Abstract
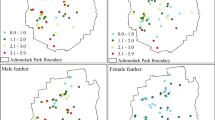
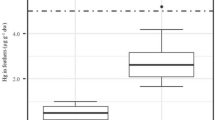
A long term field study was initiated by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources in 1992 to elucidate patterns of common loon (Gavia immer) mercury (Hg) exposure. Analysis of loon blood and feather samples collected from recaptured adult loons in Wisconsin 1992–2000 found evidence of a decline in overall body burdens of mercury in common loons for this region. The interval between sampling individual loons spanned 2–8 years, a sufficient length of time to observe a change in tissue Hg concentrations. Loon chick blood Hg levels declined by 4.9% annually for chicks sampled on 33 lakes during the period 1992–2000. This is the first evidence we are aware of showing a recent regional annual decrease in common loon Hg exposure. Repeated captures of wild loon chicks in Wisconsin shows that blood Hg concentrations can increase during the period of rapid feather growth (weeks 2–5), although the rate of increase is very slow. Mean egg Hg levels ranged from 0.19 to 0.87 µg Hg/g wet weight (ww) in samples collected 1996–2000. Egg Hg concentration was inversely and significantly related to lake pH (p<0.0001; r 2=0.55). Adults and chicks were often captured simultaneous during the period 1992–2000. Correlations were highest between sibling blood Hg levels (r=0.88) and chick blood and adult blood (male r=0.61, female r=0.52) Hg levels, likely reflecting the influence of the Hg content of prey from the natal lake on loon blood Hg levels. The relationship between feathers and blood of adults and that of chick blood and adult feathers was weaker.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr, J.F. (1986). Population dynamics of the common loon (Gavia immer) associated with mercury-contaminated waters in northwestern Ontario. Can. Wildl. Serv. Occas. Pap. No. 56.
Barr, J.F. (1996). Aspects of common loon (Gavia immer) feeding biology on its breeding ground. Hydrobiologia 32, 119-44.
Barrie, L., Macdonald, T., Bidleman, T., Diamond, M., Gregor, D., Semkin, R., Strachan, W., Alaee, M., Backus, S., Bewers, M., Gobeil, C., Halsall, C., Hoff, J., Li, A., Lockhart, L., Mackay, D., Muir, D., Pudykiewicz, J., Reimer, K., Smith, J., Stern, G., Shcroeder, W., Wagemann, R., Wania, F. and Yunker, M. (1997). Sources, occurrence and pathways. In J. Jensen, K. Adare and R. Shearer (eds) Canadian Arctic Contaminants Assessment Report, pp. 25-182. Ottawa, Canada: Indian and Northern Affairs Canada.
Braselton, W.E. Animal Health and Diagnostic Laboratory. Electronic correspondence. 31 May, 2002.
Braune, B.M., Donaldson, G.M. and Hobson, K.A. (2001). Contaminant residues in seabird eggs from the Canadian Arctic. Part I. Temporal trends in 1975–1998. Environ. Poll. 114, 39-59.
Clary, A.F. University of Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene. Electronic correspondence. 3 June, 2002.
Coundard, C.J. Mercury exposure and effects on common loon (Gavia immer) behavior in the upper midwestern United States. M. S. Thesis U. of Minnesota, January, 2001.
Eisler, R. (1987). Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Biol. Rpt. 85(1.10).
Evers, D.C. (1992). A replicable capture method for adult and juvenile common loons on their nesting lakes. In S. Stockwell (ed.) Proceedings, pp. 214-21. American Loon Conference, Bar Harbor, ME, USA, August 22–24.
Evers, D.C. (1994). Activity budgets of a marked common loon (Gavia immer) nesting population. Hydrobiologia 279/280, 415-20.
Evers, D.C., Kaplan, J.D., Meyer, M.W., Reaman, P.S., Braselton, W.E., Major, A., Burgess, N. and Scheuhammer, A.M. (1998). Geographic trend in mercury measured in common loon feathers and blood. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 173-83.
Fournier, F., Karasov, W.H., Kenow, K., Meyer, M.W. and Hines, R.K. (2002). The oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of methylmercury in common loon (Gavia immer) chicks. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. (in press).
Gostomski, T.J. and Evers, D.C. (1998). Time-activity budget for Common Loons, (Gavia immer), nesting on Lake Superior. Can. Field Nat. 112, 191-7.
Heinz, G.H. (1979). Methylmercury: reproductive and behavioral effects on three generations of mallard ducks. J. Wildl. Manag. 43, 394-401.
Hrabik, T.R. and Watras, C.J. (2002). Recent declines in mercury concentration in a freshwater fishery: isolating the effects of de-acidification and decreased atmospheric mercury deposition in Little Rock Lake. Sci. Tot. Environ. (in press).
Koster, M.D., Ryckman, D.P., Weseloh, D.V.C. and Struger, J. (1996). Mercury levels in Great Lakes herring gull (Larus argentatus) eggs. Environ. Poll. 93, 261-70.
