Abstract
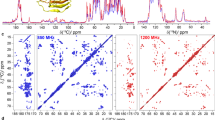
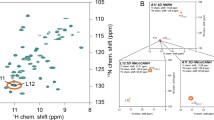
A novel automated approach for the sequence specific NMR assignments of 1HN, 13Cα, 13Cβ, 13C′/1Hα and 15N spins in proteins, using triple resonance experimental data, is presented. The algorithm, TATAPRO (Tracked AuTomated Assignments in Proteins) utilizes the protein primary sequence and peak lists from a set of triple resonance spectra which correlate 1HN and 15N chemical shifts with those of 13Cα, 13Cβ and 13C′/1Hα. The information derived from such correlations is used to create a `master_list' consisting of all possible sets of 1HN i, 15Ni, 13Cα i, 13Cβ i, 13C′i/1Hα i, 13Cα i−1, 13Cβ i−1 and 13C′i−1/ 1Hα i−1 chemical shifts. On the basis of an extensive statistical analysis of 13Cα and 13Cβ chemical shift data of proteins derived from the BioMagResBank (BMRB), it is shown that the 20 amino acid residues can be grouped into eight distinct categories, each of which is assigned a unique two-digit code. Such a code is used to tag individual sets of chemical shifts in the master_list and also to translate the protein primary sequence into an array called pps_array. The program then uses the master_list to search for neighbouring partners of a given amino acid residue along the polypeptide chain and sequentially assigns a maximum possible stretch of residues on either side. While doing so, each assigned residue is tracked in an array called assig_array, with the two-digit code assigned earlier. The assig_array is then mapped onto the pps_array for sequence specific resonance assignment. The program has been tested using experimental data on a calcium binding protein from Entamoeba histolytica (Eh-CaBP, 15 kDa) having substantial internal sequence homology and using published data on four other proteins in the molecular weight range of 18–42 kDa. In all the cases, nearly complete sequence specific resonance assignments (> 95%) are obtained. Furthermore, the reliability of the program has been tested by deleting sets of chemical shifts randomly from the master_list created for the test proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartels, C., Billeter, M., Güntert, P. and Wüthrich, K. (1996) J. Biomol. NMR, 7, 207-213.
Bax, A. and Grzesiek, S. (1993) Acc. Chem. Res., 26, 131-138.
Buchler, N.E.G., Zuiderweg, E.R.P., Wang, H. and Goldstein, R.A. (1997) J. Magn. Reson., 125, 34-42.
Choy, W.Y., Sanctuary, B.C. and Zhu, G. (1997) J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 37, 1086-1094.
Clubb, R.T., Thanabal, V. and Wagner, G. (1992a) J. Magn. Reson., 97, 213-217.
Clubb, R.T., Thanabal, V. and Wagner, G. (1992b) J. Biomol. NMR, 2, 203-210.
Clubb, R.T. and Wagner, G. (1992) J. Biomol. NMR, 2, 389-394.
Friedrichs, M.S., Mueller, L. and Wittekind, M. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR, 4, 703-726.
Gardner, K.H. and Kay, L.E. (1998) Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 27, 357-406.
Gardner, K.H., Zhang, X., Gehring, K. and Kay, L.E. (1998) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 120, 11738-11748.
Gronwald, W., Willard, L., Jellard, T., Boyko, R.F., Rajarathnam, K., Wishart, D.S., Sönnichsen, F.D. and Sykes, B.D. (1998) J. Biomol. NMR, 12, 395-405.
Grzesiek, S. and Bax, A. (1992) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 114, 6291-6293.
Grzesiek, S. and Bax, A. (1993) J. Biomol. NMR, 3, 185-204.
Hare, B.J. and Prestegard, H. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR, 4, 35-46.
Ikura, M., Kay, L.E. and Bax, A. (1990) Biochemistry, 29, 4659-4667.
Kay, L.E., Ikura, M., Tschudin, R. and Bax, A. (1990) J. Magn. Reson., 89, 496-514.
Li, K.-B. and Sanctuary, B.C. (1997) J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 37, 467-477.
Li, S.C., Zwahlen, C., Vincent, S.J., McGlade, C.J., Kay, L.E., Pawson, T. and Forman-Kay, J.D. (1998) Nat. Struct. Biol., 5, 1075-1083.
Leutner, M., Gschwind, R.M., Liermann, J., Schwarz, C., Gemmecker, G. and Kessler, H. (1998) J. Biomol. NMR, 11, 31-43.
Loria, J.P., Rance, M. and Palmer, A.G. (1999) J. Magn. Reson., 141, 180-184.
Lukin, J.A., Gove, A.P., Talukdar, S.N. and Ho, C. (1997) J. Biomol. NMR, 9, 151-166.
Meadows, R.P., Olejniczak, E.T. and Fesik, S.W. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR, 4, 79-96.
Metzler, W.J., Constantine, K.L., Friedrichs, M.S., Bell, A.J., Ernst, E.G., Lavoie, T.B. and Mueller, L. (1993) Biochemistry, 32, 13818-13829.
Montelione, G.T., Rios, C.B., Swapna, G.V.T. and Zimmerman, D.E. (1999) In Biological Magnetic Resonance, Volume 17: Structure, Computation and Dynamics in Protein NMR (Eds., Krishna, R. and Berliner, L.), Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp. 81-130.
Moseley, H.N.B. and Montelione, G.T. (1999) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 9, 635-642.
Moy, F.J., Pisano, M.R., Chandra, P.K., Urbano, C., Killar, L.M., Sung, M.L. and Powers, R. (1997) J. Biomol. NMR, 10, 9-19.
Olson Jr., J.B. and Markley, J.L. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR, 4, 385-410.
Pham, T.-N. and Koide, S. (1998) J. Biomol. NMR, 11, 407-414.
Sahu, S.C., Atreya, H.S., Chauhan, S., Bhattacharya, A., Chary, K.V.R. and Govil, G. (1999) J. Biomol. NMR, 14, 93-94.
Salzmann, M., Pervushin, K., Wider, G., Senn, H. and Wüthrich, K. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 13585-13590.
Salzmann, M., Wider, G., Pervushin, K., Senn, H. and Wüthrich, K. (1999) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 121, 844-848.
Seavey, B.R., Farr, E.A., Westler, W.M. and Markley, J.L. (1991) J. Biomol. NMR, 1, 217-236.
Wittekind, M. and Mueller, L. (1993) J. Magn. Reson., B101, 201-205.
Wüthrich, K. (1986) NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids, Wiley, New York, NY.
Zimmerman, D.E., Kulikowski, C., Wang, L.L., Lyons, B.A. and Montelione, G.T. (1994) J. Biomol. NMR, 4, 241-256.
Zimmerman, D.E., Kulikowski, C.A., Huang, Y., Feng, W., Tashiro, M., Shimotakahara, S., Chien, C., Powers, R. and Montelione, G.T. (1997) J. Mol. Biol., 269, 592-610.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atreya, H., Sahu, S., Chary, K. et al. A tracked approach for automated NMR assignments in proteins (TATAPRO). J Biomol NMR 17, 125–136 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008315111278
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008315111278