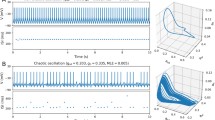
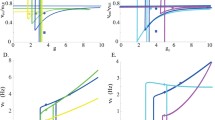
Abstract
Rhythmic, synchronous firing of groups of neurons is associated with behaviorally relevant states, and it is thus of interest to understand the mechanisms by which synchronization may be achieved. In hippocampal slice preparations, networks of excitatory and inhibitory neurons have been seen to synchronize when strong stimulation is applied at separated sites between which any coupling must be subject to a significant axonal delay. We extend previous work on synchronization in a model system based on the network architecture of these hippocampal slices. Our new analysis addresses the effects of heterogeneous populations and noisy inputs on the stability of synchronous solutions in the system. We find that, with experimentally motivated constraints on the coupling strength, sufficiently large heterogeneity in the input currents renders synchrony unstable. The addition of noise, however, restores stable near-synchrony. We analytically reduce the high-dimensional biophysical equations for the full population to a simple three-dimensional map, and show that the map's stability properties correctly predict both the loss of stability and the restabilizing effect of the noise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin A, Ross J, McAdams HH (1998) Stochastic kinetic analysis of developmental pathway bifurcation in phage λ-infected Escherichia coli cells. Genetics 149: 1633-1648.
Bragin A, Jando G, Nadasdy Z, Hetke J, Wise K, Buzsaki G (1995) Gamma (40-100 Hz) oscillation in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. Journal of Neuroscience 15: 47-60.
Collins JJ (1999) Fishing for function in noise. Nature 402: 241-242.
Collins JJ, Imhoff TT, Grigg P (1996) Noise-enhanced tactile sensation. Nature 383: 770.
Collins JJ, Imhoff TT, Grigg P (1996a) Noise-enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via aperiodic stochastic resonance. Journal of Neurophysiology 76(1): 642-645.
De Pascalis V, Ray WJ (1998) Effects of memory load on eventrelated patterns of 40 Hz EEG during cognitive and motor tasks. Journal of Psychophysiology 28: 301-315.
Douglass JK, Wilkens L, Pantazelou E, Moss F (1993) Noise enhancement of information transfer in crayfish mechanoreceptors by stochastic resonance. Nature 365: 337-340.
Ermentrout GB, Kopell N (1998) Fine structure of neural spiking and synchronization in the presence of conduction delays. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 95: 1259-1264.
Farmer SF (1998) Rhymicity, synchronization, and binding in human and primate motor systems. Journal of Physiology 509: 3-14.
Fries P, Reynolds JH, Rorie AE, Desimone R (2001) Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291: 1560-1563.
Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F (1998) Stochastic resonance. Reviews of Modern Physics 70(1): 223-287.
Gomez C, Vasquez M, Vaquero E, Lopez-Mendoza D, Cardoso M (1998) Frequency analysis of the EEG during spatial selective attention. International Journal of Neuroscience 95: 17-32.
Gray CM, Konig P, Engel AK, Singer W (1989) Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature 338(6213): 334-337.
Hasty J, Collins JJ (2002) Translating the noise. Nature Genetics 31: 13-14.
Hu B, Zhou C (2000) Phase synchronization in coupled nonidentical excitable systems and array-enhanced coherence resonance. Physical Review E 61(2): R1001-R1004.
Joliot M, Ribary U, Llinas R (1994) Human oscillatory brain activity near 40 Hz coexists with cognitive temporal binding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 91: 11748-11751.
Karbowski J, Kopell N (2000) Multispikes and synchronization in a large neural network with temporal delays. Neural Computation 12: 1573-1606.
Kocarev L, Tasev Z (2002) Lyapunov exponents, noise-induced synchronization, and Parrondo’s paradox. Physical Review E 65: 046215.
Lai C-H, Zhou C (1998) Synchronization of chaotic maps by symmetric common noise. Europhysics Letters 43(4): 376-380.
Laing CR, Longtin A (2001) Noise-induced stabilization of bumps in systems with long-range spatial coupling. Physica D 160: 149-172.
Manjarrez E, Rojas-Piloni JG, Mendez I, Martinez I, Velez D, Vazquez D, Flores A (2002) Internal stochastic resonance in the coherence between spinal and cortical neuronal ensembles in the cat. Neuroscience Letters 326: 93-96.
