Abstract
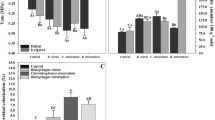
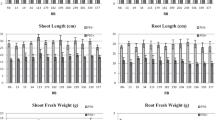
The effect of soil moisture at different temperatures on root rot of wheat seedlings caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-8 was studied in temperature controlled water tanks under glasshouse conditions. Four moisture levels (15, 30, 50 and 75% of soil water holding capacity at saturation which were equal to −10, −7, −5 and −3 kPa, respectively) were tested in tanks maintained 10, 15, 20 or 25 °C. The role of microbial activity in the effect of soil moisture and temperature on disease severity was also studied by including treatments of steam treated soil. Results showed that at soil moisture levels optimum for plant growth (50 and 75% WHC) disease was more severe at a lower temperature (10 °C), but under relatively dry conditions (15% WHC) disease levels were similar at all temperatures tested. In warm soils (20 and 25 °C) at high soil moisture levels (50 and 75% WHC), disease was more severe in steam treated soil than in non-steam treated soil, indicating that the suppression of disease in natural soil under these conditions was associated with high soil microbial activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asher C J, Ozanne P G and Loneragan J F 1965 A method of conttrolling the ionic environment of plant roots. Soil Sci. 100, 149–156.
Baker R and Martinson C A 1970 Epidemology of disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani. In Rhizoctonia solani: Biology and Pathology. Ed. JR Parmeter pp 172–188. University of California Press, Berkeley, Calif.
Biederbeck V O and Campbell C A 1973 Soil microbial activity as influenced by temperature trends and fluctuations. Can. J. Soil Sci. 53, 363–376.
Boddy L 1983 Effect of temperature and water potential on the growth rate of wood rotting basidiomycetes. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 80, 141–149.
Carling D E and Leiner R H 1990 Effect of temperature on virulence of Rhizoctonia solani and other Rhizoctonia on potato. Phytopathology 80, 930–934.
Chen W, Hoitink H A J and Madden L V 1988 Microbial activity and biomass in container media for predicting suppressiveness to damping-off caused by Pythium ultimum. Phytopathology 78, 1447–1450.
Dube A J 1971 Studies on the growth and survival of Rhizoctonia solani. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia.
Gill J S, Sivasithamparam K and Smettem K R J 2000 Soil types with different soil texture affects Rhizoctonia root rot of wheat seedlings. Plant Soil 221, 113–120.
Glick B R 1995 The enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 41, 109–117.
Griffin D M 1972 Ecology of Soil Fungi, Chapman and Hall, London. pp 71-85
Gross MK, Santini JB, Tikhonova I and Latin R 1998 The influence of temperature and leaf wetness duration on infection of perennial ryegrass by Rhizoctonia solani. Plant Dis. 82, 1012–1016.
Hendrix P F, Crossley D A, Jr., Coleman D C, Parmelee R W and Bear M H 1987 Carbon dynamics in soil microbes and fauna in conventional and no tillage agroecosystem. Intecol. Bull. 15, 59–63.
Hide G A and Firmager J P 1989 Effect of soil temperature and moisture on stem canker (Rhizoctonia solanti) disease of potatoes. Potato Res. 32, 75–80.
Kousik C S, Snow J P, Berggren G T and Harville B G 1995 Effect of temperature on virulence of Rhizoctonia solanti on soybean leaves and seedlings. Plant Pathol. 44, 580–586.
Kumar S, Sivasithamparam K, Gill J S and Sweetingham MW 1999 Temperature and water potential effects on growth and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani Anastomosis Group 11 to lupin. Can. J. Microbiol. 45, 389–395.
Lynch J M 1990 The Rhizosphere. Wiley Inter Science, Chichester, UK.
Lootsma M and Scholte K 1997 Effect of soil moisture content on the suppression of Rhizoctonia stem canker on potato by the nematode Aphelenchus avenae and the springtail Folsomia flimetaria. Plant Pathol. 46, 209–215.
MacDonald H J and Rovira A D 1985 Development of inoculum technique for Rhizoctonia solani and its application to screening cereal cultivars. In Ecology and Management of Soil-borne Plant Pathogens. Eds. C A Parker, A D Rovira, K J Moore, P T W Wong and J F Kollmorgen. The Americ. Phytopathol. Soc., St. Paul, Minn., USA pp, 174–176.
Martin S B and Lucas L T 1984 Chracterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia sp. and binuleate Rhizoctonia- like fungi from turf grasses in North Carolina. Phytopathology 74, 170–175.
Shehata M A, Davis D W and Anderson N A 1984 Resistance to Rhizoctonia stem rot in peas as influenced by temperature, watering method and period of disease development. Plant Dis. 68, 22–24.
Smiley R W and Uddin W 1993 Influence of soil temperature on Rhizoctonia root rot (R. solani AG-8 and R. oryzae) of winter wheat. Phytopathology 83, 777–785.
Sumner D R 1974 Ecology and control of seedling diseases of crucifers. Phytopathology 64, 692–697.
Sussman A S 1965 Dormancy of soil micro-organisms in relation to survival. In Ecology of Soil-borne Plant Pathogens: Prelude to Biological Control. Eds. KF Baker and WC Snyder pp 99–109. University of California Press, Berkeley, Calif.
Teo B K, Yitbarek S M, Verma P R and Morrall R A A 1988 In-fluence of soil moisture, seedling date and Rhizoctonia solani isolates (AG 2-1 and AG 4) on disease incidence and yield in canola. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 10, 151–168.
You M P and Sivasithamparam K 1994 Changes in microbial populations of an avocado plantation mulch suppressive of Phytophthora cinnamomi. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2, 33–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, J.S., Sivasithamparam, K. & Smettem, K.R.J. Effect of soil moisture at different temperatures on Rhizoctonia root rot of wheat seedlings. Plant and Soil 231, 91–96 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010394119522
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010394119522