Abstract
Protein array technology has emerged as a new tool to enable ordered screening of proteins for expression and molecular interactions in high throughput. Besides classical solid-phase substrates, such as micro-titre plates and membrane filters, protein arrays have recently been devised with chip-sized supports. Several applications on protein chips have been described, but to our knowledge no studies using plant protein chips were published so far.
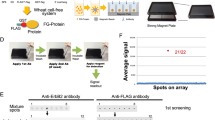
The aim of this study was to generate Arabidopsis protein chips and to demonstrate the feasibility of the protein chip technology for the investigation of antigen-antibody interactions. Therefore, Arabidopsis cDNAs encoding 95 different proteins were cloned into a GATEWAY-compatible Escherichia coli expression vector. RGS-His6-tagged recombinant proteins were purified in high throughput and robotically arrayed onto glass slides coated either with a nitrocellulose based polymer (FAST slides) or polyacrylamide (PAA slides). Using an anti-RGS-His6 antibody all proteins were detected on the chips. The detection limit was ca. 2–3.6 fmol per spot on FAST slides or 0.1–1.8 fmol per spot on PAA slides. The Arabidopsis protein chips were used for the characterisation of monoclonal antibodies or polyclonal sera. We were able to show that a monoclonal anti-TCP1 antibody and anti-MYB6 and anti-DOF11 sera bound specifically to their respective antigens and did not cross-react with the other 94 proteins including other DOF and MYB transcription factors on the chips. To enable screening of antibodies or other interacting molecules against thousands of Arabidopsis proteins in future, we generated an ordered cDNA expression library and started with high-throughput cloning of full-length cDNAs with GATEWAY technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angenendt, P., Glökler, J., Murphy, D., Lehrach, H. and Cahill, D.J. 2002. Towards optimized antibody microarrays: a comparison of current microarray support materials. Anal. Biochem. 309: 253–260.
Arenkov, P., Kukhtin, A., Gemmell, A., Voloshchuk, S., Chupeeva, V. and Mirzabekov, A. 2000. Protein microchips: use for immunoassay and enzymatic reactions. Anal. Biochem. 278: 123–131.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Braun, P., Hu, Y., Shen, B., Halleck, A., Koundinya, M., Harlow, E. and LaBaer, J. 2002. Proteome-scale purification of human proteins from bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 2654–2659.
Büssow, K., Cahill, D., Nietfeld, W., Bancroft, D., Scherzinger, E., Lehrach, H. and Walter, G. 1998. A method for global protein expression and antibody screening on high-density filters of an arrayed cDNA library. Nucl. Acids Res. 26: 5007–5008.
Büssow, K., Konthur, Z., Lueking, A., Lehrach, H. and Walter, G. 2001. Protein array technology. Potential use in medical diagnostics. Am. J. Pharmacogenomics 1: 37–43.
Cahill, D.J. 2001. Protein and antibody arrays and their medical applications. J. Immunol. Meth. 250: 81–91.
Clark, M.D., Panopoulou, G.D., Cahill, D.J., Büssow, K. and Lehrach, H. 1999. Construction and analysis of arrayed cDNA libraries [Review]. Meth. Enzymol. 303: 205–233.
Cordonnier, M.M., Greppin, H. and Pratt, L.H. 1986. Identification of a highly conserved domain on phytochrome from angiosperms to algae. Plant Physiol. 80: 982–987.
Feilner, T., Kersten, B., Immink, R.G.H., Wehrmeyer, S., Gutjahr, C., Horn, S., Possling, A., Angenent, G.C., Lehrach, H. and Cahill, D.J. 2002. Construction of an ordered Arabidopsis cDNA expression library for the generation of protein arrays and chips. Abstract. 1st Plant-GEMs Meeting, 29 September–2 October 2002, Berlin, Germany.
Haab, B.B., Dunham, M.J. and Brown, P.O. 2001. Protein microarrays for highly parallel detection and quantitation of specific proteins and antibodies in complex solutions. Genome Biol. 2: 1–13.
Hellens, R.P., Edwards, E.A., Leyland, N.R., Bean, S. and Mullineaux, P.M. 2000. pGreen: a versatile and flexible binary Ti vector for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. 42: 819–832.
Heyman, J.A., Cornthwaite, J., Foncerrada, L., Gilmore, J.R., Gontang, E., Hartman, K.J., Hernandez, C.L., Hood, R., Hull, H.M., Lee, W.Y., Marcil, R., Marsh, E.J., Mudd, K.M., Patino, M.J., Purcell, T.J., Rowland, J.J., Sindici, M.L. and Hoeffler, J.P. 1999. Genome-scale cloning and expression of individual open reading frames using topoisomerase I-mediated ligation. Genome Res. 9: 383–392.
