Abstract
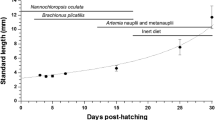
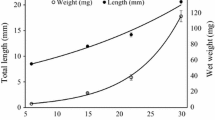
The objective of this experiment was to analyse the digestive enzyme profile of Solea senegalensis post larvae fed two diets, live Artemia sp. metanauplii and ICES diet. The experiment lasted 46 days and the ICES diet group was co-fed with a decreasing percentage of Artemia sp. for 39 days. Post larvae were fed twice a day and the amount of food supplied was determined based on the predicted maximum growth attainable. The Artemia treatment exhibited higher growth and survival rates than the ICES treatment. Trypsin, amylase, pepsin, alkaline phosphatase and leucine-alanine peptidase activities (specific activity: U mg protein−1; segmental activity: U larva−1) were measured in the post larvae digestive tract. Amylase secretion was significantly higher in the ICES treatment, while trypsin secretion was lower. Alkaline phosphatase was adversely and significantly affected by the ICES diet. Leucine-alanine peptidase specific activity was higher in the ICES treatment indicating a delay in the enterocyte maturation also evidenced by the enterocyte maturation index. Alkaline phosphatase and amylase segmental activity had a good correlation with larval growth rate, and may function as a nutritional indicator. This study suggests that compound diet can be included in the feeding sequences of sole larvae as early as 36 day post hatching (697 degree days).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, L., Zambonino-Infante, J., Cahu, C. et al. Digestive enzymes profile of Solea senegalensis post larvae fed Artemia and a compound diet. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 27, 61–69 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:FISH.0000021817.98363.47
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:FISH.0000021817.98363.47