Abstract
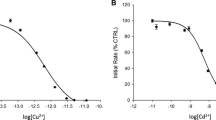
The pH dependent activation of calcineurin by exogenous metal ion was studied over the pH range from 6.5 to 9.0 in increments of 0.5 pH units. Calcineurin activated by Co2+, Ni2+, or Mg2+ was characterized and compared to the pH dependency of the Mn2+-activated enzyme (Martin, B.L., and Graves, D.J. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 14545–14550). The pH dependency of the kinetic parameters varied with metal ion and subsequent analysis yielded estimates for the pKa values for the enzyme-metal ion and the enzyme-metal ion-substrate complexes with each of the exogenous metal ions characterized. The evaluated pKas for enzyme-metal ion (EM) complexes showed an inverse relationship with the pKas of the M2+-H2O complex. In contrast, variation of the pKas for the enzyme-metal ion-substrate (EMS) complexes showed no trend. These data support the hypothesis that exogenous metal ion functions to facilitate a proton transfer before the turnover of substrate with the acidity of the exogenous metal ion as a primary determinant of its participation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogumil R, Namagaladze D, Schaarschmidt D, Schmachtel T, Hellstern S, Mutzel R, Ullrich, V. 2000 Inactivation of calcineurin by hydrogen peroxide and phenylarsine oxide. Eur J Biochem 267, 1407-1415.
Bradford MM. 1976 A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation for microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72, 248-254.
Cai L, Chu Y, Wilson SE, Schlender KK. 1995 A metal-dependent form of protein phosphatase 2A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 208, 274-279.
Carballo M, Marquez G, Conde M, Martin-Nieto J, Monteseirin J, Conde J, Pintado E, Sobrino F. 1999 Characterization of calcineurin in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 274, 93-100.
Chu Y, Lee EYC, Schlender KK. 1996 Activation of protein phosphatase 1. Formation of a metalloenzyme. J Biol Chem 271, 2574-2577.
Cohen PTW, Brewis ND, Hughes V, Mann DJ. 1990 Protein serine/ threonine phosphatases; an expanding family. FEBS Lett 268, 355-359.
Coleman JE. 1992 Structure and mechanism of alkaline phosphatase. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng 21, 441-483.
Egloff M-P, Cohen PTW, Reinemer P, Barford D. 1995 Structural basis for the recognition of regulatory subunits by the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1. J Mol Biol 254, 942-959.
Ferri A, Gabbianelli R, Casciati A, Paolucci E, Rotilio G, Carri MT. 2000 Calcineurin activity is regulated both by redox compounds and by mutant familial amytrophic lateral sclerosissuperoxide dismutase. J Neurochem 75, 606-613.
Fersht AR. 1999 Structure Mechanism in Protein Science. WH Freeman Press, New York.
Furuke K, Shiraishi M, Mostowski HS, Bloom ET. 1999 Fas ligand induction in human NK cells is regulated by redox through a calcineurin-nuclear factors of activated T cell-dependent pathway. J Immunol 162, 1988-1993.
Goldberg J, Huang H-b, Kwon Yg, Greengard P, Nairn AC, Kuriyan J. 1995 Three-dimensional structure of the catalytic subunit of protein serine/threonine phosphatase-1. Nature 376, 745-753.
Gopalakrishna R, Anderson WG. 1982 Biochem Biophys Res Commun Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site chromatography on calmodulin, application to purification of calmodulin by phenyl sepharose affinity chromatography. 104, 830-836.
Griffith JP, Kim JL, Kim EE, Sintchak MD, Thomson JA, Fitzgibbon MJ, Fleming MA, Caron PR, Hsiao K, Navia MA. 1995 X-Ray structure of calcineurin inhibited by the immunophilinimmunosuppressant FKBP12-FK506 Complex. Cell 82, 507-522.
Gupta RC, Khelwal RL, Sulakhe PV. 1984 Intrinsic phosphatase activity of bovine brain calcineurin requires a tightly bound trace metal. FEBS Lett 169, 251-255.
Haddy A, Sharp RR, Rusnak F. 1996 The Interaction of Mn2+ with calcineurin studied using NMR proton relaxation enhancement. Biophys J 70, A393.
Hengge AC, Martin BL. 1997 Isotope effect studies on the calcineurin phosphoryl-transfer reaction: transition state structure and the effect of calmodulin and Mn2+. Biochemistry 36, 10185-10191.
Ingebritsen TS, Cohen P. 1983 Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science 221, 331-338.
Kim EE, Wyckoff HW. 1991 Reaction mechanism of alkaline phosphatase based on crystal structures. Two-metal ion catalysis. J Mol Biol 218, 449-464.
King MM, Huang CY. 1983 Activation of calcineurin by nickel ions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 114, 955-961.
King MM, Huang CY. 1984 The calmodulin-dependent activation and deactivation of the phosphoprotein phosphatase, calcineurin, and the effect of nucleotides, pyrophosphate, and divalent metal ions. Identification of calcineurin as a Zn and Fe metalloenzyme. J Biol Chem 259, 8847-8856.
Kissinger CR, Perge HE, Knighton DR, Lewis CT, Pelletier LA, Tempczyk A, Kalish VJ, Tucker KD, Showalter RE, Moomaw EW, Gastinel LN, Habuka N, Chen X, Maldonado F, Barker JE, Bacquet R, Villafranca JE. 1995 Crystal structures of human calcineurin and the human fkbp12-fk506-calcineurin complex. Nature 378, 641-644.