Holz, C., Lueking, A., Bovekamp, L., Gutjahr, C., Bolotina, N., Lehrach, H. and Cahill, D.J. 2001. A human cDNA expression library in yeast enriched for open reading frames. Genome Res. 11: 1730–1735.
Kersten, B., Bürkle, L., Kuhn, E.J., Giavalisco, P., Konthur, Z., Lueking, A., Walter, G., Eickhoff, H. and Schneider, U. 2002. Large-scale plant proteomics. Plant Mol. Biol. 48: 133–141.
Lueking, A., Horn, M., Eickhoff, H., Büssow, K., Lehrach, H. and Walter, G. 1999. Protein microarrays for gene expression and antibody screening. Anal. Biochem. 270: 103–111.
Lueking, A., Holz, C., Gotthold, C., Lehrach, H. and Cahill, D.J. 2000. A novel system for dual protein expression in Pichia pastoris and Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purific. 20: 372–378.
Lueking, A., Konthur, Z., Eickhoff, H., Büssow, K., Lehrach, H. and Cahill, D.J. 2001. Protein microarrays: a tool for the postgenomic era. Curr. Genom. 2: 151–159.
MacBeath, G. and Schreiber, S.L. 2000. Printing proteins as microarrays for high-throughput function determination. Science 289: 1760–1763.
Minet, M., Dufour, M.E. and Lacroute, F. 1992. Complementation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae auxotrophic mutants by Arabidopsis thaliana cDNAs. Plant J. 2: 417–422.
Newman, T., de Bruijn, F.J., Green, P., Keegstra, K., Kende, H., McIntosh, L., Ohlrogge, J., Raikhel, N., Somerville, S. and Thomashow, M. 1994. Genes galore: a summary of methods for accessing results from large-scale partial sequencing of anonymous Arabidopsis cDNA clones. Plant Physiol. 106: 1241–1255.
Pandey, A. and Mann, M. 2000. Proteomics to study genes and genomes. Nature 405: 837–846.
Robinson, W.H., DiGennaro, C., Hueber, W., Haab, B.B., Kamachi, M., Dean, E.J., Fournel, S., Fong, D., Genovese, M.C., de Vegvar, H.E., Skriner, K., Hirschberg, D.L., Morris, R.I., Muller, S., Pruijn, G.J., van Venrooij, W.J., Smolen, J.S., Brown, P.O., Steinman, L. and Utz, P.J. 2002. Autoantigen microarrays for multiplex characterization of autoantibody responses. Nature Med. 8: 295–301.
Seki, M., Narusaka, M., Kamiya, A., Ishida, J., Satou, M., Sakurai, T., Nakajima, M., Enju, A., Akiyama, K., Oono, Y., Muramatsu, M., Hayashizaki, Y., Kawai, J., Carninci, P., Itoh, M., Ishii, Y., Arakawa, T., Shibata, K., Shinagawa, A. and Shinozaki, K. 2002. Functional annotation of a full-length Arabidopsis cDNA collection. Science 296: 141–145.
Templin, M.F., Stoll, D., Schrenk, M., Traub, P.C., Vohringer, C.F. and Joos, T.O. 2002. Protein microarray technology. Trends Biotechnol. 20: 160–166.
Walhout, A.J., Temple, G.F., Brasch, M.A., Hartley, J.L., Lorson, M.A., van den Heuvel, S. and Vidal, M. 2000. GATEWAY recombinational cloning: application to the cloning of large numbers of open reading frames or ORFeomes. Meth. Enzymol. 328: 575–592.
Walter, G., Büssow, K., Cahill, D.J., Lueking, A. and Lehrach, H. 2000. Protein arrays for gene expression and molecular interaction screening. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3: 298–302.
Zhu, H. and Snyder, M. 2001. Protein arrays and microarrays. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5: 40–45.
Zhu, H. and Snyder, M. 2003. Protein chip technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7: 55–63.
Zhu, H., Klemic, J.F., Chang, S., Bertone, P., Casamayor, A., Klemic, K.G., Smith, D., Gerstein, M., Reed, M.A. and Snyder, M. 2000. Analysis of yeast protein kinases using protein chips. Nature Genet. 26: 283–289.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kersten, B., Feilner, T., Kramer, A. et al. Generation of Arabidopsis protein chips for antibody and serum screening. Plant Mol Biol 52, 999–1010 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025424814739
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025424814739