Abstract
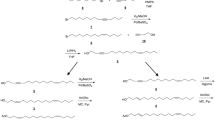
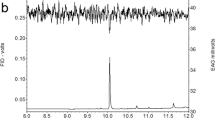
The sex pheromone of Agrotis ipsilon had been previously identified as a blend of (Z)-7-dodecenyl acetate (Z7–12:Ac) and (Z)-9-tetradecenyl acetate (Z9–14:Ac). A synthetic blend of Z7–12:Ac and Z9–14:Ac (30 μg:10 μg) is effective in attracting males in the field. In several countries, addition of (Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate (Z11–16:Ac) to the previously identified blend increases male captures, but this had not been demonstrated in North America. We found Z11–16:Ac, in addition to Z7–12:Ac and Z9–14:Ac, from pheromone gland extracts of females from North America. The mean ratio of Z7–12:Ac, Z9–14:Ac, and Z11–16:Ac produced by individual females was 70.5:14.2:15.3, respectively. In Kentucky, addition of Z11–16:Ac (60 μg) to a two-component blend of Z7–12:Ac and Z9–14:Ac significantly increased the trap capture rate in the field. Traps baited with this three-component blend were 3.3 times (1995) and 4.6 times (1996) more effective in capturing male A. ipsilon than the two-component blend. This improved effectiveness resulted in detection of A. ipsilon in 60% more of the sampling periods in the two years. In the wind tunnel, males flew upwind and contacted a rubber septum loaded with a three-component blend including Z11–16:Ac significantly more frequently than they did to any two-component blend. These results demonstrate that Z11–16:Ac is a pheromone component in this North American population of A. ipsilon.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arn, H., Esbjerg, P., Bues, R., TÓth, M., SzÖcs, G., Guerin, P., and Rauscher, S. 1983. Field attraction of Agrotis segetum males in four European countries to mixtures containing three homologous acetates. J. Chem. Ecol. 9:267–276.
Arn, H., Toth, M., and Priesner, E. 1997. The Pherolist, Internet ed. (www.nyaes.cornell.edu/pheronet).
Baker, T. C., Gaston, L. K., Mistrot Pope, M., Kuenen, L. P. S., and Vetter, R. S. 1981. A high-efficiency collection device for quantifying sex pheromone volatilized from female glands and synthetic sources. J. Chem. Ecol. 7:961–968.
Buleza, V. V. 1991. Role of components of sex pheromone in reproductive behavior of male black cutworm (Agrotis ipsilon). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 318:271–273.
Byers, J. R., and Struble, D. L. 1990. Identification of sex pheromones of two sibling species in dingy cutworm complex, Feltia jaculifera (Gn.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 16:2981–2992.
Byers, J. R., Struble, D. L., Herle, C. E., Kozub, G. C., and Lafontaine, J. D. 1990. Electroantennographic responses differentiate sibling species of dingy cutworm complex, Feltia jaculifera (Gn.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 16:2969–2980.
Causse, R., Bues, R., Barthes, J., and Toubon, J. F. 1988. Mise en évidence expérimentale de nouveaux constituants des phéromones sexuelles de Scotia ipsilon Hufn. et Mamestra suasa Schiff. (Lépidoptères, Noctuidae). Les Colloques de l'INRA, no. 46, Paris.
Clement, S. L., Hill, A. S., Levine, E., and Roelofs, W. L. 1981. Trap catches of male Agrotis ipsilon with synthetic sex pheromone emitted from different dispensers. Environ. Entomol. 10:521–523.
Clement, S. L., Show, E. D., and Way, M. O. 1982. Black cutworm pheromone trapping in strawberries. Calif. Agric. 36:20–21.
Clement, S. L., Kaster, L. V., Showers, W. B., and Schmidt, R. S. 1985. Seasonal changes in the reproductive condition of female black cutworm moths (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 58:62–68.
Hendrix III, W. H., Gunnarson, D. F., and Showers, W. B. 1991. Modification of a meridic diet for rearing black cutworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 64:45–50.
Hill, A. S., and Roelofs, W. L. 1977. Sex pheromone of the black cutworm moth, Agrotis ipsilon (Hufnagel) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). N.Y. Entomol. Soc. 85:179–180.
Hill, A. S., Rings, R. W., Swier, S. R., and Roelofs, W. L. 1979. Sex pheromone of the black cutworm moth, Agrotis ipsilon. J. Chem. Ecol. 5:439–457.
Kaster, L. V., and Showers, W. B. 1982. Evidence of spring immigration and autumn reproductive diapause of the adult black cutworm in Iowa. Environ. Entomol. 11:306–312.
Klun, J. A., and Cooperators. 1975. Insect sex pheromones: Intraspecific pheromonal variability of Ostrinia nubilalis in North America and Europe. Environ. Entomol. 4:891–894.
