Abstract
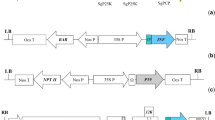
The production and characterisation of transgenic tobacco plantsexpressing a precursor of a regulatory peptide from Aedesaegypti (Trypsin Modulating and Oostatic Factor, Aea-TMOF) whichinterferes with the development of tobacco budworm larvae is described. Tobaccoplants were transformed with a synthetic gene containing 6 TMOF units spaced bydibasic residues, Arg-Arg, as potential post-translational cleavage sites.Peptide extracts from transgenic plants had TMOF activity and inhibitedin vitro the biosynthesis of serine proteases. Thisactivity was consistently present in T1 plants and absent in control plants.Tobacco budworm larvae, fed with transgenic leaves showed a reduced growth ratecompared to those fed with control plants. The low rather than acute toxicityofthis low impact gene is discussed in the context of alternative integrated pestmanagement strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G., Ebert P.R., Mitra A. and Ha S.B. 1988. Binary vectors. In: Gelvin S.B., Schilperoort R.A. and Verma D.P.S. (eds), Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp. 1-19.
Bavoso A., Falabella P., Giacometti R., Halane A.J., Ostuni A., Pennacchio F. et al. 1995. Instestinal absorption of proctolin in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae) larvae. REDIA 78: 173-185.
Boethel D.J. and Eikenbary R.D. 1986. Interactions of plant resistance and parasitoid and predators of insects. Ellis Horwood Ltd, Chichester, England.
Borovsky D. and Schlein Y. 1988. Quantitative determinations of trypsin like and chymotrypsin like enzymes in insects. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 8: 249-260.
Borovsky D., Mahmood F. and Carlson D.A. 1989. Mosquito oostatic hormone, and its potential as unique adulticide and larvicide. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association 60: 66-70.
Borovsky D., Carlson D.A., Griffin P.R., Shabanowitz J. and Hunt D.F. 1990. Mosquito oostatic factor: a novel decapeptide modulating trypsin-like enzymes biosynthesis in the midgut. Federation of American Society of Experimental Biologists Journal 4: 3015-3020.
Borovsky D., Carlson D.A., Griffin P.R., Shabanowitz J. and Hunt D.F. 1993. Mass spectrometry and characterization of Aedes aegypti trypsin modulating oostatic factor (TMOF) and its analogs. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 23: 703-712.
Borovsky D., Powell C.A., Nayar J.K., Blalock J.E. and Hayes T.K. 1994. Characterization and localization of mosquito-gut receptors for trypsin modulating oostatic factor using a complementary peptide and immunocytochemistry. Federation of American Experimental Biologists Journal 8: 350-355.
Bottrell D.G., Barbosa P. and Gould F. 1997. Manipulating natural enemies by plant variety selection and modification: a realistic strategy? Annual Review of Entomology 43: 347-367.
Croy E.J., Ikemura T., Shirsat A. and Croy R.R.D. 1993. Plant nucleic acids. Plant molecular biology, LabFax 2: 37-42.
De Loof A., Bylemans D., Schoofs L., Janssen I. and Huybrechts R. 1995. The folliculostatins of two dipteran insect species, their relation to matrix proteins and prospects for practical applications. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 77: 1-9.
De Loof A., Bylemans D., Schoofs L., Janssen I., Spittaels K., Vanden Broeck J. et al. 1995. Folliculostatin, gonadotropins and a model for control of growth in the grey fleshfly, Neobelleria (Sarcophaga) bullata. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 25: 661-667.
De Loof A. 1996. Endogenous insect regulatory peptides: a novel lead towards insect control. Agro-Food-Industry, High Tech: Nov-Dec pp 23-25.
Devine G.J., Wright D.J. and Denholm I. 2000. A parasitic wasp (Eretmocerus mundus Mercet) can exploit chemically induced delays in the development rates of its whitefly host (Bemisia tabaci Genn.). Biological Control 19: 64-75.
Dowson Day M.J., Ashurst J.L. and Dixon R.A. 1994. Plant expression cassette for enhanced translational efficiency. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 12: 347-357.
Dowson Day M.J., Ashurst J.L., Mathias S.F., Watts J.W., Wilson T.M.A. and Dixon R.A. 1993. Plant viral leaders influence expression of a reporter gene in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 23: 97-109.
