Abstract
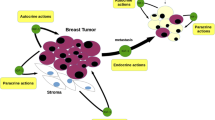
The development of the mammary gland requires the coordinated expression of hormones and growth factors. Likewise, some transformed breast cells continue to respond to these same extracellular signals. Thus, understanding the mechanisms that control normal development of tissues can lead to new therapeutic targets. The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system plays an important role in the normal development and function of the mammary gland. Accumulating evidence suggests that the IGFs are also key regulators of the malignant phenotype. The IGFs stimulate proliferation, promote survival, and enhance metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. Although multiple receptors for the IGFs have been identified, the IGFs primarily exert their biologic effects through ligation of the type I IGF receptor tyrosine kinase (IGF1R). IGF binding to the IGF1R initiates an intracellular signaling cascade that leads to changes in gene expression and cell biology. This review will focus on the evidence that the IGF1R is a relevant treatment target in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleinberg DL, Feldman M, Ruan W: IGF-I: An essential factor in terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 5: 7–17, 2000
Beatson GT: On the treatment of inoperable cases of carcinoma of the mamma. Suggestions for a new method of treatment with illustrative cases. Lancet 2: 104–107, 1896
Allen E, Doisy EA: An ovarian hormone: Preliminary report on its localiszation, extraction, and partial purification and action in test animals. JAMA 81: 819–821, 1923
Osborne CK, Zhao H, Fuqua SA: Selective estrogen receptor modulators: Structure, function, and clinical use. J Clin Oncol 18: 3172–3186, 2000
Osborne CK: Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 339: 1609–1618, 1998
LeRoith D: Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center: Insulin-like growth factors. New England Journal of Medicine 336: 633–640, 1997
DeChiara TM, Efstratiadis A, Robertson EJ: A growth deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature 345: 78–80, 1990
Powell-Braxton L, Hollingshead P, Warburton C, Dowd M, Pitts-Meek S, Dalton D, Gillett N, Stewart TA: IGF-I is required for normal embryonicgrowth in mice. Genes Dev 7: 2609–2617, 1993
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A: Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulinlike growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75: 59–72, 1993
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D: Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7324–7329, 1999
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, Henzel W, Le Bon T, Kathuria S, Chen E, Jacobs S, Francke U, Ramachandran J, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y: Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: Comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define hormonal specificity. EMBO J 5: 2503–2512, 1986
Steele-Perkins G, Turner J, Edman JC, Hari J, Pierce SB, Stover C, Rutter WJ, Roth RA: Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem 263: 11486–11492, 1988
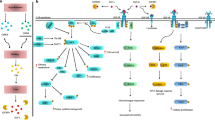
Giorgetti S, Pelicci PG, Pelicci G, Van Obberghen E: Involvement of Src-homology/collagen (SHC) proteins in signaling through the insulin receptor and the insulin-likegrowth-factor-I-receptor. Eur J Biochem 223: 195–202, 1994
Lamothe B, Bucchini D, Jami J, Joshi RL: Interaction of p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase with insulin and IGF-1 receptors analyzed by using the two-hybrid system. FEBS Lett 373: 51–55, 1995
Morrione A, Valentinis B, Li S, Ooi JY, Margolis B, Baserga R: Grb10: A new substrate of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res 56: 3165–3167, 1996
Baron V, Calleja V, Ferrari P, Alengrin F, Van Obberghen E: p125Fak focal adhesion kinase is a substrate for the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I tyrosine kinase receptors. J Biol Chem 273: 7162–7168, 1998
Arbet-Engels C, Tartare-Deckert S, Eckhart W: C-terminal Srckinase associates with ligand-stimulated insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. J Biol Chem 274: 5422–5428, 1999
Butler AA, Blakesley VA, Koval A, deJong R, Groffen J, LeRoith D: in vivo regulation of CrkII and CrkL protooncogenes in the uterus by insulin-like growth factor-I. Differential effects on tyrosine phosphorylation and Tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: Biology and therapeutic relevance 333 association with paxillin. J Biol Chem 272: 27660–27664, 1997
