Abstract
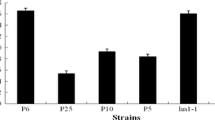
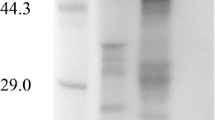
The invertase-encoding of AINV gene Arxula adeninivorans was isolated and characterized. The gene includes a coding sequence of 2700 bp encoding a putative 899 amino acid protein of 101.7 kDa. The identity of the gene was confirmed by a high degree of homology of the derived amino acid sequence to that of α-glucosidases from different sources. The gene activity is regulated by carbon source. In media supplemented with sucrose induction of the AINV gene and accumulation of the encoded invertase in the medium was observed. In addition the extracellular enzyme level is influenced by the morphological status of the organism, with mycelia secreting the enzyme in titres higher than those observed in budding yeasts. The enzyme characteristics were analysed from isolates of native strains as well as from those of recombinant strains expressing the AINV gene under control of the strong A. adeninivorans-derived TEF1 promoter. For both proteins a molecular mass of 600 kDa was determined, a pH optimum at pH 4.5 and a temperature optimum at 55 °C. The preferred substrates for the enzyme included the ß-D-fructofuranosides sucrose, inulin and raffinose. Only a weak enzyme activity was observed for the α-D-glucopyranosides maltotriose, maltose and isomaltose. Thus the invertase primarily is a ß-fructosidase and not an α-glucosidase as suggested by the homology to such enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Bui D.M., Kunze I., Förster S., Wartmann T., Horstmann C., Manteuffel R. and Kunze G. 1996. Cloning and expression of an Arxula adeninivorans glucoamylase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 44: 610–619.
Büttner R., Schubert U., Bode R. and Birnbaum D. 1990. Purifi-cation and partial characterization of external and internal invertases from two strain of Trichosporon adeninovorans. Acta Biotechnol. 10: 361–370.
Büttner R., Bode R. and Birnbaum D. 1991. Characterization of extracellular acid phosphatase from the yeast Arxula adeninivorans. Zbl. Mikrobiol. 146: 399–406.
Chavez F., Pons T., Delgado J.M. and Rodriguez L. 1998. Cloning and sequence analysis of the gene encoding invertase (INV1) from the yeast Candida utilis. Yeast 14: 1223–1232.
Chiba S. 1988. α-Glucosidase.. In: Handbook of amylases and related enzymes The Amylase Reseach Society of Japan, ed.Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, pp 104–116.
Chiba S. 1997. Molecular mechanism in α-glucosidase and glucoamylase}. Biosci. Biotechnol. 61: 1233–1239.
Costaglioli P., Meilhoc F., Janatova I., Klein R. and Masson J. 1997. Secretion of invertase from Schwanniomyces occidentalis.Biotechnol. Lett. 19: 623–627.
Coutinho P.M. and Herissat B. 1999. Carbohydrate-active enzymes.
Davis E., Larkins B.A. and Knight R.H. 1972. Polysomes from peas. An improved method for their isolation in the absence of ribonuclease inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 50: 581–584.
Fontana A., Ghommidh C., Guiraud J. and Navarro J. 1992. Continuous alcoholic fermentation of sucrose using flocculating yeast. The limits of invertase activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 14: 505–510.
Gienow U., Kunze G., Schauer F., Bode R. and Hofemeister J. 1990. The yeast genus Trichosporon spec. LS3; molecular characterization of genomic complexity. Zbl. Mikrobiol. 145: 3–12.
Gua Z. and Sherman F. 1995. 3'-end-forming signals of yeast mRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 15: 5983–5990.
Gunasekaran P., Karunakaran B., Cami B., Mukundan A.G., Preziosi L. and Baratti J. 1990. Cloning and sequencing of the sacA gene: characterization of a sucrase from Zymomonas mobilis. J.Bacteriol. 172: 6727–6735.