Levine, E., Clement, S. L., Kaster, L. V., Keaster, A. J., Ruesink, W. G., Showers, W. B., and Turpin, F. T. 1982. Black cutworm, Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), pheromone trapping: A regional research effort. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 28:139–412.
Linn, C. E., Campbell, M. G., and Roelofs, W. L. 1987. Pheromone components and active spaces: What do moths smell and where do they smell it? Science 237:650–652.
LÖfstedt, C., LÖfqvist, J., Lanne, B. S., Van Der Pers, J. N. C., and Hansson, B. S. 1986. Pheromone dialects in European turnip moths Agrotis segetum. Oikos 46:250–257.
Metcalf, R. L., and Metcalf, R. A. 1993. Destructive and Useful Insects: Their Habits and Control, 5th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Miller, J. R., and Roelofs, W. L. 1978. Sustained-flight tunnel for measuring insect responses to wind-borne sex pheromones. J. Chem. Ecol. 4:187–198.
PeÑa, A., Arn, H., Buser, M. R., Rausher, S., Bigler, F., Brunetti, R., Maini, S., and TÓth, M. 1988. Sex pheromone of European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis: Polymorphism in various laboratory and field strains. J. Chem. Ecol. 14:1359–1366.
Picimbon, J. F., Gadenne, C., BÉcard, J. M., ClÉment, J. L., and Sreng, L. 1997. Sex pheromone of the French black cutworm moth, Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Identification and regulation of a multicomponent blend. J. Chem. Ecol. 23:211–230.
Radcliffe, E. B., Flanders, K. L., Ragsdale, D. W., and Noetzel, D. M. 1991. Pest management systems for potato insects, pp. 587–622, in D. Pimentel (ed.). Handbook of Pest Management in Agriculture, 2nd ed., Vol. III. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Rings, R. W., Arnold, F. J., Keaster, A. J., and Musick, G. J. 1974. A worldwide, annotated bibliography of the black cutworm, Agrotis ipsilon (Hufnagel). Ohio Agric. Res. Dev. Cent. Res. Circ. 198:1–106.
Ryan, T. 1960. Significance tests for multiple comparisons of proportions, variances, and other statistics. Psychol. Bull. 57:318–328.
Showers, W. B. 1997. Migratory ecology of the black cutworm. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 42:393–425.
Showers, W. B., Smelser, R. B., Keaster, A. J., Whitford, F., Robinson, J. F., Lopez, J. D., and Taylor, S. E. 1989. Recapture of marked black cutworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) males after long-range transport. Environ. Entomol. 18:447–458.
Showers, W. B., Keaster, A. J., Raulston, J. R., Hendrix III, W. H., Derrick, M. E., McCorcle, M. D., Robinson, J. F., Way, M. O., Wallendorf, M. J., and Goodenough, J. L. 1993. Mechanism of southward migration of a noctuid moth [Agrotis ipsilon (Hufnagel)]: A complete migrant. Ecology 74:2303–2314.
Story, R. N., and Keaster, A. J. 1982. The overwintering biology of the black cutworm, Agrotis ipsilon, in field cages (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 55:621–624.
Swier, S. R., Rings, R. W., and Musick, G. J. 1977. Age-related calling behavior of the black cutworm, Agrotis ipsilon. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 70:919–924.
TÓth, M., LÖfstedt, C., Blair, B. W., Cabello, T., Farag, A., Hansson, B., Kovalev, B. G., Maini, S., Nesterov, E. A., Pajor, I., Sazonov, A. P., Shamshev, I. V., Subchev, M., and SzÖcs, G. 1992. Attraction of male turnip moths Agrotis segetum (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to sex pheromone components and their mixtures at 11 sites in Europe, Asia, and Africa. J. Chem. Ecol. 18:1337–1347.
Troester, S. J., Meyer, R. H., Steffey, K., Godfrey, G. L., Bremer, C. D., Briggs, S. P., Kuhlman, D. E., and Shaw, J. T. 1983. Projecting the beginning of black cutworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) damage to field corn. J. Econ. Entomol. 76:363–367.
Wakamura, S., Struble, D. L., Matsuura, H., Sato, M., and Kegasawa, K. 1986. Sex pheromone of the black cutworm moth, Agrotis ipsilon Hufnagel (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Attractant synergist and improved formulation. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 21:299–304.
Willson, H. R., Semel, M., Tebcherany, M., Prostak, D. J., and Hill, A. S. 1981. Evaluation of sex attractant and blacklight traps for monitoring black cutworm and variegated cutworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 74:517–519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gemeno, C., Haynes, K.F. Chemical and Behavioral Evidence for a Third Pheromone Component in a North American Population of the Black Cutworm Moth, Agrotis ipsilon . J Chem Ecol 24, 999–1011 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022398318465
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022398318465