Abstract
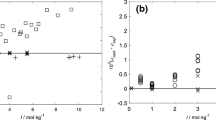
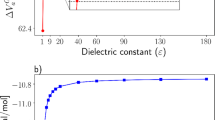
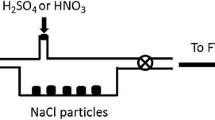
Henry's law constants K′H (mol kg-1 atm-1) have been measured between 278.15 K and 308.15 K for the following organic acids: CH2FCOOH (ln(K′H[298.15 K]) = 11.3 ± 0.2), CH2ClCOOH (11.59 ± 0.14), CH2BrCOOH (11.94 ± 0.21), CHF2COOH (10.32 ± 0.10), CHCl2COOH (11.69 ± 0.11), CHBr2COOH (12.33 ± 0.29), CBr3COOH (12.61 ± 0.21), and CClF2COOH (10.11 ± 0.12). The variation of K′H with temperature was determined for all acids except CH2FCOOH and CBr3COOH, with Δr H° for the dissolution reaction ranging from −85.2 ± 2.6 to −57.1 ± 2.5 kJ mol-1, meaning that their solubility is generally more sensitive to temperature than is the case for the simple carboxylic acids. The Henry's law constants show consistent trends with halogen substitution and, together with their high solubility compared to the parent (acetic) acid (ln(K′H[298.15 K]) = 8.61), present a severe test of current predictive models based upon molecular structure. The solubility of haloacetic acids and strong dissociation at normal pH mean that they will partition almost entirely into cloud and fog in the atmosphere (0.05–1.0 g H2O m-3), but can reside in both phases for the liquid water contents typical of aerosols (10-5-10-4 g H2O m-3).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFEAS (Alternative Fluorocarbons Acceptability Study), 1994: AFEAS Workshop on the Environmental Fate of Trifluoroacetic Acid, Miami Beach, FL.
Bell, R. P. and Kuhn, A. T., 1963: Dissociation constants of some acids in deuterium oxide, Trans. Faraday Soc. 59, 1789–1793.
Bonner, O. D., Jackson, R., and Rogers, O. C., 1962: Determining ionization constants from ion exchange equilibrium measurements, J. Chem. Educ. 39, 37–39.
Bowden, D. J., Clegg, S. L., and Brimblecombe, P., 1996: The Henry's law constant of trifluoroacetic acid and its partitioning into liquid water in the atmosphere, Chemosphere 32, 405–420.
Bowden, D. J., Clegg, S. L., and Brimblecombe, P., 1997: The Henry's law constant of trichloroacetic acid, Water, Air Soil Pollut., in press.
Bowden, K., Hardy, M., and Parkin, D. C., 1968: The transmission of polar effects. Part V. The kinetics of esterification with dazodiphenylmethane and the ionization of substituted acetic and propionic acids in several solvents, Can. J. Chem. 46, 2929–2940.
Brimblecombe, P. and Dawson, G. A., 1984: Wet removal of highly soluble gases, J. Atmos. Chem. 2, 95–107.
Carslaw, K. S., Clegg, S. L., and Brimblecombe, P., 1995: A thermodynamic model of the system HCl–HNO3–H2SO4–H2O, including solubilities of HBr, from 328 K to <200 K, J. Phys. Chem. 99, 11557–11574.
Clegg, S. L. and Brimblecombe, P., 1985: The Henry's law constant of methanesulphonic acid and its implications for atmospheric chemistry, Environ. Technol. Lett. 6, 269–278.
Clegg, S. L. and Brimblecombe, P., 1988: Equilibrium partial pressures of strong acids over concentrated saline solutions. Part I. HNO3, Atmos. Environ. 22, 91–100.
Clegg, S. L., Pitzer, K. S., and Brimblecombe, P., 1992: Thermodynamics of multicomponent, miscible, ionic solutions. II. Mixtures including unsymmetrical electrolytes, J. Phys. Chem. 96, 9470–9479; 1994, 98, 1368; 1995, 99, 6755.
Clegg, S. L. and Whitfield, M., 1991: Activity coefficients in natural waters, in K. S. Pitzer (ed.), Activity Coefficients in Electrolyte Solutions, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, Chap. 6.
Crafts, A. S. and Robbins, P., 1962: Weed Control, McGraw–Hill, New York.
Dawson, H. M. and Lowson, W., 1929: Acid and salt effects in catalysed reactions. Part XX. The ionisation of acids in salt solutions, J. Chem. Soc. 1217–1229.
Dean, J. A. and Lange, N. A., 1992: Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 14th edn, McGraw–Hill, New York.
Dictionary of Organic Compounds, 1982: Vol. 5, Chapman and Hall, London.
Frank, H., Klein, A., and Renschen, D., 1996: Environmental trifluoroacetate, Nature 382, 34.
Frank, H., Renschen, D., Klein, A., and Scholl, H., 1995: Trace analysis of airborne haloacetates, J. High Resol. Chromatogr. 18, 83–88.
Grosselin R. E., Smith R. P., and Hodge N. C., 1984: Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Harned, H. S. and Ehlers, R. W., 1933: The dissociation constant of acetic acid from 0° to 60 °C, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 652–656.
Harned, H. S. and Hawkins, J. E., 1928: The catalysis of ethyl formate by mono–chloroacetic acid and ethyl acetate by dichloro–acetic acid in neutral salt solutions, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 50, 85–93.
Hine, J. and Mookerjee, P. K., 1975: The intrinsic hydrophilic character of organic compounds. Correlations in terms of structural contributions, J. Org. Chem. 40, 292–298.
Ives, D. J. G. and Pryor, J. H., 1955: The conductometric evaluation of the ionisation functions of the monohalogenoacetic acids, J. Chem. Soc., 2104–2114.