Hanahan D. 1983. Studies on transformation of E. coli with plasmids.J. Mol. Biol. 166: 557–580.
Henrissat B. 1991. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 280: 309–316.
Henrissat B. and Bairoch A. 1993. New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities.Biochem. J. 293: 781–788.
Hermans M.M.P., Kroos M.A., van Beeuman J., Oostra B.A. and Reuser A.J.J. 1991.Human lysosomal α-glucosidase. Characterization of the catalytic site}. J. Biol. Chem.266: 13507–13512.
Ingram C., Brawner M., Youngman P. and Westpheling J. 1989. xylE functions as an efficient reporter gene in Streptomyces spp.: use for the study of galP1, a catabolite-controlled promoter. J.Bacteriol. 171: 6617–6624.
Iwanami S., Matsui H., Kimura A., Iti H., Mori H., Honma M. and Chiba S. 1995. Chemical modification and amino acid sequence of active site in sugar beet α-glucosidase}. Biosci. Biotechnol.Biochem. 59: 459–463.
Kimura A., Takata M., Fukushi Y., Mori H., Matsui H. and Chiba S. 1997. A catalytic amino acid and primary structure of activesite in Aspergillus niger α-glucosidase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 61: 1091–1098.
Kunze G. and Kunze I. 1994a. Characterization of Arxula adeninivorans strains from different habitats. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 65: 607–614.
Kunze G. and Kunze I. 1994b. Comparative study of morphological characteristics and secretory invertase activities of Arxula adeninivorans strains. Microbiol. Europe 2: 24–28.
Kunze I., Nilsson C., Adler K., Manteuffel R., Horstmann C., Bröker M. and Kunze G. 1998. Correct targeting of a vacuolar tobacco chitinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae — post-translational modifications are dependent on the host strain}. Biochim.Biophys. Acta 1395: 329–344.
Middelhoven J.W., Hoogkamer-Te Niet M.C. and Kreger van Rij N.J.W. 1984. Trichosporon adeninovorans sp. nov., a yeast species utilizing adenine, xanthine, uric acid, putrescine and primary n-alkylamines as the sole source of carbon, nitrogen and energy.Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 50: 369–387.
Middelhoven W.J., de Jonge I.M. and Winter M. 1991. Arxula adeninivorans, a yeast assimilating many nitrogenous and aromatic compounds. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 60: 129–137.
Middelhoven W.J., Coenen A., Kraakman B. and Gelpke M.D.S. 1992. Degradation of some phenols and hydroxybenzoates by the imperfect ascomycetous yeasts Candida parapsilosis and Arxula adeninivorans: evidence for an operative gentisate pathway.Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 62: 181–187.
Minetoki T., Gomi K., Kitamoto K., Kumagai C. and Tamura G. 1995. Nucleotide sequence and expression of alpha-glucosidaseencoding gene (agdA) from Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol.Biochem. 59: 1516–1521.
Nakamura A., Nishimura I., Yokoyama A., Lee D.G., Hidaka M., Masaki H., Rimura A., Chiba S. and Uozumi T. 1997. Cloning and sequencing of an alpha-glucosidase gene from Aspergillus niger and its expression in A. nidulans. J. Biotechnol. 28: 75–84.
Okuyama M., Okuno A., Shimizu N., Mori H., Kimura A. and Chiba S. 2001. Carbonyl group of residue Asp647 as possibleproton donor in catalytic reaction of α-glucosidase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eur. J. Biochem. 268:2270–2280.
Perez J.A., Rodriguez J., Rodriguez L. and Ruiz T. 1996. Cloning and sequence analysis of the invertase gene INV1 from the yeast Pichia anomala. Curr. Genet. 29:234–240.
Rose M.D., Winston F. and Hieter P. 1990. Methods in yeast genetics.A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, New York, USA.
Rösel H. and Kunze G. 1998. Integrative transformation of the dimorphic yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3 based on Hygromycin B resistance. Curr. Genet. 33: 157–163.
