Abstract
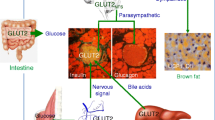
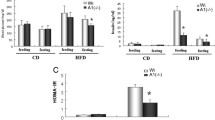
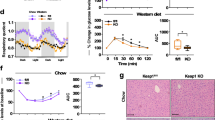
This review focuses on the effects of varying levels of GLUT4, the insulin-sensitive glucose transporter, on insulin sensitivity and whole body glucose homeostasis. Three mouse models are discussed including MLC-GLUT4 mice which overexpress GLUT4 specifically in skeletal muscle, GLUT4 null mice which express no GLUT4, and the MLC-GLUT4 null mice which express GLUT4 only in skeletal muscle. Overexpressing GLUT4 specifically in the skeletal muscle results in increased insulin sensitivity in the MLC-GLUT4 mice. In contrast, the GLUT4 null mice exhibit insulin intolerance accompanied by abnormalities in glucose and lipid metabolism. Restoring GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle in the MLC-GLUT4 null mice results in normal glucose metabolism but continued abnormal lipid metabolism. The results of experiments using these mouse models demonstrates that modifying the expression of GLUT4 profoundly affects whole body insulin action and consequently glucose and lipid metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thorens B, Charron MJ, Lodish HF: Molecular physiology of glucose transporters. Diabetes Care 13: 209–218, 1990
Waddell ID, Zomerschoe AG, Voice MW, Burchell A: Cloning and expression of a hepatic microsomal glucose transport protein. Comparison with liver plasma-membrane glucose-transport protein GLUT 2. Biochem J 286: 173–177, 1992
Mueckler M: Family of glucose-transporter genes: implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes 39: 6–11, 1990
Kayano T, Burant CF, Fukumoto H, Gould GW, Fan YS, Eddy RL, Byers MG, Shows TB, Seino S, Bell GI: Human facilitative glucose transporters. Isolation, functional characterization, and gene localization of cDNAs encoding an isoform (GLUT5) expressed in small intestine, kidney, muscle, and adipose tissue and an unusual glucose transporter pseudogene-like sequence (GLUT6). J Biol Chem 265: 13276–13282, 1990
Kahn BB: Glucose transport: Pivotal step in insulin action. Diabetes 45: 1644–1654, 1996
Charron MJ, Brosius FC III., Alper SL, Lodish HF: A glucose transport protein expressed predominantly in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2535–2539, 1989
Birnbaum MJ: Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell 57: 305–315, 1989
James DE, Strube M, Mueckler M: Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature 338: 83–87, 1989
Kaestner KH, Christy RJ, McLenithan JC, Braiterman LT, Cornelius P, Pekala PH, Lane MD: Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 3150–3154, 1989
Fukumoto H, Kayano T, Buse JB, Edwards Y, Pilch PF, Bell GI, Seino S: Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem 264: 7776–7779, 1989
Cushman SW, Wardzala LJ: Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 255: 4758–4762, 1980
Suzuki K, Kono T: Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 2542–2545, 1980
Satoh S, Nishimura H, Clark AE, Kozka IJ, Vannucci SJ, Simpson IA, Quon MJ, Cushman SW, Holman GD: Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem 268: 17820–17829, 1993
Kahn BB: Facilitative glucose transporters: Regulatory mechanisms nd dysregulation in diabetes. J Clin Invest 89: 1367–1374, 1992
Birnbaum MJ: The insulin-sensitive glucose transporter. Int Rev Cytol 137: 239–297, 1992
Kasanicki MA, Pilch PF: Regulation of glucose transporter function. Diabetes Care 13: 1990
Baldini G, Hohman R, Charron MJ, Lodish HF: Insulin and non-hydrolyzable GTP analogs induce translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane in alpha-toxin-permeabilized rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem 266: 4037–4040, 1991
Smith RM, Charron MJ, Shah N, Lodish HF, Jarett L: lmmunoelectron microscopic demonstration of insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane of isolated rat adipocytes and masking of the carboxyl-terminal epitope of intracellular GLUT4. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 88: 6893–6897, 1991
Klip A, Ramlal T, Young DA, Holloszy JO: Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscle. FEBS Lett 224: 224–230, 1987
Wallberg-Henriksson H: Glucose transport into skeletal muscle. Influence of contractile activity, insulin, catecholamines and diabetes mellitus. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 564: 1–80, 1987
Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Wardzala LJ, Horton ED, Horton ES: Identification of an intracellular pool of glucose transporters from basal and insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 265: 987–991, 1990
Lund S, Holman GD, Schmitz O, Pedersen O: Glut4 content in the plasma membrane of rat skeletal muscle: Comparative studies of the subcellular fractionation method and the exofacial photolabelling technique using ATB-BMPA. FEBS Lett 330: 312–318, 1993
