Abstract
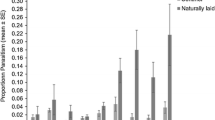
Blue oat mites, Penthaleus spp., and redlegged earth mites, Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) are major winter pests of a variety of crops and pastures. In southern Australia earth mites exhibit a facultative egg diapause to survive unfavorable summer conditions. The initiation of diapause egg production in earth mites was investigated using field and shade-house experiments. Species differed in their timing of diapause. H. destructor mainly produced diapausing eggs towards the end of the active mite season in spring, although small numbers were also produced in winter. In contrast, Penthaleus major (Dugés) produced diapause eggs almost immediately after emergence in autumn and continued producing these eggs throughout the season. Penthaleus falcatus (Qin and Halliday) also produced diapause eggs in early winter, although the first appearance of these eggs was slightly later in the season than for P. major. The diapause response of an undescribed species was also somewhat later than in P. major and P. falcatus, but earlier than in H. destructor. Electrophoresis of P. major samples indicated that clones of this parthenogenic species may differ in their timing of diapause egg production, providing another potential selective factor contributing to the maintenance of clonal diversity within this group. The results highlight the importance of determining species composition when devising control strategies for earth mite outbreaks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annells A.J.and Ridsdill-Smith T.J.1991.TheeffectofmoistureonaestivatingeggsofHalotydeusdestructor(Tucker)(Acari:Penthaleidae).In:Ridsdill-Smith T.J.(ed)ProceedingsofaNationalWorkshoponRedleggedEarthMite,LucerneFleaandBlueOatMite.DepartmentofAgriculture, Perth,Australia,pp.7-9.
Danks H.V.1994.Diversityandintegrationoflife-cyclecontrolsininsects.In:Danks H.V.(ed)InsectLife-cyclePolymorphism:Theory,EvolutionandEcologicalConsequencesforSeasonalityandDiapauseControl.KluwerAcademicPublishers, Dordrecht,TheNetherlands,pp.5-40.
Gillespie D.J.1991.IdentificationofresistancetoredleggedearthmiteHalotydeusdestructorinpasturelegumes.PlantProtectQuart6:170-171.
Grimm M., Michael P., Hyder M.and Doyle P.1995.Effectsofpasturepestdamageandgrazingmanagementonefficiencyofanimalproduction.PlantProtect.Quart.10:62-64.
Halliday R.B.1991.TaxonomicbackgroundoftheredleggedearthmiteHalotydeusdestructor(Tucker)(Acarina:Penthaleidae).PlantProtect.Quart.6:162-165.
Hoffmann A.A., Porter S.and Kovacs I.1997.Theresponseofthemajorcropandpasturepest,theredleggedearthmite(Halotydeusdestructor)topesticides:dose-responsecurvesandevidencefortolerance.Exp.Appl.Acarol.21:151-162.
James D.G.1991.EnvironmentalfactorsaffectingautumnegghatchandpopulationdevelopmentofHalotydeusdestructor(Tucker)(Acari:Penthaleidae).In:Ridsdill-Smith T.J.(ed)ProceedingsofaNationalWorkshoponRedleggedEarthMite,LucerneFleaandBlueOatMite.DepartmentofAgriculture, Perth,Australia,pp.32-34.
James D.G.1995.Biologicalcontrolofearthmitesinpastureusingendemicnaturalenemies.PlantProt.Quart.10:58-59.
James D.G.and O'Malley K.J.1993.PhenologyofeggproductionanddiapauseinHalotydeusdestructorTuckerandPenthaleusmajorDugés(Acari:Penthaleidae)insouthernNewSouthWalesduring1988/89.GeneralAppl.Entomol.24:33-38.
Jeppson L.R., Keifer H.H.and Baker E.W.1975.MitesInjurioustoEconomicPlants.UniversityofCaliforniaPress, Berkeley,CA.
Krysan J.L., Jackson J.J.and Lew A.C.1984.FieldterminationofeggdiapauseinDiabroticawithnewevidenceofextendeddiapauseinD.barberi(Coleoptera:Chrysomelidae).Environ.Entomol.13:1237-1240.
Lake A.W.H.and Howie J.H.1995.SelectionforredleggedearthmiteresistanceinannualMedicagospecies.PlantProtect.Quart.10:45-46.
Larsson P.1991.IntraspecificvariabilityinresponsetostimuliformaleandephippiaformationinDaphniapulex.Hydrobiologia225:281-290.
Lees A.D.1955.ThePhysiologyofDiapauseinArthropods.CambridgeUniversityPress, London,UK.
Levin E., Spencer J.L., Isard S.A., Onstad D.W.and Gray M.E.2002.Adaptationofthewesterncornrootwormtocroprotation:evolutionofanewstraininresponsetoamanagementpractice.Am.Entomol.48:94-107.
Masaki S.1980.Summerdiapause.Ann.Rev.Entomol.25:1-25.