Juuti, S., Norokorpi, Y., Helle, T., and Ruuskanen, J., 1996: Trichloroacetic acid in conifer needles and arboreal lichens in forest environments, Sci. Total Environ. 180, 117–124.
Kendall, J. and King, C. V., 1925: Additive compounds in the ternary system: Ester – acid – water, J. Chem. Soc., 1778–1791.
Khan, I., Brimblecombe, P., and Clegg, S. L., 1995: Solubilities of pyruvic acid and the lower (c 1– c 6) carboxylic acids. Experimental determination of equilibrium vapour pressures above pure aqueous and salt solutions, J. Atmos. Chem. 22, 285–302.
Klotz, I. M. and Rosenberg, R. M., 1972: Chemical Thermodynamics, Basic Theory and Methods, Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park, CA.
Kolenbrander, J., 1995: Estimating Physico–Chemical Properties of Organic Compounds Using DESOC, Stanford University Bookstore, Stanford, CA.
Kurz, J. L. and Farrar, J. M., 1969: The entropies of dissociation of some moderately strong acids, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91, 6057–6062.
Lindstrom, K. and Osterberg, F., 1986: Chlorinated carboxylic acids in softwood Kraft pulp spent bleach liquors, Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 133–138.
Long, F. A. and McDevit, W. F., 1952: Activity coefficients of nonelectrolyte solutes in aqueous salt solutions, Chem. Rev. 51, 119–169.
Macaskill, J. B. and Bates, R. G., 1983: Osmotic coefficients and activity coefficients of aqueous hydrobromic acid at 25 °C, J. Soln. Chem. 12, 607–619.
McDougall, A. O. and Long, F. A., 1962: Relative hydrogen bonding of deuterium. II. Acid ionization constants in H2O and D2O, J. Phys. Chem. 66, 429–433.
Metzler, D. E., 1977: Biochemistry. The Chemical Reactions of Living Cells, Academic Press, New York.
Meylan, W. H. and Howard, P. H., 1991: Bond contribution method for estimating Henry's law constants, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10, 1283–1293.
Miller, J. W. and Uden, P. C., 1983: Characterisation of nonvolatile aqueous chlorination products of humic substances, Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 150–157.
Pitzer, K. S., 1995: Chemical Thermodynamics, McGraw–Hill, New York.
Pitzer, K. S., 1991: Ion interaction approach: theory and data correlation, in K. S. Pitzer (ed.), Activity Coefficients in Electrolyte Solutions, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, Chap. 3.
Plumacher, J. and Renner, I., 1993: Determination of volatile chlorinated hydrocarbons and trichloroacetic acid in conifer needles by headspace gas chromatography, Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 347, 129–135.
Randall, M. and Failey, C. F., 1927: Activity coefficients of the undissociated part of weak electrolytes, Chem. Rev. 4, 291–318.
Reimann, S., Grob, K. and Frank, H., 1996: Chloroacetic acids in rainwater, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 2340–2344.
Rodriguez, J. M., Ko, M. K. W., Sze, N. D., and Heisey, C. W., 1993: Two–dimensional assessment of the degradation of HFC–134a: tropospheric accumulations and deposition of trifluoroacetic acid, in Kinetics and Mechanisms for the Reactions of Halogenated Organic Compounds in the Troposphere, STEP–HALOCSIDE/AFEAS Workshop, pp. 104–112.
Russell, C. J., Dixon, S. L., and Jurs, P. C., 1992: Computer assisted study of the relationship between molecular structure and Henry's law constant, Anal. Chem. 64, 1350–1355.
Saxena, P. and Hildemann, L. M., 1996: Water–soluble organics in atmospheric particle – a critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds, J. Atmos. Chem. 24, 57–109.
Saxton, B. and Langer, T.W., 1933: The ionization constant of monochloroacetic acid, at 25 °C, from conductance measurements, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 3638–3645.
Shmidt, L. L., 1960: Total and partial vapour pressure of chloroacetic acid solutions in water, Tr. Talinsk. Politekhn. Inst. Ser. A, 221–244.
Staudinger, J. and Roberts, P. V., 1996: A critical review of Henry's law constants for environmental applications, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 205–297.
Suzuki, T., Ohtaguchi, K., and Koide, K., 1992: Application of principal components analysis to calculate Henry's constant from molecular structure, Computers Chem. 16, 41–52.
Tromp, T. K., Ko, M. K. W., Rodriguez, J. M., and Sze, N. D., 1995: Potential accumulation of CFC–replacement degradation product in seasonal wetlands, Nature 376, 327–330.
Tromp, T. K., Rodriguez, J. M., Ko, M. K. W., Heisey, C. W., and Sze, N. D., 1994: Scenarios for delivery of TFA to the global environment: model predictions of environmental load, in AFEAS Workshop on the Environmental Fate of Trifluoroacteic Acid, Miami Beach, FL.
Weast R. C., 1988: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Williams, D. T., Le Bel, G. L., and Benoit, F.M., 1997: Disinfection by–products in Canadian drinking water, Chemosphere 34, 299–316.
Wine, P. H. and Chameides, W. I., 1989: Possible atmospheric lifetimes and chemical reaction mechanisms for selected HCFCs, HFCs, CH3CCl and their degradation products against dissolution and/or degradation in seawater and cloud water, in Scientific Assessment of Stratospheric Ozone: 1989, WMO Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project, Report No. 20, Vol. II, pp. 273–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowden, D.J., Clegg, S.L. & Brimblecombe, P. The Henry's Law Constants of the Haloacetic Acids. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry 29, 85–107 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005899813756
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005899813756