Abstract
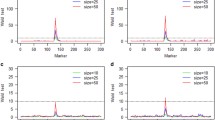
Theoretical comparisons for quantitativetrait loci (QTL) mapping properties wereconducted among simulated recombinantinbred (RI) populations developed bysingle-hill (SH), complete bulk, and singleseed descent (SSD) procedures by MonteCarlo simulations based on variouspopulation sizes, heritabilities, and QTLeffects. Our simulations includedestimation of QTL effects, QTL positions,and statistical testing power in the RIpopulations by comparing the estimates withpreset values. The simulation resultsshowed that the single hill (SH) bulk andsingle seed descent RI populations weregenerally not significantly different withrespect to quality of estimated QTL effectsand positions. Furthermore, when each RIpopulation had 150 lines, each couldprovide desirable properties for QTLmapping. The results implied that a SH RIpopulation consisting of 75 or moreF2-derived families with two lines perfamily (corresponding population size of150 or above) was appropriate for QTLmapping and was not significantly differentthan a SSD RI population of 150. Thus, theSH method could be used to develop largenumbers of RI lines for achieving betterresults in QTL mapping. Simulations alsoshowed that there was no significantdifference between means using SH methodswith 10 and 100 fruits per family. However, RI populations developed by thecomplete bulk method where F2identities are lost were not suitable forQTL mapping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, D.W., 1981. Recombinant inbred strains and bilineal congenic strains. In: H.J. Foster, J.D. Small & J.G. Fox (Eds.), The Mouse in Biomedical Research, Vol. 1, pp. 223-239, Academic Press, New York.
Burr, B. & F.A. Burr, 1991. Recombinant inbreds for molecular mapping in maize: theoretical and practical considerations. Trends Genet 7: 55-60.
Burr, B., F.A. Burr, K.H. Thompson, M.C. Albertson & C. Stuber, 1988. Gene mapping with recombinant inbreds in maize. Genetics 118: 519-526.
Empig, L.T. & W.R. Fehr, 1971. Evaluation of methods for generation advance in bulk hybrid soybean populations. Crop Sci 11: 51-54.
Fehr, W., 1987. Principles of Cultivar Development: Volume 1, Theory and Technique. Macmillan Publishing Co., New York.
Haldane, J.B.S., 1919. The combination of linkage values and the calculation of distance between the loci of linked factors. J Genet 8: 299-309.
Haldane, J.B.S. & C.H. Waddington, 1931. Inbreding and linkage. Genetics 16: 357-374.
Haley, S.D., L.K. Afanador, P.N. Miklas, J.R. Stavely & J.D. Kelly, 1994. Heterogeneous inbred population are useful as source of near-isogenic lines from RAPD marker localization. Theor Appl Genet 88: 337-342.
Ittu, M., N.N. Saulescu, I. Hagima, G. Ittu & P. Mustatea, 2000. Association of fusarium head blight resistance with gliadin loci in a winter wheat cross. Crop Sci 40: 62-67.
Jansen, R.C., 1993. Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics 135: 205-211.
Lander, E.S. & D. Botstein, 1989. Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121: 185-199.
Li, Z.K., S.R.M. Pinson, J.W. Stansel & W.D. Park, 1995. Indentification of QTL for heading date and plant height in rice using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 91: 374-381.
Liste, C. & D. Dean, 1993. Recombinant inbred lines for mapping RFLP and phenotype markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 4: 745-750.
Lubberstedt, T., A.E. Melchinger, C.C. Schon, H. Utz & D. Klein, 1997. QTL mapping in testcrosses of European flint lines of maize. I. Comparison of different testers for forage yield traits. Crop Sci 37: 921-931.
Macchiavelli, R. & J.S. Beaver, 2001. Effect of number of seed bulked and population size on genetic variability when using the multiple-seed procedure of SSD. Crop Sci 41: 1513-1516.
Mather, K. & J.L. Jinks, 1982. Biometrical Genetics, 3rd Edn. Chapman and Hall, London.
Messmer, M.M., R. Seyfarth, M. Keller, G. Schachermayr, M. Winzeler, S. Zanetti, C. Feuillet & B. Keller, 2000. Genetic analysis of durable leaf rust resistance in winter wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100: 419-431.