Merton E., McDonald G.and Hoffmann A.1995.Culturalcontrolofredleggedearthmite,blueoatmiteandlucernefleaincanola.PlantProtect.Quart.10:65-66.
Michael P.1995.BiologicalcontrolofredleggedearthmiteandlucernefleabypredatorsAnystiswallaceiandNemologuscapillatus.PlantProtect.Quart.10:55-57.
Moritz K.and McDonald G.1995.Developingredleggedearthmiteresistanceincanola.In:Potter T.D.(ed)ProceedingsoftheAustralianResearchAssemblyonBrassicas.SouthAustralianResearchandDevelopmentInstitute, Adelaide,Australia,pp.30-35.
Narayan D.S.1962.Morphological,biologicalandecologicalstudiesonthewintergrainmite,Penthaleusmajor(Dugés),Penthaleidae;AcarinaPart1.J.Zool.Soc.India14:45-63.
Qin T.K.and Halliday R.B.1996.TheAustralianspeciesofChromotydeusBerleseandPenthaleusKoch,C.L.(Acarina:Penthaleidae).J.Nat.History30:1833-1848.
Ridsdill-Smith T.J.1997.BiologyandcontrolofHalotydeusdestructor(Tucker)(Acarina:Penthaleidae)-areview.Exp.Appl.Acarol.21:195-224.
Ridsdill-Smith T.J.and Annells A.J.1997.SeasonaloccurrenceandabundanceofredleggedearthmiteHalotydeusdestructor(Acari:Penthaleidae)inannualpasturesofsouthwesternAustralia.Bull.Entomol.Res.87:413-423.
Ridsdill-Smith T.J.and Pavri C.1998.Springsprayingforredleggedearthmites.WesternFocus(AustralianGrain):1-4.
Ridsdill-Smith T.J.and Pavri C.2000.Singlespringsprayprotectspastures.FarmingAhead103:60-63.
Ridsdill-Smith T.J., Jiang Y.and Ghisalberti E.L.1995.Amethodtotestcompoundsforfeedingdeterrencetowardsredleggedearthmites(Acarina:Penthaleidae).Ann.Appl.Biol.127:593-600.
Robinson M.R.and Hoffmann A.A.2001.Thepeststatusanddistributionofthreecrypticblueoatmitespecies(Penthaleusspp.)andtheredleggedearthmite(Halotydeusdestructor)insoutheasternAustralia.Exp.Appl.Acarol.25:699-716.
Rossi V., Gandolfi A.and Menozzi P.1996.EggdiapauseandclonalstructureinparthenogeneticpopulationsofHeterocyprisincongruens(Ostracoda).Hydrobiologia320:45-54.
Tauber M.J., Tauber C.A.and Masaki S.1984.Adaptationstohazardousseasonalconditions:dormancy,migration,andpolyphenism.In:Huffaker C.B.and Rabb R.L.(eds)EcologicalEntomology.Wiley, NewYork,pp.149-183.
Umina P.A.and Hoffmann A.A.1999.Toleranceofcrypticspeciesofblueoatmites(Penthaleusspp.)andtheredleggedearthmite(Halotydeusdestructor)topesticides.Aust.J.Exp.Agric.39:621-628.
Wallace M.M.H.1970a.DiapauseintheaestivatingeggofHalotydeusdestructor(Acari:Eupodidae).Aust.J.Zool.18:295-313.
Wallace M.M.H.1970b.Theinfluenceoftemperatureonpost-diapausedevelopmentandsurvivalintheaestivatingeggsofHalotydeusdestructor(Acari:Eupodidae).Aust.J.Zool.18:315-329.
Wallace M.M.H.and Mahon J.A.1971.ThedistributionofHalotydeusdestructorandPenthaleusmajor(Acari:Eupodidae)inAustraliainrelationtoclimateandlanduse.Aust.J.Zool.19:65-76.
Weeks A.R.and Hoffmann A.A.1998.Intenseselectionofmiteclonesinaheterogeneousenvironment.Evolution52:1325-1333.
Weeks A.R.and Hoffmann A.A.1999.ThebiologyofPenthaleusspeciesinsoutheasternAustralia.Entomol.Exp.Appl.92:179-189.
Weeks A.R.and Hoffmann A.A.2000.Competitiveinteractionsbetweentwopestspeciesofearthmites,HalotydeusdestructorandPenthaleusmajor(Acarina:Penthaleidae).Ecol.Behav.93:1183-1191.
Weeks A.R., Fripp Y.J.and Hoffmann A.A.1995.GeneticstructureofHalotydeusdestructorandPenthaleusmajorpopulationsinVictoria(Acari:Penthaleidae).Exp.Appl.Acarol.19:633-646.
Yampolsky L.Y.1992.Geneticvariationinthesexualreproductionratewithinapopulationofcyclicparthenogen,Daphniamagna.Evolution46:833-873.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umina, P.A., Hoffmann, A.A. Diapause and implications for control of Penthaleus species and Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) in southeastern Australia. Exp Appl Acarol 31, 209–223 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000010378.91111.16
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000010378.91111.16