Abstract
Purpose. The objective of this work is to prepare microspheres by the emulsion-solvent evaporation process using MPOE-PLA copolymers as the matrix material and/or the surfactant. This preparation was studied in order to avoid the use of PVA as the surfactant in the process.
Methods. Two series of MPOE-PLA copolymers were synthesised. The first, with a long and constant length PLA chain (45,000 g.mol-1), was used as the matrix material, the second, with short PLA chains (≤ 2,200 g.mo1-1), and different HLB as the surfactant. Microspheres were prepared by the "simple” and "double” emulsion methods. The steric stabilization effect of the copolymers was investigated using confocal microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS).
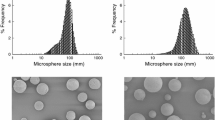
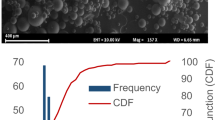
Results. Confocal microscopy and XPS analysis showed that the microspheres prepared using MPOE5K-PLA0.5K as the surfactant and MPOE-PLA45K copolymers as the matrix material had an MPOE coating present at the microsphere surface. This hydrophilic layer ensures steric stabilization of the particles.
Conclusions. MPOE-PLA copolymers can be used for the preparation of particles instead of PVA and their use can be extended whenever a biocompatible and bioeliminable surfactant is required for biological or medical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. E. Cutright, J. D. Beasley, and B. Perez. Histologic comparison of polylactic and polyglycolic acid sutures. Oral Surg. 32:165–173 (1971).
P. H. Craig, J. A. Williams, K. W. Davis, A. D. Magoun, A. J. Levy, S. Bogdansky, and J. P. Jones Jr. A biologic comparison of polylactic 910 and polyglycolic acid synthetic absorbable sutures. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 141:1–10 (1975).
H. T. Wang, E. Schmitt, D. R. Flanagan, and R. J. Linhardt. Influence of formulation methods on the in vitro controlled release of proteins from poly(ester) microspheres, J. Contr. Rel. 17: 23–31 (1991)
Y. Tabata, S. Gutta, and R. Langer. Controlled delivery systems for proteins using polyanhydride microspheres. Pharm. Res. 10:487–496 (1993).
G. Crotts, H. Sah, and T. G. Park. Adsorption determines in vitro protein release rate from biodegradable microspheres: quantitative analysis of surface area during degradation. J. Contr. Rel. 41:101–111 (1997).
E. Celikkaya, E. B. Denkbas, and E. Piskin. Rifampicin carrying poly(D,L-lactide)/poly(ethylene glycol) microspheres: loading and release. Artificial Organs. 20:743–751 (1996).
K. J. Youxin, C. Volland, and T. Kissel. In vitro degradation and bovine serum albumin release of the ABA triblock copolymers consisting of poly(L(+) lactic acid) or poly(L(+) lactic acid or glycolic acid) A-blocks attached to central polyoxyethylene B-blocks. J. Control. Rel. 32:121–128 (1994).
S. Stolnik, S. E. Dunn, M. C. Garnett, M. C. Davies, A. G. A. Coombes, D. C. Taylor, M. P. Irving, S. C. Purkiss, T. F. Tardros, S. Davis, and L. Illum. Surface modification of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres by biodegradable poly(lactide)-poly-(ethylene glycol) copolymers. Pharm. Res. 11:1800–1808 (1994).
X. S. G. Hu, H. J. Liu, and I. L Pan. Inhibition of bovine serum albumin adsorption by poly (ethylene glycol) soft segment in biodegradable poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(L-lactide) copolymers. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 50:1391–1396 (1993).
S. Stolnick, L. Illum, and S. S. Davis. Long circulating microparticulate drug carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 16:195–214 (1995).
D. Bazile, C. Prud'homme, M. T. Bassoulet, M. Marlard, G. Spenlehauer, and M. Veillard. Stealth MePEG-PLA nanoparticles avoid uptake by the mononuclear phagocyte system. J. Pharm. Sci. 84:493–498 (1995).
A. M. Leray, M. Vert, J. C. Gautier, and J. P. Benoit. Fate of [C-14] poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles after intravenous and oral-administration to mice. Int. J. Pharm. 106:201–211 (1994).
H. Rafati, E. C. Lavelle, A. G. A. Coombes, J. Holland, and S. S. Davis. The immune response to a model antigen associated with PLG microparticles prepared using different surfactants. Vaccine. 15:1888–1897 (1997).
T. Yamaoka, Y. Tabata, and Y. Ikada. Accumulation of poly(vinyl alcohol) at inflamatory site. ACS Symposium Series. 545:163–171 (1994).
T. Yamaoka, Y. Tabata, and Y. Ikada. Comparison of body distribution of poly(vinyl alcohol) with other water-soluble polymers after intravenous administration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47:479–486 (1995).
W. C. Hueper. Carcinogenic studies of water-soluble and insoluble macromolecules. Arch. Pathol. 67:589–617 (1959).
P. Bouillot, A. Petit, and E. Dellacherie. Protein encapsulation in biodegradable amphiphilic microspheres I. Polymer synthesis and characterization, and microsphere elaboration. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 68:1695–1702 (1998).
H. R. Kricheldorf and C. Boettcher. Polylactones 27. Anionic polymerisation of L-lactide. Variation of end groups and synthesis of block copolymers with poly(ethylene oxide). Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Symp. 73:47–64 (1993).
R. Gref, V. Babak, P. Bouillot, I. Lukina, M. Borodev, and E. Dellacherie. Interfacial and emulsion stabilising properties of amphiphilic water-soluble poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) copolymers for the fabrication of biocompatible nano-and microparticles. Colloids and Surfaces. A. Physico-chemical and engineering aspects. In press.
M. C. Davies, R. D. Short, M. A. Kahn, J. F. Watts, A. Brown, M. J. Eccles, P. Humphrey, J. C. Vickerman, and M. Vert. An XPS and SIMS analysis of biodegradable biomedical polyesters. Surf. Interface Anal. 14:115–120 (1989).
K. M. Shakesheff, C. Evora, I. Soriano, and R. Langer. The adsorption of poly(vinyl alcohol) to biodegradable microparticles studied by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 185:538–547 (1997).
M. Penco, S. Marcioni, P. Ferruti, S. D'antone, and R. Deghenghi. Degradation behaviour of block copolymers containing poly(lactic-glycolic acid) and poly(ethylene glycol) segments. Biomaterials. 17:1583–1590 (1996).
A. Carrio, G. Schwach, J. Coudane, and M. Vert. Preparation and degradation of surfactant-free PLAGA microspheres. J. Control. Rel. 37:113–121 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouillot, P., Babak, V. & Dellacherie, E. Novel Bioresorbable and Bioeliminable Surfactants for Microsphere Preparation. Pharm Res 16, 148–154 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018895417915
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018895417915