Xiao S, Rose DW, Sasaoka T, Maegawa H, Burke TR Jr., Roller PP, Shoelson SE, Olefsky JM: Syp (SH-PTP2) is a positive mediator of growth factor-stimulated mitogenic signal transduction. J Biol Chem 269: 21244–21248, 1994
Myers MG Jr., Sun XJ, White MF: The IRS-1 signaling system. Trends Biochem Sci 19: 289–293, 1994
He W, Craparo A, Zhu Y, O'Neill TJ, Wang LM, Pierce JH, Gustafson TA: Interaction of insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) with the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors. Evidence for two distinct phosphotyrosine-dependent interaction domains within IRS-2. J Biol Chem 271: 11641–11645, 1996
Qu BH, Karas M, Koval A, LeRoith D: Insulin receptor substrate-4 enhances insulin-like growth factor-I-induced cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 274: 31179–31184, 1999
Tsuruzoe K, Emkey R, Kriauciunas KM, Ueki K, Kahn CR: Insulin receptor substrate 3 (IRS-3) and IRS-4 impair IRS-1-and IRS-2-mediated signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21: 26–38, 2001
Jackson JG, White MF, Yee D: Insulin receptor substrate-1 is the predominant signaling molecule activated by insulinlike growth factor-I, insulin, and interleukin-4 in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 273: 9994–10003, 1998
Morgan DO, Edman JC, Standring DN, Fried VA, Smith MC, Roth RA, Rutter WJ: Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature 329: 301–307, 1987
Papa V, Pezzino V, Costantino A, Belfiore A, Giuffrida D, Frittitta L, Vannelli GB, Brand R, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R: Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 86: 1503–1510, 1990
Sciacca L, Costantino A, Pandini G, Mineo R, Frasca F, Scalia P, Sbraccia P, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R, Belfiore A: Insulin receptor activation by IGF-II in breast cancers: Evidence for a new autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Oncogene 18: 2471–2479, 1999
Siddle K, Soos MA, Field CE, Nave BT: Hybrid and atypical insulin/insulin-like growth factor I receptors. Horm Res 41: 56–64; discussion 65, 1994
Shaw LM: Identification of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and IRS-2 as signaling intermediates in the alpha6beta4 integrin-dependent activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and promotion of invasion. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5082–5093, 2001
Belfiore A, Pandini G, Vella V, Squatrito S, Vigneri R: Insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptors play a major role in IGF-I signaling in thyroid cancer. Biochimie 81: 403–407, 1999
Pandini G, Vigneri R, Costantino A, Frasca F, Ippolito A, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Siddle K, Goldfine ID, Belfiore A: Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor overexpression in breast cancers leads to insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptor overexpression: Evidence for a second mechanism of IGF-I signaling. Clin Cancer Res 5: 1935–1944, 1999
Soos MA, Siddle K: Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J 263: 553–563, 1989
Kleinberg DL, Ruan W, Catanese V, Newman CB, Feldman M: Non-lactogenic effects of growth hormone on growth and insulin-like growth factor-I messenger ribonucleic acid of rat mammary gland. Endocrinology 126: 3274–3276, 1990
Ruan W, Newman CB, Kleinberg DL: Intact and aminoterminally shortened forms of insulin-like growth factor I induce mammary gland differentiation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10872–10876, 1992
Ruan W, Kleinberg DL: Insulin-like growth factor I is essential for terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis during mammary development. Endocrinology 140: 5075–5081, 1999
Hadsell DL, Greenberg NM, Fligger JM, Baumrucker CR, Rosen JM: Targeted expression of des(1–3) human insulinlike growth factor I in transgenic mice influences mammary gland development and IGF-binding protein expression. Endocrinology 137: 321–330, 1996
Neuenschwander S, Schwartz A, Wood TL, Roberts CT Jr., Henninghausen L, LeRoith D: Involution of the lactating mammary gland is inhibited by the IGF system in a transgenicmouse model. J Clin Invest 97: 2225–2232, 1996
Hadsell DL, Murphy KL, Bonnette SG, Reece N, Laucirica R, Rosen JM: Cooperative interaction between mutant p53 and des(1–3)IGF-I accelerates mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 19: 889–898, 2000
Kaleko M, Rutter WJ, Miller AD: Overexpression of the human insulinlike growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastictransformation. Mol Cell Biol 10: 464–473, 1990
Baserga R, Sell C, Porcu P, Rubini M: The role of the IGFI receptor in the growth and transformation of mammalian cells. Cell Prolif 27: 63–71, 1994