Rubico M.C., Runco R. and Navarro A.R. 2002. Invertase from a strain of Rhodotorula glutinis. Phytochemistry 61: 605–609.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F. and Maniatis T. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, New York, USA.
Samsonova I.A., Kunze G., Bode R. and Böttcher F. 1996. A set of genetic markers for the chromosomes of the imperfect yeast Arxula adeninivorans. Yeast 12: 1209–1217.
Smith C.L., Klo S. and Cantor C.R. 1988. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis and technology of large DNA molecules.. In: Davis K. (ed.), Genome analysis, a practical approach. IPL Press, Oxford, UK, pp 41–72.
Stoltenburg R., Wartmann T., Kunze I. and Kunze G. 1995. Reliable method to separate free and membrane-bound polysomes from different yeast species. Bio/Techniques18: 564–568.
Sturtevant J., Dixon F., Wadsworth E., Latge J.P., Zhao X.J. and Calderone R. 1999. Identification and cloning of GCA1, a gene that encodes a cell surface glucoamylase from Candida albicans.Med. Mycol. 37: 357–366.
Tanaka A., Ohnishi N. and Fukui S. 1967. Studies on the formation of vitamins and their function in hydrocarbon fermentation.Production of vitamin B6 by Candida albicans in hydrocarbon medium. J. Ferment. Technol. 45: 617–623.
Van der Walt J.P., Smith M.T. and Yamada Y. 1990. Arxula gen.nov. (Candidaceae), a new anamorphic, arthroconidial yeast genus.Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 57: 59–61.
Wartmann T., Krüger A., Adler K., Bui M.D., Kunze I. and Kunze G. 1995. Temperature dependent dimorphism of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 68: 215–223.
Wartmann T., Rösel H., Kunze I., Bode R. and Kunze G. 1998.AILV1 gene from the yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3-a new selective transformation marker. Yeast 14: 1017–1025.
Wartmann T. and Kunze G. 2000. Genetic transformation and biotechnological application of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans.Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54: 619–624.
Wartmann T., Erdmann J., Kunze I. and Kunze G. 2000. Morphology-related effects on gene expression and protein accumulation of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3. Arch. Microbiol. 173: 253–261.
Wartmann T., Böer E., Huarto-Pico A., Sieber H., Bartelsen O., Gellissen G. and Kunze G. 2002a. High-level production and secretion of recombinant proteins by the dimorphic yeast Arxula adeninivorans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2: 363–369.
Wartmann T., Stephan U.W., Bube I., Böer E., Melzer M., Manteuffel R., Stoltenburg R., Guengerich L., Gellissen G. and Kunze G. 2002b. Post-translational modifications of the AFET3 gene product-a component of the iron transport system in budding cells and mycelia of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans. Yeast 19: 849–862.
Wartmann T., Stoltenburg R., Böer E., Sieber H., Bartelsen O., Gellissen G. and Kunze G. 2003. The ALEU2 gene-a new component for an Arxula adeninivorans-based expression platform.FEMS Yeast Res. 3: 223–232.
Wartmann T., Bellebna C., Böer E., Gellissen G. and Kunze G. 2003b. The constitutive AHSB4 promoter-a novel component of the Arxula adeninivorans — based expression platform. Appl.Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62: 528–535.
Wiseman A. 1979. New and modified invertases and their applications.In: Wiseman ed., Topics in enzyme and fermentation biotechnology. Chapter 6. Wiley and Sons, New York, New York,USA, pp 267–284.
Yang X.X., Wartmann T., Stoltenburg R. and Kunze G. 2000. Halotolerance of the yeast Arxula adeninivorans LS3. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 77: 303–311. 134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böer, E., Wartmann, T., Luther, B. et al. Characterization of the AINV gene and the encoded invertase from the dimorphic yeast Arxula adeninivorans . Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 86, 121–134 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ANTO.0000036135.69810.df
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ANTO.0000036135.69810.df