Etgen GJ Jr, Memon AR, Thompson GA Jr, Ivy JL: Insulin-and contraction-stimulated translocation of GTP-binding proteins and GLUT4 protein in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 268: 20164–20169, 1993
Zierath JR: In vitro studies of human skeletal muscle: Hormonal and metabolic regulation of glucose transport. Acta Physiol Scand 155: 1–96, 1995
Marette A, Burdett E, Douen A, Vranic M, Klip A: Insulin induces the translocation of GLUT4 from a unique intracellular organelle to transverse tubules in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 41: 1562–1569, 1992
Dohm GL, Eiton CW, Raju MS, Mooney ND, DiMarchi R, Pories WJ, Flickinger EG, Atkinson SM Jr, Caro JF: IGF-I-stimulated glucose transport in human skeletal muscle and IGF-I resistance in obesity and NIDDM. Diabetes 39: 1028–1032, 1990
Cartee GD, Douen AG, Ramlal T, Klip A, Holloszy JO: Stimulation of glucose transport in skeletal muscle by hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 70: 1593–1600, 1991
Zierath JR, Bang P, Galuska D, Hall K, Wallberg-Henriksson H: Insulin-like growth factor II stimulates glucose transport in human skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 307: 379–382, 1992
Goodyear LJ, Hirshman MF, King PA, Horton ED, Thompson CM, Horton ES: Skeletal muscle plasma membrane glucose transport and glucose transporters after exercise. J Appl Physiol 68: 193–198, 1990
Ren JM, Semenkovich CF, Guive EA, Gao J, Holloszy JO: Exercise induces rapid increases in GLUT4 expression, glucose transport capacity, and insulin-stimulated glycogen storage in muscle. J Biol Chem 269: 14396–14401, 1994
Coderre L, Kandror KV, Vallega G, Pilch PF: Identification and characterization of an exercise-sensitive pool of glucose transporters in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 270: 27584–27588, 1995
Sherman LA, Hirshman MF, Cormont M, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Goodyear LJ: Differential effects of insulin and exercise on Rab4 distribution in rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinol 137: 266–273, 1996
Cartee GD, Young DA, Sleeper MD, Zierath J, Wallberg-Henriksson H, Holloszy JO: Prolonged increase in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in muscle after exercise. Am J Physiol 256: E494–E499, 1989
Veroni MC, Proietto J, Larkins RG: Evolution of insulin resistance in New Zealand obese mice. Diabetes 40: 1480–1487, 1991
Greenfield MS, Doberne L, Kraemer F, Tobey T, Reaven G: Assessment of insulin resistance with the insulin suppression test and the euglycemic clamp. Diabetes 30: 387–392, 1981
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R: Glucose clamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 237: E214–E223, 1979
Charron MJ, Kahn BB: Divergent molecular mechanisms for insulin-resistant glucose transport in muscle and adipose cells in vivo. J Biol Chem 265: 7994–8000, 1990
Pedersen O, Kahn CR, Kahn BB: Divergent regulation of the GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporters in isolated adipocytes from Zucker rats. J Clin Invest 89: 1964–1973, 1992
Ezaki O, Fukuda N, Itakura H: Role of two types of glucose transporters in enlarged adipocytes from aged obese rats. Diabetes 39: 1543–1549, 1990
Storlien LH, Jenkins AB, Chisholm DJ, Pascoe WS, Khouri S, Kraegen EW: Influence of dietary fat composition on development of insulin resistance in rats. Relationship to muscle triglyceride and omega-3 fatty acids in muscle phospholipid. Diabetes 40: 280–289, 1991
Storlien LH, James DE, Burleigh KM, Chisholm DJ, Kraegen EW: Fat feeding causes widespread in vivo insulin resistance, decreased energy expenditure, and obesity in rats. Am J Physiol 251: E576–E583, 1986
Wake SA, Sowden JA, Storlein LH, James DE, PW C, Shine J, Chisholm DJ: Effects of exercise training and dietary manipulation on insulin-regulatable glucose transporter mRNA in rat muscle. Diabetes 40: 275–279, 1991
Borkman M, Chisholm DJ, Furier SM, Storlien LH, Kraegen EW, Simons LA, Chesterman CN: Effects of fish oil supplementation on glucose and lipid metabolism in NIDDM. Diabetes 38: 1314–1319, 1989
Sinha MK, Raineri-Maidonado C, Buchanan C, Pories WJ, Carter-Su C, Pilch PF, Caro JO: Adipose tissue glucose transporters in NIDDM. Decreased levels of muscle/fat isoform. Diabetes 40: 472–477, 1991
Kahn BB, Charron MJ, Lodish HF, Cushman SW, Flier JS: Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest 84: 404–411, 1989
Kahn BB, Rosen AS, Bak JF, Andersen PH, Damsbo P, Lund S, Pedersen O: Expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporters in skeletal muscle of humans with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: regulatory effects of metabolic factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 74: 1101–1109, 1992
Bonadonna RC, Saccomani MP, Seely L, Zych KS, Ferrannini E, Cobelli C, DeFronzo RA: Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle. The in vivo response to insulin. Diabetes 42: 191–198, 1993