Morrione A, DeAngelis T, Baserga R: Failure of the bovine papillomavirus to transform mouse embryo fibroblasts with a targeted disruption of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor genes. J Virol 69: 5300–5303, 1995
Sell C, Rubini M, Rubin R, Liu JP, Efstratiadis A, Baserga R: Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen is unable to transform mouse embryonicfibroblasts lacking type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 11217–11221, 1993
Sell C, Dumenil G, Deveaud C, Miura M, Coppola D, DeAngelis T, Rubin R, Efstratiadis A, Baserga R: Effect of a null mutation of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene on growth and transformation of mouse embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 14: 3604–3612, 1994
Resnicoff M, Coppola D, Sell C, Rubin R, Ferrone S, Baserga R: Growth inhibition of human melanoma cells in nude mice by antisense strategies to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 54: 4848–4850, 1994
Cullen KJ, Yee D, Sly WS, Perdue J, Hampton B, Lippman ME, Rosen N: Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and function in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 48–53, 1990 334 Gross and Yee
Papa V, Gliozzo B, Clark GM, McGuire WL, Moore D, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Vigneri R, Goldfine ID, Pezzino V: Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 53: 3736–3740, 1993
Pollak MN: Endocrine effects of IGF-I on normal and transformed breast epithelial cells: Potential relevance to strategies for breast cancer treatment and prevention. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47: 209–217, 1998
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Pollak M: Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 351: 1393–1396, 1998
Devi GR, De Souza AT, Byrd JC, Jirtle RL, MacDonald RG: Altered ligand binding by insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptors bearing missense mutations in human cancers. Cancer Res 59: 4314–4319, 1999
Hankins GR, De Souza AT, Bentley RC, Patel MR, Marks JR, Iglehart JD, Jirtle RL: M6P/IGF2 receptor: A candidate breast tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 12: 2003–2009, 1996
Oates AJ, Schumaker LM, Jenkins SB, Pearce AA, DaCosta SA, Arun B, Ellis MJ: The mannose 6-phosphate/ insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (M6P/IGF2R), a putative breast tumor suppressor gene. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47: 269–281, 1998
Lee AV, Hilsenbeck SG, Yee D: IGF system components as prognostic markers in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47: 295–302, 1998
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J, Beuscart R, Djiane J, Demaille A: Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer and their relation to estradiol and progesterone receptors. Cancer Res 48: 6429–6433, 1988
Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP, Beuscart R, Demaille A: Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 6931–6935, 1990
Rocha RL, Hilsenbeck SG, Jackson JG, VanDenBerg CL, Weng C, Lee AV, Yee D: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and insulin receptor substrate-1 in breast cancer: Correlation with clinical parameters and disease-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 3: 103–109, 1997
Karey KP, Sirbasku DA: Differential responsiveness of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and T47D to growth factors and 17 beta-estradiol. Cancer Res 48: 4083–4092, 1988
Yee D, Lee AV: Crosstalk between the insulin-like growth factors and estrogens in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 5: 107–115, 2000
Dupont J, Le Roith D: Insulin-like growth factor 1 and oestradiol promote cell proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells: New insights into their synergistic effects. Mol Pathol 54: 149–154, 2001
Buzdar AU: Endocrine therapy in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol 28: 291–304, 2001
Stewart AJ, Westley BR, May FE: Modulation of the proliferative response of breast cancer cells to growth factors by oestrogen. Br J Cancer 66: 640–648, 1992
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK, Yee D: Enhancement of insulinlike growth factor signaling in human breast cancer: estrogen regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol Endocrinol 13: 787–796, 1999
Oesterreich S, Zhang P, Guler RL, Sun X, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Osborne CK, Lee AV: Re-expression of estrogen receptor alpha in estrogen receptor alpha-negative MCF-7 cells restores both estrogen and insulin-like growth factor-mediated signaling and growth. Cancer Res 61: 5771–5777, 2001
