Abstract
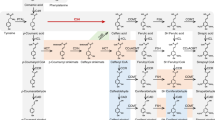
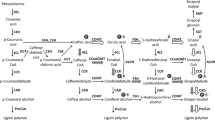
Seasonal expression of caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.104) was analyzed in aspen developing secondary xylem in parallel with caffeate O-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.68). Enzyme activity and mRNA levels for both enzymes peaked in the middle of the growing season. These results strongly suggest that both forms of O-methyltransferase were actively participating in lignin precursor biosynthesis during the growing season. To determine the role of each enzyme form, xylem extracts from two days in the growing season were assayed with four substrates: caffeoyl-CoA, 5-hydroxyferuloyl-CoA, caffeate acid and 5-hydroxyferulic acid. Recombinant forms of caffeoyl-CoA and caffeate O-methyltransferase were also assayed with these substrates. The recombinant enzymes have different substrate specificity with the caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase being essentially specific for CoA ester substrates with a preference for caffeoyl-CoA, while caffeate O-methyltransferase utilized all four substrates with a preference for the free acid forms. We suggest that caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase is likely to be responsible for biosynthesis of lignin precursors in the guaiacyl pathway and may represent a more primitive enzyme form leftover from very early land plant evolution. Caffeate O-methyltransferase is more likely to be responsible for lignin precursor biosynthesis in the syringyl pathway, especially since it can catalyze methylation of 5-hydroxyferuloyl-CoA quite effectively. This latter enzyme form then may be considered a more recently evolved component of the lignin biosynthetic pathways of the evolutionarily advanced plants such as angiosperms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugos RC, Chiang VLC, and Campbell WH: cDNA cloning, sequencing analysis and seasonal expression of lignin-bispecific caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid O- methyltransferase of aspen. Plant Mol Biol 17: 1203–1215 (1991).
Bugos RC, Chiang VLC, and Campbell WH: Characterization of bispecific caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid O- methyltransferase from aspen. Phytochemistry 31: 1495–1498 (1992).
Bugos RC, Chiang VLC, Zhang XH, Campbell ER, Podila GK, Campbell WH: RNA isolation from plant tissues recalcitrant to extraction in guanidine. BioTechiques 19: 734–737 (1995).
Eom TJ, Meshitsuka G, Nakano J: Chemical characteristics of lignin in the differentiating xylem of a hardwood II. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 33: 576–581 (1987).
Grand C: Ferulic acid 5-hydroxylase: A new cytochrome P-450-dependent enzyme from higher plant microsomes involved in lignin synthesis. FEBS Lett 169: 7–11 (1984).
Gross GG: Recent advances in the chemistry and biochemistry of lignin. In: Swain T, Harborne JB, van Sumere CF (eds) Recent Advances in Phytochemistry, Vol. 12, pp. 177–220. Plenum Press, New York (1979).
Higuchi T: Lignin biochemistry: biosynthesis and biodegradation. Wood Sci Technol 24: 23–63 (1990).
Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S, Kimura T, Hosouchi T, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Naruo K, Okumura S, Shimpo S, Takeuchi C, Wada T, Watanabe A, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Tabata S: Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions. DNA Res 3: 109–136 (1996).
Kneusel RE, Matern U, Nicolay K: Formation of transcaffeoyl-CoA from trans-4-coumaroyl-CoA by Zn2+-dependent enzymes in cultured plant cells and its activation by an elicitor-induced pH shift. Arch Biochem Biophys 269: 455–462 (1989).
Kramer PJ, Kozlowski TT: Physiology of Woody Plants. Academic Press, Orlando (1979).
Li L, Popko JL, Zhang XH, Osakabe K, Tsai CJ, Joshi CP, Chiang VL: A novel multifunctional O-methyltransferase implicated in a dual methylation pathway associated with lignin biosynthesis in loblolly pine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 5461–5466 (1997).
Luderitz T, Schatz G, Grisebach H: Enzymatic synthesis of lignin precursors: purification and properties of 4-coumarate:CoA ligase from cambial sap of spruce (Picea abies L.). Eur J Biochem 123: 583–586 (1982).
Meng H, Campbell WH: Cloning of aspen (Populus tremuloides) xylem caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase (GenBank U27116). Plant Physiology 108: 1749; Plant Gene Register PGR95–040 (1995).
Meng H, Campbell WH: Characterization and site-directed mutagenesis of aspen lignin-specific O-methyltransferase expressed in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 330: 329–341 (1996).
Meng H, Campbell WH: Facile enzymatic synthesis of caffeoyl CoA. Phytochemistry 44: 605–608 (1997).
Meng H, Campbell WH: Biochemistry and molecular biology of lignin-specific O-methyltransferases from woody species. In: Lewis N, Sarkanen S (eds) ACS Symposium on Lignin and Lignan Biosynthesis. American Chemical Society, Washington, D. C., in press (1997).
Pakusch AE, Kneusel, RE, Matern U: S-Adenosyl-L-methionine: trans-ceffeoyl-coenzyme A 3-O-methyltransferase from elicitor-treated parsley cell suspension cultures. Arch Biochem Biophys 271: 488–494 (1989).
Schmitt D, Pakusch AE, Matern U: Molecular cloning, induction, and taxonomic distribution of caffeoyl-CoA 3-O- methyltransferase, an enzyme involved in disease resistance. J Biol Chem 266: 17416–17423 (1991).
Whetten R, Sederoff R: Lignin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7: 1001–1013 (1995).
Ye ZH, Kneusel RE, Matern U, Varner JE: An alternative methylation pathway in lignin biosynthesis in zinnia. Plant Cell 6: 1427–1439 (1994).
Ye ZH, Varner JE: Differential expression of two O- methyltransferases in lignin biosynthesis in Zinnia elegans. Plant Physiol 108: 459–467 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, H., Campbell, W.H. Substrate profiles and expression of caffeoyl coenzyme A and caffeic acid O-methyltransferases in secondary xylem of aspen during seasonal development. Plant Mol Biol 38, 513–520 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006071708728
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006071708728