Abstract
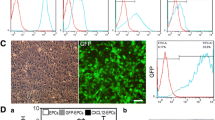
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent endothelial cell mitogen and morphogen, which stimulates angiogenesis in a wide variety of tissues and lesions in vivo. In this study, we applied adenoviral vector delivered human VEGF165 cDNA to develop focal non-tumor angiogenesis in the mature mouse brain. Seventy-two adult CD-1 mice underwent AdhVEGF, AdlacZ, and saline injection for up to four weeks. An adenoviral suspension containing 1 × 109 particles was injected stereotactically into the right hemisphere of the brain. The results showed that VEGF expression was increased in the AdhVEGF transduced mice compared to AdlacZ or saline injected mice (P < 0.05). VEGF-positive cells were mainly located in the injection hemisphere of AdhVEGF transduced mice. Quantitative vessel counting showed that microvessels in the AdhVEGF transduced mice increased following 2 weeks of AdhVEGF gene transfer compared to the other two groups (AdhVEGF:241 ± 19 vs. AdlacZ:148 ± 17 and Saline:150 ± 14 vessels/mm2, P < 0.05). Morphology showed typical angiogenic changes. PCNA-positive staining confirmed these microvessels were actively proliferating. Our study demonstrates that AdhVEGF-induced VEGF hyper-stimulation causes focal angiogenesis in the mature mouse brain. This novel method of inducing in vivo brain focal angiogenesis provides an opportunity to study the molecular mechanisms independent of the confounding effects of upstream inciting stimuli such as ischemia or tumor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Machein MR, Plate KH. VEGF in brain tumors. J Neurooncol 2000; 50(1-2): 109–20.
Alon T http://www.attwireless.com/personal/products/compare. jhtml et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med 1995; 1(10): 1024–8.
Rebar EJ, Huang Y, Hickey R et al. Induction of angiogenesis in a mouse model using engineered transcription factors. Nat Med 2002; 8(12): 1427–32.
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Tsang W et al. Correlation of VEGF and angiopoietin expression with disruption of blood-brain barrier and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002; 22(4): 379–92.
Sonstein WJ, Kader A, Michelsen WJ et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in pediatric and adult cerebral arteriovenous malformations: An immunocytochemical study. J Neurosurg 1996; 85(5): 838–45.
Chang JH, Gabison EE, Kato T et al. Corneal neovascularization. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2001; 12(4): 242–9.
Springer ML, Chen AS, Kraft PE et al. VEGF gene delivery to muscle: Potential role for vasculogenesis in adults. Mol Cell 1998; 2(5): 549–58.
Zhang D, Gai L, Fan R et al. Efficacy and safety of therapeutic angiogenesis from direct myocardial administration of an adenoviral vector expressing vascular endothelial growth factor 165. Chin Med J (Engl) 2002; 115(5): 643–8.
Hofman P, Blaauwgeers HG, Vrensen GF et al. Role of VEGF-A in endothelial phenotypic shift in human diabetic retinopathy and VEGF-A-induced retinopathy in monkeys. Ophthalmic Res 2001; 33(3): 156–62.
Fraser HM, Lunn SF. Angiogenesis and its control in the female reproductive system. Br Med Bull 2000; 56(3): 787–97.
Alitalo K, Carmeliet P. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 2002; 1(3): 219–27.
Rosenstein JM, Mani N, Silverman WF et al. Patterns of brain angiogenesis after vascular endothelial growth factor administration in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95(12): 7086–91.
Krum JM, Mani N, Rosenstein JM Angiogenic and astroglial responses to vascular endothelial growth factor administration in adult rat brain. Neuroscience 2002; 110(4): 589–604.
Hsich G, Sena-Esteves M, Breakefield XO et al. Critical issues in gene therapy for neurologic disease. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13(5): 579–604.
Mulligan RC. The basic science of gene therapy. Science 1993; 260: 926–32.
Betz AL, Yang GY, Davidson BL et al. Attenuation of stroke size in rats using an adenoviral vector to induce overexpression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1995; 15(4): 547–51.
Pang L, Ye W, Che XM et al. Reduction of inflammatory response in the mouse brain with adenoviral-mediated transforming growth factor-ss1 expression. Stroke 2001; 32(2): 544–52.
Wesseling P, Ruiter DJ, Burger PC et al. Angiogenesis in brain tumors; pathobiological and clinical aspects. J Neurooncol 1997; 32(3): 253–65.
Bossi P, Viale G, Lee AK et al. Angiogenesis in colorectal tumors: Microvessel quantitation in adenomas and carcinomas with clinicopathological correlations. Cancer Res 1995; 55(21): 5049–53.
Harris AL, Zhang H, Moghaddam A et al. Breast cancer angiogenesis - new approaches to therapy via antiangiogenesis, hypoxic activated drugs, and vascular targeting. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1996; 38(1): 97–108.
Carmeliet P, Lampugnani M-G, Moons L et al. Targeted deficiency or cytosolic truncation of the VE-cadherin gene in mice impairs VEGF-mediated endothelial survival and angiogenesis. Cell 1999; 98(2): 47–157.
Lee RJ, Springer ML, Blanco-Bose WE et al. VEGF gene delivery to myocardium: Deleterious effects of unregulated expression. Circulation 2000; 102(8): 898–901.
Proescholdt MA, Heiss JD, Walbridge S et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) modulates vascular permeability and inflammation in rat brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1999; 58(6): 613–27.
Harrigan MR, Ennis SR, Masada T et al. Intraventricular infusion of vascular endothelial growth factor promotes cerebral angiogenesis with minimal brain edema. Neurosurgery 2002; 50(3): 589–98.
Zsengeller ZK, Wert SE, Bachurski CJ et al. Recombinant adenoviral vector disrupts surfactant homeostasis in mouse lung. Human Gene Ther 1997; 8(11): 1331–44.
Hermens WT, Verhaagen J. Adenoviral vector-mediated gene expression in the nervous system of immunocompetent Wistar and T cell-deficient nude rats: Preferential survival of transduced astroglial cells in nude rats. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8(9): 1049–63.
Ferrara N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in regulation of physiological angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2001; 280(6): C1358–66.
Josko J, Gwozdz B, Jedrzejowska-Szypulka H et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its effect on angiogenesis. Med Sci Monit 2000; 6(5): 1047–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, GY., Xu, B., Hashimoto, T. et al. Induction of focal angiogenesis through adenoviral vector mediated vascular endothelial cell growth factor gene transfer in the mature mouse brain. Angiogenesis 6, 151–158 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AGEN.0000011803.56605.78
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AGEN.0000011803.56605.78