Abstract
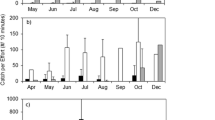
We provide here the first information on the abundance, settlement patterns and microhabitat use of settlers of two Lessepsian siganid species, Siganus rivulatus and S. luridus, in comparison with the two main native herbivores, Sparisoma cretense (Scaridae) and Sarpa salpa (Sparidae). S. rivulatus was the most abundant species (72%), followed by S. cretense (20%) and S. luridus (8%), whereas S. salpa was rare (<1%). A clear pattern of settlement could be established for S. rivulatus and S. cretense, with similar timing in 1999 and 2000. S. cretense settled in schools late June, while S. rivulatus settled mid-July. A few solitary settlers of S. luridus were observed in July and August, but none of S. salpa. All these herbivorous fish species settled in protected shallow areas offering hard substrates and algal communities. S. rivulatus was the most tolerant and adaptable species, able to settle on a large range of substrates and habitats, including rock pools, muddy harbours and sea grass beds. In the eastern Mediterranean Sea, S. rivulatus might have benefited from a release of competition pressure due to the low diversity and abundance of native herbivores. It has probably replaced S. salpa on the coast of Lebanon, being more competitive than the native sparid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bariche, M., M. Harmelin-Vivien & J.P. Quignard. 2003. Reproductive cycles and spawning periods of two Lessepsian siganid fishes on the Lebanese coast. J. Fish Biol. 62: 129-142.
Ben-Tuvia, A. 1964. Two siganid fishes of Red Sea origin in the eastern éMediterranean. Bull. Sea Fish. Res. Stn. 37: 3-9.
Ben-Tuvia, A., G.W. Kissil & D. Popper. 1973. Experiments in rearing rabbit fish (Siganus rivulatus) in seawater. Aquaculture 1: 359-364.
Bouchon-Navaro, Y. & M. Harmelin-Vivien. 1981. Quantitative distribution of herbivorous reef fishes in the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Mar. Biol. 63: 79-86.
Boudouresque, C.F. 1999. The Red Sea-Mediterranean link: Unwanted effects of canals. pp. 213-228. In: O.T. Sandlund, P.J. Schei & Å. Viken (ed.) Invasive Species and Biodiversity Management, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Brothers, E.B., D.M.B. Williams & P.F. Sale. 1983. Length of larval life in twelve families of fishes at ‘One Tree Lagoon’, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Biol. 76: 319-324.
Bryan, P.G. & B.B. Madraisau. 1977. Larval rearing and development of Siganus lineatus (Pisces: Siganidae) from hatching through metamorphosis. Aquaculture: 10: 243-252.
Choat, J.H. 1991. The biology of herbivorous fishes on coral reefs. pp. 120-155. In: P.F. Sale (ed.) The Ecology of Fishes on Coral Reefs, Academic Press, San Diego.
DeGirolamo, M., M. Scaggiante & M.B. Rasotto. 1999. Social organization and sexual pattern in the Mediterranean parrot-fish Sparisoma cretense (Teleostei: Scaridae). Mar. Biol. 135: 353-360.
Diamant, A., A. Ben-Tuvia, A. Baranes & D. Golani. 1986. An analysis of rocky coastal eastern Mediterranean fish assemblages and a comparison with an adjacent small artificial reef. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 97: 269-285.
Doherty, P.J. 2002. Variable replenishment and the dynamics of reef fish populations. pp. 327-355. In: P.F. Sale (ed.) Coral Reef Fishes: Dynamics and Diversity in a Complex Ecosystem, Academic Press, San Diego.
Fasola, M., L. Canova, F. Foschi, O. Novelli & M. Bressan. 1997. Resource use by a Mediterranean rocky slope fish assemblage. PSZNI: Mar. Ecol. 18: 51-66.
Fishelson, L. 2000. Marine animal assemblages along the littoral of the Israeli Mediterranean seashore: The Red-Mediterranean Seas communities of species. Ital. J. Zool. 67: 393-415.
Fredj, G. & C. Maurin. 1987. Les poissons dans la banque de donées MEDIFAUNE. Application à l'étude des caractéristiques de la faune ichtyologique Méditerranéenne. Cybium 11: 217-299.
Galil, B.S. 2000. A sea under siege-alien species in the Mediterranean. Biol. Inv. 2: 177-186.
Garcia Charton, J.A. & A. Pérez Ruzafa. 1998. Correlation between habitat structure and a rocky reef fish assemblage in SW Mediterranean. PSZNI: Mar. Ecol. 19: 111-128.
Garcia Rubies, A. & E. Macpherson. 1995. Substrate use and temporal pattern of recruitment in juvenile fishes of the Mediterranean littoral. Mar. Biol. 124: 35-42.
George, C.J. 1972. Notes on the breeding and movements of the rabbitfishes, Siganus rivulatus (Forsskål) and S. luridus Rüppell, in the coastal waters of the Lebanon. Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat. Geneva 79: 32-44.
George, C.J. & V. Athanassiou. 1967. A two year study of the fishes appearing in the seine fishery of St George Bay, Lebanon. Ann. Mus. Civ. Storia Nat. Genova 76: 237-294.