Miklas, P.N., R. Delorme, V. Stone, M.J. Daly, J.R. Stavely, M.J Bassett & J.S. Beaver, 2000. Bacterial, fungal, and viral disease resistance loci mapped in a recombinant inbred common bean population ('Dorado'/XAN 176). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125: 476-481.
Park, S.O., D.P. Coyne, N. Mutlu, G. Jung & J.R. Steadman, 1999. Confirmation of molecular markers and flower color associated with QTL for resistance to common bacterial blight in common beans. Annual Report 42: 5-6.
Quarrie, S.A., M. Gulli, C. Calestani, A. Steed & N. Marmiroli, 1994. Location of gene regulating drought-induced abscisic acid production on the long arm of chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 89: 794-800.
Reiter, R.S., J.G.K. Williams, K.A. Feldmann, J.A. Rafalski, S.V. Tinggey & P.A. Scolnik, 1992. Global and local genome mapping in Arabidopsis thialiana by unsing recombinant inbred lines and amplified polymorphic DNAs. Proc Natl Acad USA 89: 1477-1481.
Schar, W.V.D., C. Alonso-Blanco, K.M. Leon-Kloosterziel, R.C. Jansen, J.W. Van Ooijen & M. Koonneef, 1997. QTL analysis of seed dormancy in Arabidopsis using recombinant inbred lines and MQM mapping. Heredity 79: 190-200.
Shappley, Z.W., J.N. Jenkins, J. Zhu & J.C. McCarty Jr., 1998. Quantitative trait loci associated with agronomic and fiber traits of upland cotton. J Cotton Sci 4: 153-163.
Simko, I., D. Vreugdenhil, C.S. Jung & G.D. May, 1999. Similarity of QTLs detected for in vitro and greenhouse development of potato plants. Mol Breed 5: 417-428.
Swarup, K., B.C. Alonso, J.R. Lynn, S.D. Michaels, R.M. Amasino, M. Koornneef & A.J. Millar, 1999. Natural allelic variation identifies new genes in the Arabidopsis circadian system. Plant J 20: 67-77.
Taylor, B.A., D.W. Bailey, M. Cherry, R. Riblet & M. Weight, 1975 Genes for immunoglobulin heavy chain and serum prealbumin protein are linked in mouse. Nature 256: 644-646.
Wang, D.L., 1998. A Mixed Model Approach for Mapping QTLs with Epistatic Effects. A dissertation of Zhejiang Agricultural University, Hangzhou.
Wang, D., J. Zhu, Z.K. Li & A.H. Paterson, 1999. Mapping QTLs with epistatic effects and QTL-environment interactions by mixed linear model approaches. Theor Appl Genet 99: 1255-1264.
Weller, J.I., 1986. Maximum likelihood techniques for mapping and analysis of quantitative trait loci with the aid of genetic markers. Biometrics 42: 627-640.
Yan, J.Q., J, Zhu, C.X. He, M. Benmoussa, P. Wu, 1998. Quantitative trait loci analysis for the developmental behavior of tiller number in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97: 267-274.
Yin, X., P. Stam, C.J. Dourleijn, M.J. Kropff, 1999. AFLP mapping of quantitative trait loci for yield-determining physiological characters in spring barley. Theor Appl Genet 99: 244-253.
Zeng, Z.B., 1994. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136: 1456-1468.
Zhu, J., 1998. Mixed model approaches for mapping complex quantitative trait loci. In: L.W. Wang & J.R. Dai (Eds.), Proc. China Nat. Conf. on Plant Breeding, pp. 11-20, Agricultural Science and Technology Press of China, Beijing, China.
Zhu, J. & B.S. Weir, 1998. Mixed model approaches for genetic analysis of quatitative traits. In: L.S. Chen, S.G. Ruan & J. Zhu (Eds.), Proc. Int. Conf. Mathematical Biology, pp. 321-330, World Scientific Publishing Co. Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Jenkins, J., Zhu, J. et al. Comparisons of quantitative trait locus mapping properties between two methods of recombinant inbred line development. Euphytica 132, 159–166 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024690711867
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024690711867