Doyle J.J. and Doyle J.L. 1987. Genomic Plant DNA preparation from fresh tissue. Phytochem Bull 19: 11-14.
Fishman L.L., Primor N. and Zlotkin E. 1984. The selective permeability of fleshfly midgut to an orally cobra cardiotoxin. J Exp Biol 108: 441-451.
Franssen H.J. 1998. Plants embrace a stepchild: the discovery of peptide growth regulators. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1: 384-387.
Gould F. 1998. Sustainability of transgenic insecticidal cultivars: integrating pest genetics and ecology. Annual Review of Entomology 43: 701-726.
Hare J.D. 1992. Effects of plant variation on herbivore-natural enemy interactions. In: Fritz R.S. and Simms E.L. (eds), Plant Resistance to Herbivores and Pathogens: Ecology, Evolution, and Genetics. Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 278-298.
Horsh R.B., Fry J.E., Hoffmann N.L., Eocholtz D., Rogers S.H. and Fraley R.T. 1987. A simple and general method for transferring genes in plants. Science, 227: 1229-1231.
Johnson M.T. and Gould F. 1992. Interaction of genetically engineered host plant resistance and natural enemies of Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in tobacco. Environmental Entomology 21: 586-597.
Keeley L.L. and Hayes 1987. Speculation on Biotechnology applications for insect neuroendocrine research. Insect Biochem 17: 639-651.
Keeley L.L., Hayes T.K. and Bradfield J.Y. 1990. Insect neuroendocrinology: its past; its present; future opportunities. In: BorKovec A.B. and Masler P. (eds), Insect Neurochemistry and Neurophysiology. Humana, Clifton, NJ, USA, pp. 163-203.
Loh Y.P., Brownstein M.L. and Gainer H. 1984. Proteolysis in neuropeptide processing and other neural functions. Annu Rev Neurosci 7: 189-222.
Matsubayashi Y., Morita A., Matsunaga E., Furuya A., Hanai A. and Sagagami Y. 1999. Physiological relationship between auxin cytokinin and a peptide growth factor phytosulfoksine-a in stimulation of asparagus cell proliferation. Planta 3207: 559-565.
Menn J.J. and Borkovec A.B. 1989. Insect Neuropeptides: Potential new control agents. J Agr Food Chem 37: 271-278.
Primor N. and Zlotkin E. 1978. Oral toxicity of venom and toxins to blowflies. In: Rosenberg P. (ed.), Toxins: Animal, Plant and Microbial. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 1087-1095.
Primor N. and Zlotkin E. 1980. Penetrability of proteins through the digestive system of sarcophaga falculata blowfly. Biochim Biophys Acta 627: 82-90.
Primor N., Teitelbaum Z. and Zlotkin E. 1980. Penetrability of orally toxic protein from cobra venom through the gut of a blowfly. Biochim Biophys Acta 627: 71-81.
Raina A.K., Rafaeli A. and Kingan T. 1994. Pheromonotropic activity of orally administred PBAN and its analogues in Helicoverpa zea. J Insect Physiol 40: 393-397.
Rao R., Manzi A., Filippone E., Manfredi P., Spasiano A., Colucci G. et al. 1996. Synthesis and expression of genes encoding putative insect neuropeptide precursor in tobacco. Gene 175: 1-5.
Ryan C. and Pearce G. 1998. Systemin: a polypeptide signal for plant defensive genes. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 14: 1-17.
Sambrook J., Fritsh E.F. and Maniatis T. 1989. Molecular cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Schneidermann H.A. 1984. What entomology has in store for biotechnology. Bull Ent Soc Am 30: 55-61.
Sokal R.R., Rohlf F. and James 1995. Biometry. 3rd edn. Freeman, NY.
SPSS Inc. 1999. Systat for Windows Statistics I., pp. 660.
Van Emden H.F. 1966. Plant insect relationships and pest control. World Rev Pest Control 5: 115-123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tortiglione, C., Fanti, P., Pennacchio, F. et al. The expression in tobacco plants of Aedes aegypti Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor (Aea-TMOF) alters growth and development of the tobacco budworm, Heliothis virescens . Molecular Breeding 9, 159–169 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019785914424
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019785914424