Klee CB, Krinks MH, Manalan AS, Draetta GF, Newton DL. 1985 Control of calcineurin protein phosphatase activity. Adv Protein Phosphatases 1, 135-146.
Ladner CJ, Czech J, Maurice J, Lorens SA, Lee JM. 1996 Reduction of calcineurin enzymatic activity in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with neuropathologic changes. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 55, 924-931.
Li H-C. 1984 Activation of brain calcineurin phosphatase toward nonprotein phosphoesters by Ca2+, calmodulin, and Mg2+. J Biol Chem 259, 8801-8807.
Li H-C, Chan WWS. 1984 Activation of brain calcineurin towards proteins containing Thr(P) and Ser(P) by Ca2+, calmodulin, and Mg2+ and transition metal ions. Eur J Biochem 144, 447-452.
Martin BL. 1997 Selective activation of the calmodulin activated phosphatase, calcineurin, by dipicolinic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys 345, 332-338.
Martin BL. 2000 Evidence for a structure-function relationship in the activation of the protein phosphatase calcineurin by exogenous metals. Bioorg Chem 28, 17-27.
Martin BL, Rhode DJ. 1999 Effect of substitution inert metal complexes on calcineurin. Arch Biochem Biophys 366, 168-176.
Martin BL, Graves DJ. 1986 Mechanistic aspects of the low molecular weight phosphatase activity of the calmodulin activated phosphatase, calcineurin. J Biol Chem 261, 14545-14550.
Martin BL, Graves DJ. 1994 Isotopic probes of the mechanism of calcineurin catalysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1206, 136-142.
Martin BL, Jurado LA. 1998 Activation of calcineurin by the trivalent metal terbium. J Protein Chem 17, 473-478.
Martin BL, Jurado LA, Hengge AC. 1999 Comparison of the reaction progress of calcineurin with Mn2+ and Mg2+. Biochemistry 38, 3386-3392.
Martin BL, Li B, Liao C, Rhode DJ. 2000 Differences between Mg2+ and transition metal ions in the activation of calcineurin. Arch Biochem Biophys 380, 71-76.
Mertz P, Yu L, Sikkink R, Rusnak F. 1997 Kinetic and spectroscopic analyses of a conserved histidine in the metallophosphatases calcineurin and ? protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem 272, 21296-21302.
Mueller EG, Crowder MW, Averill BA, Knowles JR. 1993 Purple acid phosphatase: a diiron enzyme that catalyzes a direct phospho group transfer to water. J Am Chem Soc 115, 2974-2975.
Pallen CJ, Wang JH. 1984 Regulation of calcineurin by metal ions. J Biol Chem 259, 6134-6141.
Perrin DD. 1974 Buffers for pH and Metal Ion Control. Halsted Press, New York.
Reiter TA, Abraham RT, Choi M, Rusnak F. 1999 Redox regulation of calcineurin in Tlymphocytes. J Biol Inorg Chem 4, 632-644.
Seki K, Chen H-C, Huang KP. 1995 Dephosphorylation of protein kinase C substrates, neurogranin, neuromodulin, and MARCKS, by calcineurin and protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. Arch Biochem Biophys 316, 673-679.
Sharma RK, Wang JH. 1979 Preparation and assay of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 10, 187-198.
Sharma RK, Taylor WA, Wang JH. 1983 Use of calmodulin affinity chromatography for purification of specific calmodulin-dependent enzymes. Methods Enzymol 102, 210-219.
Sommer D, Fakata KL, Swanson SA, Stemmer PM. 2000 Modulation of the phosphatase activity of calcineurin by oxidants and antioxidants in vitro. Eur J Biochem 267, 2312-2322.
Stewart AA, Ingebritsen TS, Cohen P. 1983 The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 5. Purification and properties of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase (2B) from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 132, 289-295.
Stewart AA, Ingebritsen TS, Manalan A, Klee CB, Cohen P. 1982 Discovery of a Ca2+-and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: probable identity with calcineurin (CaM-BP80). FEBS Lett 137, 80-84.
Sträter N, Kablunde T, Tucker P, Witzel H, Krebs B. 1995 Crystal structure of a purple acid phosphatase containing a dinuclear Fe(III)-Zn(II) active site. Science 268, 1489-1492.
Wang X, Culotta VC, Klee CB. 1996 Superoxide dismutase protects calcineurin from inactivation. Nature 383, 434-437.
Winkler MA, Merat DL, Tallant EA, Hawkins S, Cheung WY. 1984 Catalytic site of calmodul-independent protein phosphatase from bovine brain residues in subunit A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81, 3054-3058.
Wolff DJ, Sved DW. 1985 The divalent cation dependence of bovine brain calmodulin-dependent phosphatase. J Biol Chem 260, 4195-4202.
Yu L, Golbeck J, Yao J, Rusnak F. 1997 Spectroscopic and enzymatic characterization of the active site dinuclear metal center of calcineurin: implications for a mechanistic role. Biochemistry 36, 10727-10734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhode, D.J., Martin, B.L. Acidity of exogenous metal ion in the activation of calcineurin. Biometals 17, 399–407 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000029435.98167.d6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000029435.98167.d6