Abstract
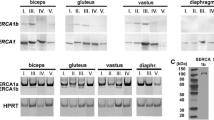
The level of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) mRNAs and proteins have been assessed by␣RT-PCR,␣immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry in the rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles during regeneration from notexin-induced necrosis. As a result of the necrosis, SERCA1 and SERCA2 declined on days 1 and 3 after␣administration of the toxin. Thereupon the mRNA of the fast isoform SERCA1 rapidly increased between days 5 and 10 to the normal level. The mRNA level of the “housekeeping” SERCA2b isoform increased markedly during the actual necrosis at days 1 and 5, probably due to invading cells. Then the mRNA level of the neonatal SERCA1b splice variant increased first, and exceeded the level of the adult SERCA1a transcript on day 5. At later stages of regeneration the neonatal form was gradually replaced by the adult SERCA1a form, thus recapitulating similar changes known to occur during normal ontogenesis. Along with S ERCA1, the levels of the slow isoform (SERCA2a) mRNA and protein increased on day 5, but the␣SERCA2a mRNA levels never rose above 10% of SERCA1 and after 10 days gradually declined again. In the normal and␣regenerated muscles, SERCA1 was expressed in 97% of the fibres which accounted for the population of fast-twitch fibres␣(type IIa, type IIb and probably type IIx/d). SERCA2a was present in 6% of the fibres of normal muscle (mostly in the␣slow-twitch type I fibres). At the end of regeneration the number of fibres expressing SERCA2a was twice as high and␣were␣found in small groups, unlike in normal EDL, but about 50% of these clustered fibres also expressed SERCA1. © Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARAI, M., OTSU, K., MACLENNAN, D. H. & PERIASAMY, M. (1992) Regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum gene expression during cardiac and skeletal muscle development. Am. J. Physiol. 262, C614–20.
ARMSTRONG, R. B. & PHELPS, R. O. (1984) Muscle fiber type composition of the rat hindlimb. Am. J. Anat. 171, 259–72.
BRANDL, C. J., GREEN, N. M., KORCZAK, B. & MACLENNAN, D. H. (1986) Two Ca2+-ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell 44, 597–607.
BRANDL, J. B., DELEON, S., MARTIN, D. R. & MACLENNAN, D. H. (1987) Adult forms of the Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: expression in developing skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 3768–74.
DE LA BASTIE, D., WISNEWSKY, C., SCHWARTZ, K. & LOMPRÉ, A-M. (1988) (Ca2+ + Mg2+) dependent ATPase mRNA from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum differs from that in cardiac and fast skeletal muscles. FEBS Lett. 229, 45–8.
DODE, L., WUYTACK, F., KOOLS, P. F. J., BABA-AISSA, F., RAEYMAEKERS, L., BRIKE, F., VAN DE VEN, W. J. M. & CASTEELS, R. (1996) cDNA cloning, expression and chromosomal localization of the human sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase 3 gene. Biochem. J. 318, 689–99.
EGGERMONT, J. A., WUYTACK, F., VERBIST, J., & CASTEELS, R. (1990a) Expression of endoplasmicreticulum Ca2+-pump isoforms and of phosphoplamban in pig smooth-muscle tissues. Biochem. J. 271, 649–53.
EGGERMONT, J. A., WUYTACK, F. & CASTEELS, R. (1990b) Characterisation of the mRNAs encoding the gene 2 sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-pump in pig smooth muscle. Biochem. J. 266, 901–7.
HARRIS, J. B., JOHNSON, M. A. & KARLSSON, E. (1975) Pathological responses of rat skeletal muscle to a single subcutaneous injection of a toxin isolated from the venom of the Australian tiger snake, Notechis scutatus scutatus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2, 383–404.
HARRIS, J. B. & JOHNSON M. A. (1978) Further observations on the pathological responses of rat skeletal muscle to toxins isolated from the venom of the Australian tiger snake, Notechis scutatus scutatus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 5, 587–600.
KANDARIAN, S. C., PETERS, D. G., TAYLOR, J. A. & WILLIAMS, J. H. (1994) Skeletal muscle overload upregulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum slow calcium pump gene. Am. J. Physiol. 266, C1190–97.
KORCZAK, B., ZARAIN-HERZBERG, A., BRANDL, C. J., INGLES, C. J., GREEN, M. N. & MACLENNAN, D. H. (1988) Structure of the rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle Ca2+ ATPase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 4813–19.
