Abstract
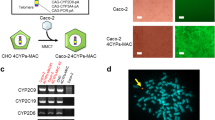
Purpose. To further characterize CYP3A4-transfected Caco-2 cells with regard to morphological, transport, and metabolic properties, and to evaluate a different Caco-2 cell strain transfected with both CYP3A4 and oxidoreductase (OR).
Methods. Transfected Caco-2 cells, Caco-2 TC7 cells, and wild-type Caco-2 cells grown onto Millicell™ were used. We determined the morphological characteristics of transfected cell monolayers using light and transmission electron microscope. We determined the transport and metabolic capabilities of the transfected cells, TC7 cells, and wild-type cells with a variety of drugs, nutrients, and marker compounds.
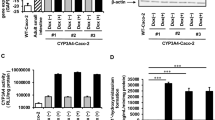
Results. The transfected Caco-2 cells formed a tight monolayer with TEER values and mannitol transport similar to the untransfected parent cell strain (wild type). However, the transfected cells (grown onto Millicell™) reached maturity approximately 33% faster than the wild-type cells. Permeabilities of propranolol, nifedipine, testosterone, linopirdine, mannitol, and cephalexin were similar in transfected and wild-type Caco-2 cells. On the other hand, the transfected cells of early passages were much more metabolically active, and metabolized standard CYP3A4 substrates (e.g., testosterone and nifedipine) as much as 100 times faster than untransfected cells. In addition, metabolism of standard substrates was inhibitable by ketoconazole and TAO. Using comparable data, the transfected cells metabolized testosterone the fastest, followed by linopirdine and nifedipine (approximate ratio: 10:6:2). The metabolites of standard substrates were generally preferably excreted to the apical membrane.
Conclusions. The monolayers of newly transfected cells (CYP3A4 + OR) have a significantly increased level of CYP3A4 activities compared to untransfected cells. These cell monolayers also have desirable morphological and transport characteristics that are similar to untransfected cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. Artursson and J. Karlsson. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 175:880-885 (1991).
J. D. Irvine, L. Takahashi, K. Lockhart, J. Cheong, J. W. Tolan, H. E. Selick, and J. R. Grove. MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells: A tool for membrane permeability screening. J. Pharm. Sci. 88:28-33. (1999).
C. L. Crespi, B. W. Penman, and M. Hu. (1996) The development of Caco-2 cells expressing high levels of cDNA-derived cytochrome P4503A4. Pharm. Res. 13:1635-1641 (1996).
L. S. L. Gan, M. A. Moseley, B. Khosla, P. F. Augustijns, T. P. Bradshaw, R. W. Hendren, and D. R. Thakker. CYP3A-like cytochrome p-450-mediated metabolism and polarized efflux of cyclosporin A in Caco-2 cells: Interaction between the two biochemical barriers to intestinal transport. Drug Metab. and Disp. 24:344-349 (1996).
J. C. Kolars, W. M. Awni, R. M. Merion, and P. B. Watkins. First-pass metabolism of cyclosporin by the gut. Lancet 338:1488-1490 (1991).
D. J. Back and S. M. Rogers. First pass metabolism by the gastrointestinal mucosa. Alimen. Pharmacol. Ther. 1:119-157 (1987).
D. R. Krishna and U. Klotz. Extrahepatic metabolism of drugs in humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 26:144-160 (1994).
C. L. Crespi and V. P. Miller. The R144C change in the CYP2C9*2 allele alters interaction of the cytochrome P450 with NADPH cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. Pharmacogenetics 7:203-210 (1997).
M. Hu, J. Chen, Y. Zhu, A. H. Dantzig, R. E. Stratford, and M. T. Kuhfeld. Mechanism and kinetics of transcellular transport of a new β-lactam antibiotic loracarbef across an human intestinal epithelial model system (Caco-2). Pharm. Res. 11:1405-1413 (1994).
M. Hu, L. Zheng, J. Chen, L. Liu, Y. Li, A. H. Dantzig, and R. E. Stratford. Peptide transporter function and prolidase activities in Caco-2 cells: a lack of coordinated expression. J. Drug Target. 3:291-300 (1995).
M. Hu, L. Zheng, J. Chen, L. Liu, Y. Zhu, A. H. Dantzig, R. E. Stratford. Mechanisms of transport of quinapril in Caco-2 cell monolayers: comparison with cephalexin. Pharm. Res. 12:1120-1125 (1995).
B. W. Penman, J. Reece, T. Smith, C. S. Yang, H. V. Gelboin, F. J. Gonzalez, and C. L. Crespi. Characterization of a human cell line expressing high levels of cDNA-derived CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 3:28-39 (1993).
V. Carrier, T. Lesuffleur, A. Barbat, M. Rousset, E. Dussaulx, P. Costet, I. Dewaziers, P. Beaune, and A. Zweibaum. Expression of cytochrome P450 3A in HT29-MTX and Caco-2 cell clone TC7. FEBS Letters. 355:247-250 (1994).
D. J. Newton, R. W. Wang, and A. Y. H. Lu. Cytochrome P450 inhibitors: Evaluation of specificities in the in vitro metabolism of therapeutic agents by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Disp. 23:154-158 (1995).
S. Diamond, D. Rakestraw, J. O'Neil, G. N. Lam, and D. D. Christ. Induction of cytochromes P-450 2B and 3A in mice following the dietary administration of the novel cognitive enhancer linopirdine. Drug Metab. Disp. 22:65-73 (1994).
L. Grushkin-Lerner. The use of PET membranes for the study of cells for electron microscopy. The Cell Line. 5:1-2 (1995).
P. A. Jones. Altering gene expression with 5-azacytidine. Cell 40:485-486 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, M., Li, Y., Davitt, C.M. et al. Transport and Metabolic Characterization of Caco-2 Cells Expressing CYP3A4 and CYP3A4 Plus Oxidoreductase. Pharm Res 16, 1352–1359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018986605929
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018986605929