relation between socioeconomic status and child conduct problems. Child Development, 65, 649-665.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., Spinrad, T. L., Fabes, R., Shepard, S., Reiser, M., et al. (2001). The relations of regulation and emotionality to children's externalizing and internalizing problem behavior. Child Development, 72, 1112-1134.
Eisenberg, N., Losoya, S., & Fabes, R. A. (2001). Parental socialization of children's dysregulated expression of emotion and externalizing problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 15, 183-205.
Fagot, B. I., & Hagan, R. (1991). Observations of parent reactions to sex-stereotyped behaviors: Age and sex effects. Child Development, 62, 617-628.
Gardner, F., & Ward, S. (2000). Parent-child interaction and children's well-being: Reducing conduct problems and promoting conscience development. In A. Buchanan (Ed.), Promoting children's emotional well-being (pp. 95-127). New York: Oxford University Press.
Gershoff, E. T. (2002). Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: A meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychological Bulletin, 128, 539-579.
Grusec, J. E., & Goodnow, J. J. (1994). Impact of parental discipline methods on the child's internalization of values: A reconceptualization of current points of view. Developmental Psychology, 30, 4-19.
Grusec, J. E., & Kuczynski, L. (1980). Direction of effect in socialization: A comparison of the parent's versus the child's behavior as determinants of disciplinary techniques. Developmental Psychology, 16, 1-9.
Hastings, P. D., Zahn-Waxler, C., Robinson, J., Usher, B., & Bridges, D. (2000). The development of concern for others in children with behavior problems. Developmental Psychology, 36, 531-546.
Hay, D. F., Castle, J., & Davies, L. (2000). Toddlers' use of force against familiar peers: A precursor of serious aggression? Child Development, 71, 457-467.
Hinshaw, S. P., & Nigg, J. T. (1999). Behavior rating scales in the assessment of disruptive behavior problems in childhood. In D. Shaffer, C. P. Lucas, & J. E. Richters (Eds.), Diagnostic assessment in child and adolescent psychopathology (pp. 91-126). New York: Guilford Press.
Hirschi, T. (1969). Causes of delinquency. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Hoffman, M. L. (1983). Affective and cognitive processes in moral internalization: An information processing approach. In E. T. Higgins, D. Ruble, & W. Hartup (Eds.), Social cognition and social development: A socio-cultural perspective (pp. 236-274). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Hoffman, M. L. (1994). Discipline and internalization. Developmental Psychology, 30, 26-28.
Hoffman, M. L. (2000). Empathy and moral development: Implications for caring and justice. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Hoffman, M. L., & Saltzstein, H. D. (1967). Parent discipline and the child moral development. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 5, 45-57.
Judd, C. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1981). Process analysis: Estimating mediation in treatment evaluations. Evaluation Review, 5, 602-619.
Keenan, K., & Shaw, D. (1997). Developmental and social influences on young girls' early problem behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 121, 95-113.
Keenan, K., Shaw, D., Delliquadri, E., Giovannelli, J., & Walsh, B. (1998). Evidence for the continuity of early problem behaviors: Application of a developmental model. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26, 441-454.
Keenan, K., & Wakschlag, L. S. (2000). More than the terrible twos: The nature and severity of behavior problems in clinic-referred preschool children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 33-46.
Kochanska, G. (1993). Toward a synthesis of parental socialization and child temperament in early development of conscience. Child Development, 64, 325-347.
Kochanska, G. (1997). Multiple pathways to conscience for children with different temperaments from toddlerhood to age 5. Development Psychology, 33, 228-240.
Kochanska, G., & Aksan, N. (1995). Mother-child mutually positive affect, the quality of child compliance to requests and prohibitions, and maternal control as correlates of early internalization. Child Development, 66, 236-254.
Kochanska, G., DeVet, K., Goldman, M., Murray, K., & Putnam, S. (1994). Maternal reports of conscience development and temperament in young children. Child Development, 65, 852-868.
Kochanska, G., Gross, J. N., Lin, M., & Nichols, K. E. (2002). Guilt in young children: Development, determinants, and relations with a broader system of standards. Child Development, 73, 461-482.
