Abstract
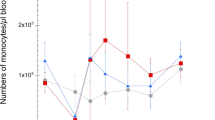
A trial was performed using 20 goats to evaluate the antibody responses to a liposome-adjuvanted Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxoid vaccine (LIPV). The antibody response was compared with those produced by epsilon toxoid vaccines prepared using aluminium hydroxide (ALV) and incomplete Freud's adjuvant (FAV). The animals were allocated to four groups at the beginning of the trial. The animals in group 1 were vaccinated with ALV, while the animals in group 2 received FAV and those in groups 3 and 4 were vaccinated with LIPV. The animals in groups 1 to 3 received three doses of the corresponding vaccine at intervals of three weeks, while those in group 4 received only 1 dose of vaccine at the beginning of the trial. A blood sample was obtained from all the goats at the beginning of the trial and then weekly for 8 weeks. The samples were analysed for epsilon toxoid antibodies by an indirect ELISA technique. No major clinical abnormalities were observed in the animals after vaccination, with the exception of those that received the FAV, which experienced transient lameness. The highest antibody response was observed in the animals vaccinated with FAV, but they presented moderate to severe inflammatory tissue reactions at the injection site. Moderately high antibody responses were obtained with the ALV, with which only minor local reactions were observed. No significant antibody responses were obtained with the LIPV, nor were local reactions observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackwell, T.E., Butler, D.G. and Bell, J.A., 1983. Enterotoxaemia in the goat: the humoral response and local tissue reaction following vaccination with two di¡erent bacterin-toxoids. Canadian Journal of Comparative Pathology and Medicine, 47, 127–132
Blood, D.C., Radostits, O.M. and Henderson, J.A., 1983. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Sheep, Goats and Horses, 6th edn, (Baillie© re-Tindall, London)
Bullen, J.J. and Batty, I.I., 1957. Enterotoxaemia of sheep.Veterinary Record, 69, 1268–1276
Jansen, B.C., 1960. The experimental reproduction of pulpy kidney disease. Journal of the South African Veterinary Medical Association, 31, 205–208
Jansen, B.C., 1967. The prevention of enterotoxaemia (pulpy kidney disease) by vaccination. Bulletin of the International O¤ce of Epizootics, 67, 1539–1567
Moore, D.S. and McCabe, G.P., 1993. Introduction to the Practice of Statistics, 2nd edn, (W.H. Freeman, New York), 713–789
Roitt, I., 1994. Essential Immunology, (Blackwell Science, Oxford), 523
Shanks, P.L., 1949. Enterotoxaemia in goats.Veterinary Record, 61, 262–264
Smith, L.D.S. and Marsh, H., 1953. The immunization of young lambs against enterotoxaemia. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 14, 408–410
Smith, M.C. and Sherman, D.M., 1994. Goat Medicine, (Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia), 620
Uzal, F.A. and Kelly, W.R., 1998. Protection of goats against experimental enterotoxaemia by vaccination with Clostridium perfringens type D epsilon toxoid.Veterinary Record, 142, 722–725
Uzal, F.A., Nielsen, K. and Kelly, W.R., 1997. Competitive and indirect ELISA detection of Clostridium perfringens type D epsilon antitoxin in serum of goats.Veterinary Microbiology, 51, 223–231
Uzal, F.A., Bodero, D.A.V., Kelly, W.R. and Nielsen, K., 1998a.Variability of serum antibody responses in goat kids to a commercial Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxoid vaccine.Veterinary Record, 143, 472–474
Uzal, F.A., Parson, P. and Kelly, W.R., 1998b. Enterotoxaemia in goats in Australia. Australian Veterinary Journal, 76, 16
Wells, P.W., Gilmour, N.J.L., Burrels, C. and Thompson, D.A., 1979. A serological comparison of Pasteurella haemolytica vaccines containing di¡erent adjuvants. Research in Veterinary Science, 27, 248–250
Wong, J.P., Cherwonogrodzky, J.M., Di Nino, V.L., Stadnyk, L.L. and Knodel, M.H., 1992. Liposome potentiation of humoral immune response to lipopolysaccharide and O-polysaccharide antigens of Brucella abortus. Immunology, 77, 123–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzal, F., Wong, J., Kelly, W. et al. Antibody Response in Goats Vaccinated with Liposome-adjuvanted Clostridium perfringens Type D Epsilon Toxoid. Vet Res Commun 23, 143–150 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006206216220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006206216220