Abstract
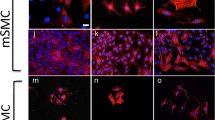
A method for establishing primary cultures of smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from the porcine coronary artery without either microdissection and/or enzymatic dispersion was developed using selective migration of cells from coronary explants in vitro. This culture method relies on the heterogeneity of cell types and differences in their migration and adherence ability to separate SMC from contaminating fibroblasts or endothelial cells. The cell type was determined by immunohistochemical staining with monoclonal antibodies to SM α-actin, SM myosin, h-caldesmon and von Willebrand factor. The first wave of migration (1-7 days) consisted of a mixture of fibroblasts and SMCs. Only SMCs were present in the second wave of migration (7-14 days). Endothelial cells, which exhibited a lower capacity for migration and adherence, were restricted to the third wave of migration (14-21 days). Cells obtained from the second wave of migration exhibited the characteristic single-layered, aligned, hill-and-valley pattern of SMCs when confluent. Quiescence was attained 4-5 days after removal of serum, as established by [3H]-thymidine incorporation. Stimulation of the quiescent SMCs with 20% FBS resulted in a synchronous re-entry into the cell-cycle with S phase reached 15-18 h later. The SMCs prepared using this protocol thus exhibit the structural markers and capacity to undergo phenotypic modulation that are characteristic of SMCs in vivo. This approach to establishing primary cultures of SMCs offers the advantage of selecting for the subpopulation of cells capable of migration in response to injury or growth factor stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reidy MA: A reassessment of endothelial injury and arterial lesion formation. Lab Invest 53: 513–520, 1985
Schwartz SM, deBlois D, O'Brien ERM: The intima: Soil for atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circ Res 77: 445–465, 1995
Okamoto E, Imataka K, Fujii J, K uro-o M, Nakahara K, Nishimura H, Yazaki Y, Nagai R: Heterogeneity in smooth muscle cell population accumulating in the neointimas and the media of poststenotic dilatation of the rabbit carotid artery. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 185: 459–464, 1992
Chamley-Campbell J, Campbell GR, Ross R: The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev 59: 1–61, 1979
Gimbrone MA, Cotran RS: Human vascular smooth muscle in culture, growth and ultrastructure. Lab Invest 33: 16–27, 1975
Ross R: The smooth muscle cell II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibres. J Cell Biol 50: 172–186, 1971
Libby P, O'Brien KV: Culture of quiescent arterial smooth muscle cells in a defined serum-free media. J Cell Physiol 115: 217–223, 1983
Zahradka P, Elliot T, Hovland K, Larson DE, Saward L: Repression of histone gene transcription in quiescent 3T6 fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem 127: 683–690, 1993
Shanahan CM, Weissberg PL, Metcalfe JC: Isolation of gene markers of differentiated and proliferating vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 73: 193–204, 1993
Wagner DD, Marder VJ: Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells: Processing steps and their intracellular localization. J Cell Biol 99: 2123–2130, 1984
Neylon CB, Avdonin PV, Dilley RJ, Larsen MA, Tkachuk VA, Bobik A: Different electrical responses to vasoactive agonists in morpho-logically distinct smooth muscle cell types. Circ Res 75: 733–741, 1994
Kasai T, Pollak OJ: Smooth muscle cells in aortic cultures of untreated and cholesterol-fed rabbits. Zeitschrift fur Zelforschung 62: 743–752, 1964
Yau L, Zahradka P: Immunodetection of activated mitogen-activated protein kinase in vascular tissues. Mol Cell Biochem, in press, 1997
Saward L, Zahradka P: Both the AT1 and AT2 receptors mediate smooth muscle cell growth by angiotensin II. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27: A103, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saward, L., Zahradka, P. Coronary artery smooth muscle in culture: migration of heterogeneous cell populations from vessel wall. Mol Cell Biochem 176, 53–59 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006870827516
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006870827516