Kochanska, G., & Murray, K. (2000). Mother-child mutually responsive orientation and conscience development: From toddler to early school age. Child Development, 71, 417-431.
Kochanska, G., Murray, K., Jacques, T. Y., Koenig, A. L., & Vandegeest, K. A. (1996). Inhibitory control in young children and its role in emerging internalization. Child Development, 67, 490-507.
Krevans, J., & Gibbs, J. C. (1996). Parents' use of inductive discipline: Relations to children's empathy and prosocial behavior. Child Development, 67, 3263-3277.
Loeber, R., Lahey, B. B., & Thomas, C. (1991). Diagnostic conundrum of oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 100, 379-390.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In E. M. Hetherington (Ed.), Mussen manual of child psychology (4th ed., Vol. 4, pp. 1-102). New York: Wiley.
MacKinnon, D. P., Warsi, G., & Dwyer, J. H. (1995). A simulation study of mediated effect. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 30, 41-62.
MacQuiddy, S. L., Maise, S. J., & Hamilton, S. B. (1987). Empathy and affective perspective-taking skills in parent-identified conduct-disordered boys. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 16, 260-268.
Nobes, G., & Smith, M. (1997). Physical punishment of children in two-parent families. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 2, 271-281.
Nobes, G., Smith, M., Upton, P., & Heverin, A. (1999). Physical punishment by mothers and fathers in British homes. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 14, 887-902.
Olson, S. L., Bates, J. E., Sandy, J. M., & Lanthier, R. (2000). Early developmental precursors of externalizing behavior in middle childhood and adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 119-133.
Olson, S. L., Kerr, D. C. R., Sameroff, A. J., & Lopez, N. L. (2004). Conscience development in young children at risk for school-age externalizing problems. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Olson, S. L., & Sameroff, A. J. (1997). Social risk and self-regulation problems in early childhood. Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Mental Health.
Olson, S. L., Sameroff, A. J., Kerr, D. C. R., Lopez, N. L., & Wellman, H. M. (2004). Developmental foundations of externalizing problems in young children: The role of effortful control. Development and Psychopathology.
Patterson, G. R., Dishion, T. J., & Bank, L. (1984). Family interaction: A process model of deviancy training. Aggressive Behavior, 10, 253-267.
Phares, V., & Compas, B. E. (1992). The role of fathers in child and adolescent psychopathology: Make room for daddy. Psychological Bulletin, 111, 387-412.
Power, T. G., Kobayashi-Winata, H., & Kelley, M. L. (1992). Childrearing patterns in Japan and the United States: A cluster analytic study. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 15, 185-205.
Preacher, K. J., & Leonardelli, G. J. (2001). Calculation for the Sobel test: An interactive calculation tool for mediation tests. Retrieved July 22, 2003, from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Web site: http://www.unc.edu/~preacher/sobel/sobel.htm
Rothbart, M. K., & Bates, J. E. (1998). Temperament. In W. Damon & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., Vol. 3, pp. 105-176). New York: Wiley.
Rothbaum, F., & Weisz, J. R. (1994). Parental caregiving and child externalizing behavior in nonclinical samples: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 116, 55-74.
Schachar, R. (1991). Childhood hyperactivity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 32, 155-191.
Smetana, J. G. (1989). Toddlers' social interaction in the context of moral and conventional transgression in the home. Developmental Psychology, 25, 499-508.
Straus, M. A., & Stewart, J. H. (1999). Corporal punishment byAmerican parents: National data on prevalence, chronicity, severity, and duration, in relation to child and family characteristics. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 2, 55-70.
Tremblay, R. E., Pihl, R. O., Vitaro, F., & Dobkin, P. L. (1994). Predicting early onset of male antisocial behavior from preschool behavior. Archives of General Psychiatry, 51, 732-739.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Cole, P. M., Welsh, J. D., & Fox, N. A. (1995). Psychophysiological correlates of empathy and prosocial behaviors in preschool children with behavior problems. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 27-48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kerr, D.C.R., Lopez, N.L., Olson, S.L. et al. Parental Discipline and Externalizing Behavior Problems in Early Childhood: The Roles of Moral Regulation and Child Gender. J Abnorm Child Psychol 32, 369–383 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JACP.0000030291.72775.96
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JACP.0000030291.72775.96