Maritan A, Banavar JR (1994) Chaos, noise, and synchronization. Physical Review Letters 72(10): 1451-1454.
Miltner W, Braun C, Arnold M, Witte H, Taub W (1999) Coherence of gamma-band EEG activity as a basis for associative learning. Nature 397: 434-436.
Murthy V, Fetz E (1992) Coherent 25-to 35-Hz oscillations in the sensorimotor cortex of awake behaving monkeys. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 89: 5670-5674.
Ozbudak E, Thattai M, Kurtser I, Grossman AD, van Oudenaarden A (2002) Regulation of noise in the expression of a single gene. Nature Genetics 31: 69-73.
Paulsson J, Berg OG, Ehrenberg M (2000) Stochastic focusing: Fluctuation-enhanced sensitivity of intracellular regulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 97(13): 7148-7153.
Pulvermuller F, Birbaumer N, Lutzenberger W, Mohr B (1997) Highfrequency brain activity: Its possible role in attention, perception, and language processing. Progress in Neurobiology 52: 427-445.
Richardson KA, Imhoff TT, Grigg P, Collins JJ (1998) Using electrical noise to enhance the ability of humans to detect subthreshold mechanical cutaneous stimuli. Chaos 8: 599-603.
Rodriguez E, George N, Lachaux J-P, Martinerie J, Renault B, Varela F (1999) Perception’s shadow: Long-distance synchronization of human brain activity. Nature 397: 430-433.
Roelfsema PR, Engel AK, Konig P, Singer W (1997) Visuomotor integration is associated with zero time-lag synchronization among cortical areas. Nature 385(6612): 157-161.
Russell DF, Wilkens LA, Moss F (1999) Use of behavioural stochastic resonance by paddle fish for feeding. Nature 402: 291-294.
Sosnovtseva OV, Setsinsky D, Fausboll A, Mosekilde E (2002) Transitions between â and ã rhythms in neural systems. Physical Review E 66: 041901.
Stacey WC, Durand DM (2001) Synaptic noise improves detection of subthreshold signals in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology 86(3): 1104-1112.
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O (1999) Oscillatory gamma activity in humans and its role in object representation. Trends in Cognitive Neurosciences 3: 151-162.
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O, Peronnet F, Pernier J (1998) Induced gamma-band (30-70 Hz) activity during the delay of a visual shortterm memory task in humans. Journal of Neuroscience 18: 4244-4254.
Taylor JR (1997) An introduction to error analysis. University Science Books, Sausalito, CA.
Thattai M, van Oudenaarden A (2001) Intrinsic noise in gene regulatory networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 98: 8614.
Tiesinga PHE, José JV (2000) Robust gamma oscillations in networks of inhibitory hippocampal interneurons. Network 11: 1-23.
Tiesinga PHE, Jos´e JV (2000) Synchronous clusters in a noisy inhibitory neural network. Journal of Computational Neuroscience 9: 49-65.
Traub R, Miles R (1991) Neuronal networks of the hippocampus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Traub RD, Whittington MA, Stanford IM, Jefferys JGR (1996) Inteneuron doublet firing allows long range synchrony of gamma frequency neuronal oscillations despite axon conduction delays. Nature 383: 621-624.
Wang Y, Chik DTW, Wang ZD (2000) Coherence resonance and noise-induced synchronization in globally coupled Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Physical Review E 61(1): 740-746.
Whittington MA, Stanford IM, Colling S, Jefferys JGR, Traub R (1997) Spatiotemporal patterns of gamma frequency oscillations tetanically induced in the rat hippocampal slice. Journal of Physiology 502(3): 591-607.
Whittington MA, Traub RD, Kopell N, Ermentrout GB, Buhl EH (2000) Inhibition-based rhythms: Experimental and mathematical observations on network dynamics. International Journal of Psychophysiology 38: 315-336.
Wiesenfeld K, Moss F (1995) Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: From ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature 373(6509): 33-36.
Zhou C, Kurths J (2002) Noise-induced phase synchronization and synchronization transitions in chaotic oscillators. Physical Review Letters 88(23): 230602.
Zhou C, Kurths J, Kiss IZ, Hudson JL (2002) Noise-enhanced phase synchronization of chaotic oscillators. Physical Review Letters 89(1): 014101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMillen, D., Kopell, N. Noise-Stabilized Long-Distance Synchronization in Populations of Model Neurons. J Comput Neurosci 15, 143–157 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025860724292
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025860724292