Abstract
Microvascular proliferation is a histopathological hallmark of glioblastomas and anaplastic oligodendrogliomas. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1/CD31) is involved in angiogenesis. PECAM-1 mediates homophilic and heterophilic interactions (with glycosaminoglycans and αVβ3), but deletion of exon 14 results in a loss of heterophilic adhesion. Expression of various PECAM-1 isoforms was searched for in brain gliomas, showing microvascular proliferation (glioblastomas and anaplastic oligodendrogliomas) or not (oligodendrogliomas). In addition, expression of αVβ3 in some tumors was studied by immunohistochemistry. Various tissues and the HUVEC primary cell line were used as controls.
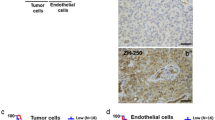
Immunohistochemistry showed that PECAM-1 was expressed by all endothelial cells in all tissues and by some tumor cells in glioblastomas and anaplastic oligodendrogliomas. Microvascular proliferation always expressed αVβ3. In addition, some tumor cells in anaplastic oligodendroglioma and glioblastomas expressed it. In all samples examined, PECAM-1 exists under at least two transcriptional isoforms: the whole length molecule and an isoform made by the splicing of exon 14. Western blot analysis revealed in all cases 130 and 110 kDa bands corresponding to the mature form and its precursor respectively.
These results suggest that splicing of exon 14 occurs in vivo in various normal and tumoral tissues and may modulate PECAM-1 adhesion according to the presence or not of other PECAM-1 ligands such as αVβ3.
Expression of PECAM-1 by tumor cells in glioblastomas and anaplastic oligodendrogliomas may favour angiogenesis by specific PECAM-1 interactions between glial and endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold F, West DC: Angiogenesis in wound healing. Pharmacol Ther 52: 407–422, 1991
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases. Nature Med 1: 27–31, 1995
Rak JW, St Croix BD, Kerbel RS: Consequences of angiogenesis for tumor progression and cancer therapy. Anti Cancer Drugs 6: 3–18, 1995
Folkman J, Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 267: 10931–10934, 1992
Bischoff J: Cell adhesion and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 99: 373–376, 1997
Cavenee WK, Bigner DD, Newcomb EW, Paulus W, Kleihues P: Diffuse astrocytomas. In: Kleihues P and Cavenee WK (eds) Pathology and genetics of tumors of the nervous system. Internat Agen Res Canc, 1997, pp 1–29
Daumas-Duport C, Varlet P, Tucker ML, Beuvon F, Cervera P, Chodkiewicz JP: Oligodendrogliomas: part I. Patterns of growth, histological diagnosis, clinical and imaging correlations: a study of 153 cases. J Neurooncol 34: 37–59, 1997
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumor angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359: 845–848, 1992
Goldberger A, Middleton KA, Oliver JA, Paddock C, Yan HC, De Lisser HM, Abelda SM, Newman PJ: Biosynthesis and processing of the cell-adhesion molecule PECAM-1 include production of a soluble form. J Biol Chem 269: 17183–17191, 1994
Newman PJ, Brendt MC, Gorsky J, White GC, Lyman S, Paddock C, Muller WA: PECAM-1 cloning and relation to adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Science 247: 1219–1222, 1990
Albelda SM, Oliver PD, Romer LH, Buck CA: EndoCam: a novel endothelial cell–cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol 110: 1227–1237, 1990
Dejana E, Corada M, Lampugnani MG: Endothelial cell-tocell junctions. Faseb J 9: 910–918, 1995
Scholz D, Schaper J: Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) is localized over the entire plasma membrane of endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 290: 623–631, 1997
Tang DG, Chen YQ, Newman PJ, Shi L, Gao X, Diglio CA, Honn KV: Identification of PECAM-1 in solid tumor cells and its potential involvement in tumor cell adhesion to endothelium. J Biol Chem 268: 22883–22894, 1993
Kirschbaum NE, Gumina RJ, Newman PJ: Organization of the gene for human platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 shows alternatively spliced isoforms and a functional complex cytoplasmic domain. Blood 84: 4028–4037, 1994
De Lisser HM, Yan HC, Newman PJ, Muller WA, Buck CA, Albelda SM: Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) mediated cellular aggregation involves cell surface glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem 268: 16037–16046, 1993
Newman PJ: The biology of PECAM-1. J Clin Invest 99: 3–8, 1997
De Lisser HM, Chiltowsky J, Yan HC, Daise ML, Buck CA, Albelda SM: Deletions in the cytoplasmic domain of platelet–endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1 CD31) result in changes in ligand binding properties. J Cell Biol 124: 195–203, 1994
Yan HC, Baldwin HS, Sun J, Buck CA, Albelda HM, De Lisser PJ: Alternative splicing of a specific cytoplasmic exon alters the binding characteristics of murine platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1). J Biol Chem 270: 23672–23680, 1995
Matsumara T, Wolff K, Petzelbauer P: Endothelial cell tube formation depends on cadherin 5 andCD31interactions with filamentous actin. J Immunol 158: 3408–3416, 1997
De Lisser HM, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Strieter RM, Burdick MDF, Robinson CS, Wexler RS, Kerr JS, Garlanda C, Merwin JR, Madri JA, Abelda SM: Involvement of endothelial PECAM-1/CD31 in angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 151: 671–677, 1997
Kim CS, Wang T, Madri JA: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 expression modulates endothelial cell migration in vitro. Lab Invest 78: 583–590, 1998
Gladson CL, Cheresh DA: Glioblastoma expression of the vitronectin and the αVβ3 integrin. Adhesion mechanism for the transformed glial cells. J Clin Invest 88: 1924–1932, 1991
Poncet C, Frances V, Gristina R, Scheiner C, Pellissier JF, Figarella-Branger D: CD24, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored molecule, is transiently expressed during the development of human central nervous system and is a marker of human neural cell lineage tumors. Acta Neuropathol 91: 400–408, 1996
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159, 1987
Arcari P, Martinelli R, Salvatore F: The complete sequence of a full length cDNA for human liver glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: evidence for multiple mRNA species. Nucl Ac Res 12: 9179–9189, 1984
Roberts GW, Palade GE: Neovasculature induced by vascular endothelial growth factor is fenestrated. Cancer Res 57: 765–772, 1997
Muller WA, Berman ME, Newman PJ, De Lisser HM, Albelda SM: A heterophilic adhesion mechanism for platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD 31). J Exp Med 175: 1401–1404, 1992
Piali L, Hammel P, Uherek C, Bachmann F, Gisler RH, Dunon D, Imhof BA: CD31/PECAM 1 is a ligand for αVβ3 integrin involved in adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium. J Cell Biol 130: 541–560, 1995
Brooks PC, Clark RAF, Cheresh DA: Requirement of vascular integrin αVβ3 for angiogenesis. Science 264: 569–571, 1994
Brooks PC, Montgomery AMP, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Kliet G, Cheresh DA: Integrin αVβ3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenesis blood vessels. Cell 79: 1157–1164, 1994
Drake CJ, Cheresh DA, Little CD: An antagonist of integrin αVβ3 prevents maturation of blood vessels during embryonic neovascularization. J Cell Sci 108: 2655–2661, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aroca, F., Renaud, W., Bartoli, C. et al. Expression of PECAM-1/CD31 Isoforms in Human Brain Gliomas. J Neurooncol 43, 19–25 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006233816724
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006233816724