Garvey WT, Maianu L, Hancock JA, Golichowski AM, Baron A: Gene expression of GLUT4 in skeletal muscle from insulin-resistant patients with obesity, IGT, GDM, and NIDDM. Diabetes 41: 465–475, 1992
Kahn BB, Rossetti L, Lodish HF, Charron MJ: Decreased in vivo glucose uptake but normal expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest 87: 2197–2206, 1991
Zierath JR, Houseknecht K, Kahn BB: Glucose transporters and diabetes. Sem Cell Dev Biol 7: 295–307, 1996
Zierath JR, Houseknecht KL, Gnudi L, Kahn BB: High-fat feeding impairs insulin-stimulated GLUT4 recruitment via an early insulin-signaling defect. Diabetes 46: 215–223, 1997
Katz EB, Burcelin R, Tsao TS, Stenbit AE, Charron MJ: The metabolic consequences of altered glucose transporter expression in transgenic mice. J Mol Med 74: 639–652, 1996
Tsao TS, Burcelin R, Katz EB, Huang L, Charron MJ: Enhanced insulin action due to targeted GLUT4 overexpression exclusively in muscle. Diabetes 45: 28–36, 1996
Katz EB, Stenbit AE, Hatton K, DePinho R, Charron MJ: Cardiac and adipose tissue abnormalities but not diabetes in mice deficient in GLUT4. Nature 377: 151–155, 1995
Tsao TS, Stenbit AE, Li J, Houseknecht K, Zierath JR, Katz EB, Charron MJ: Muscle-specific transgenic complementation of GLUT4-deficient mice normalizes glucose but not lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest 100: 671–677, 1997
DeFronzo RA: Lilly Lecture 1987: The triumvirate: β-cell, muscle, liver: A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes 37: 667–687, 1988
Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulman RG: Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Eng J Med 322: 223–228, 1990
Zierath JR, He L, Guma A, Wahlstrom EO, Klip A, Wallberg-Henriksson H: Insulin action on glucose transport and plasma membrane GLUT4 content in skeletal muscle from patients with NIDDM. Diabetologia 39: 1180–1189, 1996
Tsao TS, Burcelin R, Charron MJ: Regulation of hexokinase II gene expression by glucose flux in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 271: 14959–14963, 1996
McCall AL, van Bueren AM, Huang L, Stenbit A, Celnik E, Charron MJ: Forebrain endothelium expresses GLUT4, the insulin-responsive glucose transporter. Brain Res 744: 318–326, 1997
Stenbit AE, Burcelin R, Katz EB, Tsao TS, Gautier N, Charron MJ, Le Marchand-Brustel Y: Diverse effects of Glut4 ablation on glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in red and white skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 98: 629–634, 1996
Heyner S, Smith RM, Schultz GA: Temporally regulated expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in early mammalian development. BioEssays 11: 171–175, 1989
Gardner HG, Kaye PL: Characterization of glucose transport in preimplantation mouse embryos. Repro Fert Dev 7: 41–50, 1995
Gardner HG, Kaye PL: Insulin increases cell numbers and morphological development in mouse pre-implantation embryos in vitro. Repro Fert Dev 3: 79–91, 1991
Kahn BB: Facilitative glucose transporters: regulatory mechanisms and dysregulation in diabetes. J Clin Invest 89: 1367–1374, 1992
Hogan A, Heyner S, Charron MJ, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Thorens B, Schultz GA: Glucose transporter gene expression in early mouse embryos. Development 113: 363–372, 1991
Aghayan M, Rao LV, Smith RM, Jarett L, Charron MJ, Thorens B, Heyner S: Developmental expression and cellular localization of glucose transporter molecules during mouse preimplantation development. Development 115: 305–312, 1992
Wiley LM, Lever JE, Pape C, Kidder GM: Antibodies to a renal Na+/giucose cotransport system localize to the apical plasma membrane domain of polar mouse embryo blastomeres. Dev Biol 143: 149–161, 1991
Smith DE, Gridley T: Differential screening of a PCR-generated mouse embryo cDNA library: Glucose transporters are differentially expressed in early postimplantation mouse embryos. Development 116: 555–561, 1992
Santalucia T, Camps M, Castello A, Munoz P, Nuel A, Testar X, Palacin M, Zorzano A: Developmental regulation of GLUT-1 (erythroid/Hep G2) and GLUT-4 (muscle/fat) glucose transporter expression in rat heart, skeletal muscle, and brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology 130: 837–846, 1992
Studelska DR, Campbell C, Pang S, Rodnick KJ, James DE: Developmental expression of insulin-regulatable glucose transporter GLUT-4. Am J Physiol 263: E102–E106, 1992
Girard J, Ferre P, Pegorier J-P, Duee P-H: Adaptations of glucose and fatty acid metabolism during perinatal period and suckling-weaning transition. Physiol Rev 72: 507–562, 1992
Katz EB, Stenbit AE, Hatton K, DePinho R, Charron MJ: Cardiac and adipose tissue abnormalities but not diabetes in mice deficient in GLUT4. Nature 377: 151–155, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, E.B. Metabolic and therapeutic lessons from genetic manipulation of GLUT4. Mol Cell Biochem 182, 143–152 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006809611658
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006809611658