Golani, D. 1996. The marine ichthyofauna of the eastern Levant-History, inventory and characterization. Isr. J. Zool. 42: 15-55.
Golani, D. 2002. The Indo-Pacific striped eel catfish, Plotosus lineatus (Thunberg, 1787), (Osteichtyes: Siluriformes) a new record from the Mediterranean. Sci. Mar. 66: 321-323.
Golani, D., L. Orsi-Relini, E. Massutí & J.-P. Quignard. 2002. CIESM Atlas of Exotic Species in the Mediterranean. Vol. 1. Fishes. Monaco: CIESM Publishers. 256 pp.
Gonzalez, J.A., I.J. Lozano & C.M. Hernandez Cruz. 1993. Fecundidad de Sparisoma (Euscarus) cretense (L.) (Osteichthyes, Scaridae) en Canarias. Bol. Inst. Esp. Oceanogr. 9: 123-131.
Goren, M. & A. Aronov. 2002. First record of the Indo-Pacific Parrot fish Scarus ghobban in the eastern Mediterranean. Cybium 26: 239-240.
Gruvel, A. 1931. Les Etats de Syrie. Richesses marines et fluviales. Exploitation actuelle-Avenir. Bibliotèque de la Faune des Colonies Françaises, Socíeté d'Editions Géographiques, Maritimes et Coloniales, Paris. 453 pp.
Harmelin-Vivien, M.L., J.G. Harmelin, C. Chauvet, C. Duval, R. Galzin, P. Lejeune, G. Barnabé, F. Blanc, R. Chevalier, J. Duclerc & G. Lasserre. 1985. Evaluation visuelle des peuplements et populations de poissons: Méthodes et problémes. Rev. Ecol. (Terre et Vie) 40: 467-539.
Harmelin-Vivien, M.L., J.G. Harmelin & V. Leboulleux. 1995. Microhabitat requirements for settlement of juvenile sparid fishes on Mediterranean rocky shores. Hydrobiologia 300/301: 309-320.
Hoerl, A.E. 1962. Application of ridge analysis to regression problems. Chem. Eng. Prog. 58: 54-59.
Levin, P.S. 1991. Effects of microhabitat on recruitment variation in a Gulf of Maine reef fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 75: 183-189.
Lodge, D.M. 1993. Biological invasions: lessons for ecology. TREE 8: 133-137.
Lundberg, B. & D. Golani. 1995. Diet adaptations of Lessepsian migrant rabbitfishes, Siganus luridus and S. rivulatus, to the algal resources of the Mediterranean coast of Israel. PSZNI: Mar. Ecol. 16: 73-89.
Lundberg, B., G. Payiatas & M. Argyrou. 1999. Notes on the diet of the Lessepsian migrant herbivorous fishes, Siganus luridus and S. rivulatus, in Cyprus. Isr. J. Zool. 45: 127-134.
MacArthur, R.H. & E.O.Wilson. 1967. The theory of Island Biogeography, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ. 224 pp.
Papaconstantinou, C., H. Garagitsou, K.I. Stergiou, V. Vasilopoulou, G. Petrakis & T. Panos. 1986. The Potential of the Coastal Fishery Development in the Waters Surrounding the Kastellorhizo Isle (Dodecanese) Greece: National Centre for Marine Research, Athens (in Greek). 89 pp.
Petrakis, G. & C. Papaconstantinou. 1990. Biology of Sparisoma cretense in the Dodecanese (Greece). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 6: 14-23.
Popper, D.M. & N. Gundermann. 1975. Some Ecological and Behavioural aspects of siganid populations in the Red Sea and Mediterranean Coast of Israel in relation to their suitability for aquaculture. Aquaculture 6: 127-141.
Popper, D.M., R. Pitt. & Y. Zohar. 1979. Experiments on the propagation of Red Sea siganids and some notes on their reproduction in nature. Aquaculture 16: 177-181.
Por, F.D., 1978. Lessepsian Migration. The Influx of Red Sea Biota into the Mediterranean by way of the Suez Canal, Ecological Studies 23, Springer Verlag, Berlin. 228 pp.
Steinitz, W. 1927. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Küstenfauna Palästinas. I Teil-Publ. Staz. Zool. Napoli 8: 311-353.
Tolimieri, N. 1995. Effects of microhabitat characteristics on the settlement and recruitment of a coral reef fish at two spatial scales. Oecologia 102: 52-63.
Verlaque, M. 1990. Relations entre Sarpa salpa (Linnaeus, 1758) (Teleostéen, Sparidae), les autres poissons brouteurs et le phytobenthos algal mediterranéen. Oceanol. Acta 13: 373-388.
Woodland, D.J. 1983. Zoogeography of the Siganidae (Pisces): An interpretation of distribution and richness patterns. Bull. Mar. Sci. 33: 713-717.
Zibrowius, H. 1992. Ongoing modification of the Mediterranean marine fauna and flora by the establishment of exotic species. Mésogée 51: 83-107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bariche, M., Letourneur, Y. & Harmelin-Vivien, M. Temporal Fluctuations and Settlement Patterns of Native and Lessepsian Herbivorous Fishes on the Lebanese Coast (Eastern Mediterranean). Environmental Biology of Fishes 70, 81–90 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EBFI.0000022928.15148.75
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EBFI.0000022928.15148.75