Abstract
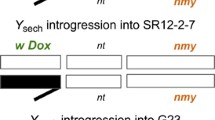
Interspecific crosses between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans usually produce sterile unisexual hybrids. The barrier preventing genetic analysis of hybrid inviability and sterility has been taken away by the discovery of a D. simulans strain which produces fertile female hybrids. D. simulans genes in the cytological locations of 21A1 to 22C1-23B1 and 30F3-31C5 to 36A2-7 have been introgressed into the D. melanogaster genetic background by consecutive backcrosses. Flies heterozygous for the introgression are fertile, while homozygotes are sterile both in females and males. The genes responsible for the sterility have been mapped in the introgression. The male sterility is caused by the synergistic effect of multiple genes, while the female sterility genes have been localized to a 170 kb region (32D2 to 32E4) containing 20 open reading frames. Thus, the female sterility might be attributed to a single gene with a large effect. We have also found that the Lethal hybrid rescue mutation which prevents the inviability of male hybrids from the cross of D. melanogaster females and D. simulans males cannot rescue those carrying the introgression, suggesting that D. simulans genes maybe non-functional in this hybrid genotype. The genes responsible for the inviability have not been separated from the female sterility genes by recombination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M.D. et al., 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195.
Agard, D.A., Y. Hiraoka, P. Shaw & J. Sedat, 1989. Fluorescence microscopy in three dimensions, pp. 353–377 in Methods in Cell Biology, Vol. 30, edited by L. Wilson. Academic Press, New York.
Ashburner, M. et al., 1999. An exploration of the sequence of a 2.9-Mb region of the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. The Adh region. Genetics 153: 179–219.
Barbash, D.A. & M. Ashburner, 2001. A novel system of fertility rescue in D. melanogaster/D. simulans species hybrids. Ann. Drosophila Res. Conf. 42: 889.
Barbash, D.A. & M. Ashburner, 2003. A novel system of fertility rescue in Drosophila hybrids reveals a link between hybrid lethality and female sterility. Genetics 163: 217–226.
Barbash, D.A., J. Roote & M. Ashburner, 2000. The Drosophila melanogaster Hybrid male rescue gene causes inviability in male and female species hybrids. Genetics 154: 1747–1771.
Barrio, R., J.F. de Celis, S. Bolshakov & F.C. Kafatos, 1999. Identification of regulatory regions driving the expression of the Drosophila spalt complex at different developmental stages. Dev. Biol. 215: 33–47.
Coulhart, M.B. & R.S. Singh, 1988. High level of divergence of male-reproductive-tract proteins between Drosophila melanogaster and its sibling species, Drosophila simulans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 5: 182–191.
Coyne, J.A., S. Simeonidis & P. Rooney, 1998. Relative paucity of genes causing inviability in hybrids between Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Genetics 150: 1091–1103.
Davis, A.W., J. Roote, T. Morley, K. Sawamura, S. Herrmann & M. Ashburner, 1996. Rescue of hybrid sterility in crosses between D. melanogaster and D. simulans. Nature 380: 157–159.
Dobzhansky, T., 1937. Genetics and the Origin of Species. Columbia University Press, New York.
Graner, M., K. Stupka & T.L. Karr, 1994. Biochemical and cytological characterization of DROP-1: a widely distributed proteoglycan in Drosophila. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 24: 557–567.
Haldane, J.B.S., 1922. Sex ratio and unisexual sterility in hybrid animals. J. Genet. 12: 101–109.
Hollocher, H. & C.-I. Wu, 1996. The genetics of reproductive isolation in the Drosophila simulans clade: X vs. autosomal effects and male vs. female effects. Genetics 143: 1243–1255.
Hutter, P. & M. Ashburner, 1987. Genetic rescue of inviable hybrids between Drosophila melanogaster and its sibling species. Nature 327: 331–333.
Hutter, P., J. Roote & M. Ashburner, 1990. A genetic basis for the inviability of hybrids between sibling species of Drosophila. Genetics 124: 909–920.
Karr, T.L., 1991. Intracellular sperm/egg interactions in Drosophila: a three-dimensional structural analysis of a paternal product in the developing egg. Mech. Dev. 34: 101–112.
Karr, T.L. & B.M. Alberts, 1986. Organization of the cytoskeleton in early Drosophila embryos. J. Cell Biol. 102: 1494–1509.