LEBERER, E. & PETTE, D. (1986) Immunochemical quantitation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase, of calsequestrin and of parvalbumin in rabbit skeletal muscles of defined fiber-composition. Eur. J. Biochem. 156, 489–96.
LEXELL, J., JARVIS, J. C., CURRIE, J., DOWNHAM, D. Y. & SALMONS, S. (1994) Fibre type composition of rabbit tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. J. Anat. 185, 95–101.
MACLENNAN, D. H., TOYOFUKU, T. & LYTTON, J. (1992) Structure-function relationships in sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum type Ca2+ pumps. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 671, 1–10.
MERTENS, L., VAN DEN BOSCH, L., VERBOOMEN, H., WUYTACK, F., DE SMEDT, H. & EGGERMONT, J. (1995) Sequence and spatial requirements for regulated muscle-specific processing of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2 gene transcript. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11004–11.
PLESSERS, L., EGGERMONT, J. A., WUYTACK, F. & CASTEELS R. (1991) A study of the organellar Ca2+ transport ATPase isozymes in pig cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J. Neurosci. 11, 650–56.
SCHIAFFINO, S., GORZA, L., SARTORE, S., SAGGIN, L., AUSONI, S., VIANELLO, M., GUNDERSEN, K. & LOMO, T. (1989) Three myosin heavy chain isoforms in type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 197–205.
SIMONIDES, W. S., VAN DER LINDEN, G. C. & VAN HARDEVELD, C. (1990) Thyroid hormone differentially affects mRNA levels of Ca-ATPase isozymes of sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast and slow skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 274, 73–6.
VAN DEN BOSCH, L., EGGERMONT, J., DE SMEDT, H., MERTENS, L., WUYTACK, F. & CASTEELS, R. (1994) Regulation of splicing is responsible for the expression of the muscle specific 2a isoform of the sarco/endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochem. J. 302, 559–66.
VOYTIK, S. L., PRZYBORSKI, M., BADYLAK, S. F. & KONIECZNY, F. (1993) Differential expression of muscle regulatory factor genes in normal and denervated adult rat hindlimb muscles. Dev. Dynamics 198, 214–24.
WU, K.-D., LEE, W. S., WEY, J., BUNGARD, D. & LYTTON, J. (1995) Localization and quantification of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform transcripts. Am. J. Physiol. 269, C775–84.
WU, K.-D. & LYTTON, J. (1993) Molecular cloning and quantification of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoforms in rat muscles. Am. J. Physiol. 264, C333–41.
WUYTACK, F., EGGERMONT, J. A., RAEYMAEKERS, L., PLESSERS, L. & CASTEELS, R. (1989) Antibodies against the non-muscle isoform of the endoplasmicreticulum Ca2+-transport ATPase. Biochem. J. 264, 765–9.
WUYTACK, F., PAPP, B., VERBOOMEN, H., RAEYMAEKERS, L., DODE, L., BOBE, R., ENOUF, J., BOKKALA, S., AUTHI, K. S. & CASTEELS, R. (1994) A sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 3-type Ca2+ pump is expressed in platelets, in lymphoid cells, and in mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1410–16.
ZADOR, E., MENDLER, L., VER HEYEN, M., DUX, L. & WUYTACK, F. (1996) Changes in mRNA levels of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoforms in the rat soleus muscle regenerating from notexin-induced necrosis. Biochem. J. 320, 107–13.
ZADOR, E., MENDLER, L., SZAKONYI, G., RACZ, G., GORBE, A., WUYTACK, F. & DUX, L. (1997) Expression of the myogenic regulatory factors and the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPases in regenerating fast and slow muscles of the rat. Neuromusc. Disorders 7, 475.
ZHANG, K.-M., HU, P., WANG, S.-W., WRIGHT, L. D., WECHSKER, A. S., SPRATT, J. A. & BRIGGS, F. N. (1997) Fast-and slow-twitch isoforms (SERCA1 and SERCA2a) of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase are expressed simultaneously in chronically stimulated muscle fibers. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 433, 766–72.
ZUBRZYCKA-GAARN, E., MACDONALD, G., PHILLIPS, L., JORGENSEN, A. O. & MACLENNAN, D. H. (1984) Monoclonal antibodies to the Ca2+ + Mg2+ dependent ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum identify polymorphic forms of the enzyme and indicate the presence in the enzyme of a classical high affinity Ca2+ binding site. J. Bioenergetics Biomembranes 16, 441–64.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendler, L., Szakonyi, G., Zádor, E. et al. Expression of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPases in the rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle regenerating from notexin-inducednecrosis. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19, 777–785 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005499304147
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005499304147