Abstract
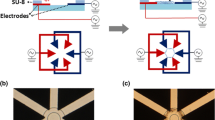
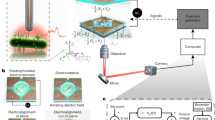
As biomolecular detection systems shrink in size, there is an increasing demand for systems that transport and position materials at micron- and nanoscale dimensions. Our goal is to combine cellular transport machinery—kinesin molecular motors and microtubules—with integrated optoelectronics into a hybrid biological/engineered microdevice that will bind, transport, and detect specific proteins, DNA/RNA molecules, viruses, or cells. For microscale transport, 1.5 μm deep channels were created with SU-8 photoresist on glass, kinesin motors adsorbed to the bottom of the channels, and the channel walls used to bend and redirect microtubules moving over the immobilized motors. Novel channel geometries were investigated as a means to redirect and sort microtubules moving in these channels. We show that DC and AC electric fields are sufficient to transport microtubules in solution, establishing an approach for redirecting microtubules moving in channels. Finally, we inverted the geometry to demonstrate that kinesins can transport gold nanowires along surface immobilized microtubules, providing a model for nanoscale directed assembly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D. Allen, N.S. Allen, and J.L. Travis, Cell Motil 1, 291 (1981).
S.B. Asokan, L. Jawerth, R.L. Carroll, R.E. Cheney, S. Washburn, and R. Superfine, Nano Letters 3, 431 (2003).
T.B. Brown and W.O. Hancock, Nano Letters 2, 1131 (2002).
J. Clemmens, H. Hess, J. Howard, and V. Vogel, Langmuir 19, 1738 (2003).
D.L. Coy, M. Wagenbach, and J. Howard, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 3667 (1999).
J.R. Dennis, J. Howard, and V. Vogel, Nanotechnology 10, 232 (1999).
R.W. Fitzgerald, Mechanics of Materials (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1982), p. 554.
F. Gittes, B. Mickey, J. Nettleton, and J. Howard, J. Cell. Biol. 120, 923 (1993).
D.D. Hackney, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 85, 6314 (1988).
W.O. Hancock and J. Howard, J. Cell. Biol. 140, 1395 (1998).
H. Hess, J. Clemmens, D. Qin, J. Howard, and V. Vogel, Nano Letters 1, 235 (2001).
Y. Hiratsuka, T. Tada, K. Oiwa, T. Kanayama, and T.Q. Uyeda, Biophys. J. 81, 1555 (2001).
J. Howard, Mechanics of Motor Proteins and the Cytoskeleton (Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA, 2001).
J. Howard, A.J. Hudspeth, and R.D. Vale, Nature 342, 154 (1989).
J. Howard, A.J. Hunt, and S. Baek, Methods Cell. Biol. 39, 137 (1993).
M.P. Hughes, Electrophoresis 23, 2569 (2002).
A. Hyman, D. Drechsel, D. Kellogg, S. Salser, K. Sawin, P. Steffen, L. Wordeman, and T. Mitchison, Methods Enzymol. 196, 478 (1991).
T.B. Jones, Electromechanics of Particles (Cambridge University Press, 1995).
N.I. Kovtyukhova and T.E. Mallouk, Chemistry 8, 4354 (2002).
L. Limberis and R.J. Stewart, Nanotechnology 11, 47 (2000).
J. Lowe, H. Li, K.H. Downing, and E. Nogales, J. Mol. Biol. 313, 1045 (2001).
S.A. Marras, F.R. Kramer, and S. Tyagi, Genet. Anal. 14, 151 (1999).
B.R. Martin, D.J. Dermody, B.D. Reiss, M. Fang, L.A. Lyon, M.J. Natan, and T.E. Mallouk, Adv. Mater. 11, 1021 (1999).
J.K.N. Mbindyo, B.D. Reiss, B.R. Martin, C.D. Keating, M.J. Natan, and T.E. Mallouk, Adv. Mater. 13, 249 (2001).
E. Meyhöfer and J. Howard, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 92, 574 (1995).
R.D. Miller and T.B. Jones, Biophys. J. 64, 1588 (1993).
S.G. Moorjani, L. Jia, T.N. Jackson, and W.O. Hancock, Nano Letters 3, 633 (2003).
H. Morgan, M.P. Hughes, and N.G. Green, Biophys. J. 77, 516 (1999).
E. Nogales, M. Whittaker, R.A. Milligan, and K.H. Downing, Cell 96, 79 (1999).
R.a.M. Pethig, G.H. Markx, Trends in Biotechnology 15, 426 (1997).
H.A. Pohl, Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Non-Uniform Electric Fields (Cambridge University Press, 1978).
B. Razavi, B.R. Martin, S.K. St. Angelo, T.E. Mallouk, and T.N. Jackson, 44th Electronic Materials Conference Digest (2002).
M. Schena, D. Shalon, R.W. Davis, and P.O. Brown, Science 270, 467 (1995).
M.J. Schnitzer, K. Visscher, and S.M. Block, Nat. Cell. Biol. 2, 718 (2000).
R. Stracke, K.J. Bohm, J. Burgold, H.-J. Schacht, and E. Unger, Nanotechnology 11, 52 (2000).
R. Stracke, K.J. Bohm, L. Wollweber, J.A. Tuszynski, and E. Unger, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293, 602 (2002).
K. Svoboda, C.F. Schmidt, B.J. Schnapp, and S.M. Block, Nature 365, 721 (1993).
R.D. Vale, B.J. Schnapp, T.S. Reese, and M.P. Sheetz, Cell 40, 559 (1985).
M. Washizu, S. Suzuki, O. Kurosawa, T. Nishizaka, and T. Shinohara, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 30, 835 (1994).
R.C. Williams, Jr. and J.C. Lee, Methods Enzymol. 85 Pt B, 376 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, L., Moorjani, S.G., Jackson, T.N. et al. Microscale Transport and Sorting by Kinesin Molecular Motors. Biomedical Microdevices 6, 67–74 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BMMD.0000013368.89455.8d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BMMD.0000013368.89455.8d