Liu, J., J.M. Mercer, L.F. Stam, G.C. Gibson, Z.-B. Zeng & C.C. Laurie, 1996. Genetic analysis of a morphological shape difference in the male genitalia of Drosophila simulans and D. mauritiana. Genetics 142: 1129–1145.
Mayr, E., 1942. Systematics and the Origin of Species. Columbia University Press, New York.
Muller, H.J. & G. Pontecorvo, 1940. Recombinants between Drosophila species the F1 hybrids of which are sterile. Nature 146: 199–200.
Nurminsky, D.I., M.V. Nurminskaya, D. De Aguiar & D.L. Hartl, 1998. Selective sweep of a newly evolved sperm-specific gene in Drosophila. Nature 396: 572–575.
Orr, H.A., 1992. Mapping and characterization of a 'speciation gene' in Drosophila. Genet. Res. 59: 73–80.
Orr, H.A. & S. Irving, 2000. Genetic analysis of the Hybrid male rescue locus of Drosophila. Genetics 155: 225–231.
Presgraves, D.C., 2003. A fine-scale genetic analysis of hybrid incompatibilities in Drosophila. Genetics 163: 955–972.
Sawamura, K., 2000. Genetics of hybrid inviability and sterility in Drosophila: the Drosophila melanogaster-Drosophila simulans case. Plant Species Biol. 15: 237–247.
Sawamura, K., A.W. Davis & C.-I. Wu, 2000. Genetic analysis of speciation by means of introgression into Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 2652–2655.
Sawamura, K., T. Taira & T.K. Watanabe, 1993. Hybrid lethal systems in the Drosophila melanogaster species complex. I. The maternal hybrid rescue (mhr) gene of Drosophila simulans. Genetics 133: 299–305.
Sawamura, K., M.-T. Yamamoto & T.K. Watanabe, 1993. Hybrid lethal systems in the Drosophila melanogaster species complex. II. The Zygotic hybrid rescue (Zhr) gene of D. melanogaster. Genetics 133: 307–313.
Sawamura, K., J. Roote, C.-I. Wu & M.-T. Yamamoto (in preparation). Reassessment of Dobzhansky-Muller model of reproductive isolation: genetic analysis of male sterility caused by interspecific introgression in Drosophila.
Singh, R.S. & R.J. Kulathinal, 2000. Sex gene pool evolution and speciation: a new paradigm. Genes Genet. Syst. 75: 119–130.
Sturtevant, A.H., 1920. Genetic studies on Drosophila simulans. I. Introduction. Hybrids with Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 5: 488–500.
Swanson, W.J., A.G. Clark, H.M. Waldrip-Dail, M.F. Wolfner & C.F. Aquadro, 2001. Evolutionary EST analysis identifies rapidly evolving male reproductive proteins in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 7375–7379.
Ting, C.-T., S.-C. Tsaur, M.-L. Wu & C.-I. Wu, 1998. A rapidly evolving homeobox at the site of a hybrid sterility gene. Science 282: 1501–1504.
True, J.R., B.S. Weir & C.C. Laurie, 1996. A genome-wide survey of hybrid incompatibility factors by the introgression of marked segments of Drosophila mauritiana chromosomes into Drosophila simulans. Genetics 142: 819–837.
Tsaur, S.-C. & C.-I. Wu, 1997. Positive selection and the molecular evolution of a gene of male reproduction, Acp26Aa of Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 14: 544–549.
Watanabe, T.K., 1979. A gene that rescues the lethal hybrids between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Jpn. J. Genet. 54: 325–331.
Wu, C.-I. & M.F. Palopoli, 1994. Genetics of postmating reproductive isolation in animals. Ann. Rev. Genet. 28: 283–308.
Wu, C.-I., N.A. Johnson & M.F. Palopoli, 1996. Haldane's rule and its legacy: why are there so many sterile males? Trends Ecol. Evol. 11: 281–284.
Yagyu, M., 1997. Master's Thesis. Kyoto Institute of Technology, Kyoto (in Japanese).
Yoshii, M., 1999. Master's Thesis. Kyoto Institute of Technology, Kyoto (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawamura, K., Karr, T.L. & Yamamoto, MT. Genetics of Hybrid Inviability and Sterility in Drosophila: Dissection of Introgression of D. simulans Genes in D. melanogaster Genome. Genetica 120, 253–260 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000017646.11191.b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000017646.11191.b0