Vignon F, Bouton MM, Rochefort H: Antiestrogens inhibit the mitogenic effect of growth factors on breast cancer cells in the total absence of estrogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 146: 1502–1508, 1987
Katzenellenbogen BS, Norman MJ: Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: Interrelationships among insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I, serum, and estrogen. Endocrinology 126: 891–898, 1990
Lee AV, Weng CN, Jackson JG, Yee D: Activation of estrogen receptor-mediated gene transcription by IGF-I in human breast cancer cells. J Endocrinol 152: 39–47, 1997
Gooch JL, Van Den Berg CL, Yee D: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I rescues breast cancer cells from chemotherapy-induced cell death-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 56: 1–10, 1999
Dunn SE, Hardman RA, Kari FW, Barrett JC: Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs. Cancer Res 57: 2687–2693, 1997
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L, Yuan J, Havre PA, Gumbs AA, Kaplan L, Burgaud JL, Carter D, Baserga R, Glazer PM: Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res 57: 3079–3083, 1997
Kulik G, Klippel A, Weber MJ: Antiapoptoticsignaling by the insulin-like growth factor I receptor, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Akt. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1595–1606, 1997
Kulik G, Weber MJ: Akt-dependent and-independent survival signaling pathways utilized by insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Cell Biol 18: 6711–6718, 1998
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G, Calabretta B, Baserga R: Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7203–7215, 1999
Samani AA, Brodt P: The receptor for the type I insulinlike growth factor and its ligands regulate multiple cellular functions that impact on metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 10: 289–312, viii. 2001
Doerr ME, Jones JI: The roles of integrins and extracellular matrix proteins in the insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 271: 2443–2447, 1996
Dunn SE, Ehrlich M, Sharp NJ, Reiss K, Solomon G, Hawkins R, Baserga R, Barrett JC: A dominant negative Tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: Biology and therapeutic relevance 335 mutant of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Res 58: 3353–3361, 1998
Lee OH, Bae SK, Bae MH, Lee YM, Moon EJ, Cha HJ, Kwon YG, Kim KW: Identification of angiogenic properties of insulin-like growth factor II in in vitro angiogenesis models. Br J Cancer 82: 385–391, 2000
Long L, Navab R, Brodt P: Regulation of the Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 58: 3243–3247, 1998
Bae MH, Lee MJ, Bae SK, Lee OH, Lee YM, Park BC, Kim KW: Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) secreted from HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells shows angiogenic activity. Cancer Lett 128: 41–46, 1998
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E: Integrin signaling. Science 285: 1026–1032, 1999
Vuori K, Ruoslahti E: Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with integrins. Science 266: 1576–1578, 1994
Lebrun P, Mothe-Satney I, Delahaye L, Van Obberghen E, Baron V: Insulin receptor substrate-1 as a signaling molecule for focal adhesion kinase pp125(FAK) and pp60(src). J Biol Chem 273: 32244–32253, 1998
Guvakova MA, Surmacz E: The activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin. Exp Cell Res 251: 244–255, 1999
Shaw LM, Rabinovitz I, Wang HH, Toker A, Mercurio AM: Activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase by the alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma invasion. Cell 91: 949–960, 1997
Mercurio AM, Bachelder RE, Chung J, O'Connor KL, Rabinovitz I, Shaw LM, Tani T: Integrin laminin receptors and breast carcinoma progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6: 299–309, 2001
Clemmons DR, Horvitz G, Engleman W, Nichols T, Moralez A, Nickols GA: Synthetic alphaVbeta3 antagonists inhibit insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated smooth muscle cell migration and replication. Endocrinology 140: 4616–4621, 1999
Brooks PC, Klemke RL, Schon S, Lewis JM, Schwartz MA, Cheresh DA: Insulin-like growth factor receptor cooperates with integrin avb5 to promote tumor cell dissemination in vivo. J Clin Invest 99: 1390–1398, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gross, J.M., Yee, D. The type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: Biology and therapeutic relevance. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22, 327–336 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023720928680
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023720928680