Lewis, S.A. and Furness, R.W. (1991). Mercury accumulation and excretion in laboratory reared black-headed gull Larus ridibundus chicks. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 21, 316-20.
Littell, R.C., Milliken, G.A., Stroup, W.W. and Wolfinger, R.D. (1996). SAS system for mixed models. pp. 663. Cary: SAS Institute.
Marks, M. En Chem, Inc. Personal correspondance. 22 June, 2002.
McIntyre, J.M.W. (1975). Biology and behavior of the common loon (Gavia immer) with reference to its adaptability in a man-altered environment. Ph.D. Thesis University of Minnesota, St. Paul.
McIntyre, J.M.W. (1988). The Common Loon: Spirit of Northern Lakes. pp. 228. Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.
Meyer, M.W., Evers, D.C., Daulton, T. and Braselton, W.E. (1995). Common loons (Gavia immer) nesting on low pH lakes in northern Wisconsin have elevated blood mercury content. Water, Air Soil Pollut. 80, 871-80.
Meyer, M.W., Evers, D.C., Hartigan, J.J. and Rasmussen, P.S. (1998). Patterns of Common loon (Gavia immer) mercury exposure, reproduction, and survival in Wisconsin, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 184-90.
Nocera, J.J. and Taylor, P.D.J. (1998). In situ behavioral response of common loons associated with elevated mercury (Hg) exposure. Conserv. Ecol. (online) 2 article 10.
Rada, R.G., Wiener, J.G., Winfrey, M.R. and Powell, D.E. (1989). Recent increases in atmospheric deposition of mercury to north-central Wisconsin lakes inferred from sediment analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 18, 175-81.
Scheuhammer, A.M., Atchison, C.M., Wong, A.H.K. and Evers, D.C. (1998). Mercury exposure in breeding common loons (Gavia immer) in central Ontari, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17(2), 191-6.
Scheuhammer, A.M. and Blancher, P.J. (1994). Potential risk to common loons (Gavia immer) from methylmercury exposure in acidified lakes. Hydrobiologia 279/280, 445-55.
Scheuhammer, A.M., Perrault, J.A. and Bond, D.E. (2001). Mercury, methylmercury, and selenium concentrations in eggs of common loons (Gavia immer) from Canada. Environ. Monitor. Assess 72, 79-94.
Simonin, H.A., Gloss, S.P., Driscol, C.T., Schofield, C.A., Kretser, W.A., Karcher, R.W. and Symula, J. (1994). Mercury in yellow perch from Adirondack drainage lakes (New York, US). In C.J. Watras and J.W. Huckabee (eds) Mercury Pollution-Integration and Synthesis, pp. 457-69. Ann Arbor: Lewis Publishers.
Stickel, L.F., Weimeyer, S.N. and Blus, N.J. (1973). Pesticide residues in eggs of wild birds: adjustment for loss of moisture and lipids. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 193-6.
Sullivan, J.R. and Delfino, J.J. (1982). The determination of mercury in fish. J. Environ. Sci. Health A17, 265-75.
Thompson, D.R. (1996). Mercury in birds and mammals. In W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, pp. 341-56. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Thompson, D.R., Becker, P.H. and Furness, R.W. (1993). Long-term changes in mercury concentrations in herring gulls Larus argentatus and common terns Sterna hirundo from the German North Sea coast. J. Appl. Ecol. 30, 316-20.
Thompson, D.R., Furness, R.W. and Walsh, P.M. (1992). Historical changes in mercury concentrations in the marine ecosystem of the north and north-east Atlantic ocean as indicated by seabird feathers. J. Appl. Ecol. 29, 79-84.
Watras, C.J., Bloom, N.S., Hudson, R.J.M., Gherini, S., Munson, R., Claas, S.A., Morrison, K.A., Hurley, J., Wiener, J.G., Fitzgerald, W.F., Mason, R., Vandal, G., Powell, D., Rada, R., Rislov, L., Winfrey, M., Elder, J., Krabbenhoft, D., Andren, A.W., Babiarz, C., Porcella, D.B. and Huckabee, J.W. (1994). Sources and fates of mercury and methylmercury in Wisconsin lakes. In C.J. Watras and J.W. Huckabee (eds) Mercury Pollution-Integration and Synthesis, pp. 153-80. Ann Arbor: Lewis Publishers.
Weiner, J.G. and Spry, D.J. (1996). Toxicological significance of mercury in freshwater fish. In W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, pp. 297-339. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Wolfe, M.F., Schwarzbach, S. and Sulaiman, R.A. (1998). Effects of mercury on wildlife: a comprehensive review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 146-60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fevold, B.M., Meyer, M.W., Rasmussen, P.W. et al. Bioaccumulation Patterns and Temporal Trends of Mercury Exposure in Wisconsin Common Loons. Ecotoxicology 12, 83–93 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022545130918
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022545130918