Abstract
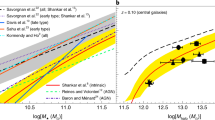
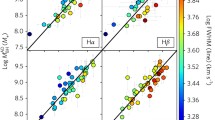
We report three new or updated techniques for probing the parameters of active galaxies based on the masses of their central black holes MBH). First, we derived a near-IR analog of the bulge luminosity versus MBH relationship. The low scatter makes it a promising new tool to study the black hole demographics. Next, we present relations between MBH and the10 μm and 2-10 keV nuclear luminosity. They may help to study the MBH evolution over wide redshift ranges. Finally, we measured MBH in quasars from z ∼ 3.4 to z ∼ 0.3 to search directly for MBH growth. Surprisingly, we found no evidence for growth implying that the majority of quasar host galaxies have undergone their last major merger at z ≥ 3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Herrero, A., Ivanov, V.D., Jayawardhana, R. and Hosokawa T.: 2002, ApJ 571, L1.
Forster, K., Green, P.J., Aldcrogt, T.L., Vestergaard, M., Foltz, C.B. and Hewett, P.C.: 2001, ApJS 134, 35.
Ho, L.C., Filippenko, A.V., Sargent, W.L.W. and Peng, C.Y.: 1997, ApJS 112, 391.
Ho, L.C.: 2002, ApJ 564, 120.
Kaufmann, G. and Haehnelt, M.: 2002, MNRAS, (astro-ph/0208215).
Kaspi, S., Smith, P.S., Netzer, H., Maoz, D., Jannuzi, B.T. and Giveon, U.: 2000, ApJ 533, 631.
McLure, R.J. and Jarvis, M.J.: 2002, MNRAS, in press (astro-ph/0204473).
Nelson, C.H. and Whittle, M.: 1995, ApJS 99, 67.
Peterson, B.M. and Wandel, A.: 1999, ApJ 521, L95.
Vestergaard, M.: 2002, ApJ 571, 733.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanov, V., Alonso-Herrero, A. Probing the nuclear activity with supermassive black holes. Astrophysics and Space Science 284, 565–568 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024045704186
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024045704186