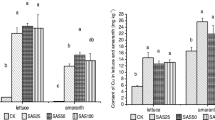
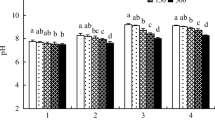
Abstract
Uptake of metals by plants growing in sewage sludge-amended soils frequently exhibits a plateau response at high sludge loading rates associated with high total concentrations of metals in the soil. This type of response has generally been attributed to attenuation of metal bioavailability by increased sorption sites provided by the sludge constituents at the high sludge loading rates. We grew Raphanus sativus L. in a soil historically amended with sewage sludge at different rates and examined concentrations of Cd and Zn in the plants and in corresponding rhizosphere soil solution. Metal concentrations in the plants displayed a plateau response. However, concentrations of total or free metals in the soil solution did not display a similar plateau response, therefore the pre-requisite for determining that metal uptake by plants was limited by sludge chemistry was not met. It was concluded that plant physiological factors were responsible for the plateau in plant metal concentrations observed in this study. Examination of data by other authors suggests that a plateau response due to plant physiological factors has routinely been misinterpreted as being the result of only attenuation by sludge chemistry. The serious implications of an incorrect interpretation of the factors underlying a plateau response are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson PR and Christensen T H 1988 Distribution coefficients of Cd, Co, Ni, and Zn in soils. J. Soil Sci. 39, 15–22.
Baker A J M 1981 Accumulators and Excluders-strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J. Plant Nutr. 3, 643–654.
Barbarick K A, Ippolito J A and Westfall D g 1995 Biosolids effect on phosphorus, copper, zinc, nickel, and molybdenum concentrations in dryland wheat. J. Environ. Qual. 24, 608–611.
Cataldo D A, Garland T R, Wildung R E 1978 Nickel in plants. I. Uptake kinetics using intact soybean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 62, 563–565.
Chaney R L 1994 Trace metal movement: soil-plant systems and bioavailability of biosolids-applied metals. In Sewage Sludge: Land Utilization and the Environment. Eds C.E. Clapp et al. pp 27–31. Soil Sci. Soc. Am., Madison, WI, USA.
Chaney R L and Ryan J A 1993 Heavy metals and toxic organic pollutants in MSW-composts: research results on phytoavailability, bioavailability, fate, etc. In Science and Engineering of Composting: Design, Environmental, Microbiological and Utilization Aspects. Eds H A J Hoitink and H M Keener. pp 451–506. Renaissance Pub, Worthington, OH.
Chang A C, Page A L and Warneke J E 1996 An experimental evaluation of Cd uptake by twelve plant species grown on sludgetreated soil: Is there a plateau? In Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements. Eds D.C. Adriano et al. Science and Technol. Letters, Northwood, UK.
Chang A C, Hae-nam Hyun and Page A L 1997 Cadmium uptake by swiss chard grown on composted sewage sludge treated field plots: Plateau or time bomb? J. Environ. Qual. 26, 11–19.
Chaudhry F M and Loneragan J F 1972 Zinc absorption by wheat seedlings and the nature of its inhibition by alkaline earth cations. J. Exp. Bot. 23, 552–560.
Christensen T H 1989 Cadmium sorption at low concentrations: VIII. Correlation with soil parameters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 44, 71–82.
Christensen T H and Tjell J C 1984 Interpretation of experimental results on cadmium crop uptake from sludge amended soil. In Processing and Use of Sewage Sludge. pp 358–370. Proc. 3rd Int. Symp. Brighton, England, Sept., 1983.
Corey R B, King L D, Lue-Hing C, Fanning D S, Street J J and Walker J M 1987 Effects of sludge properties on accumulation of trace elements by crops. In Land Application of Sludge, Food Chain Implications. Eds A L Page et al. pp 25–51. Lewis Pub., Chelsea, MI.
Davies B E 1993 Radish as an indicator plant for derelict land: uptake of zinc at toxic concentrations. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 24, 1883–1895.
Dowdy R H, Larson W E, Titrud J M and Latterell J J 1978 Growth and metal uptake of snap beans grown on sewage sludgeamended soil: a four-year field study. J. Environ. Qual. 7, 252–257.
Grotz N, Fox T, Connolly E, Park W, Guerinot M L and Eide D 1998 Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7220–7224.
Guerinot M L and Eide D 1999 Zeroing in on zinc uptake in yeast and plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2, 244–249.
Hamon R E 1995 Identification of factors governing cadmium and zinc bioavailability in polluted soils. PhD Thesis. University of Nottingham, UK.
Hamon R E, Lorenz S E, Holm P E, Christensen T H and McGrath S P 1995 Changes in trace metal species and other components 64 of the rhizosphere during growth of radish. Plant Cell Environ. 18, 749–756.
Hassan M M and Tang Van Hai. 1976. Kinetics of zinc uptake by citrus roots. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 79, 177–181.
Holm P E, Christensen T H, Tjell J C and McGrath S P 1995 Speciation of cadmium and zinc in small soil solution samples. J. Environ. Qual. 24, 183–190.
Hae-nam Hyun, Chang A C, Parker D R and Page A L 1998 Cadmium solubility in sludge-treated soil: effects of soil organic carbon. J. Environ. Qual. 27, 329–334.
Ibekwe A M, Angle J S, Chaney R L and van Berkum P 1996 Zinc and cadmium toxicity to alfalfa and its microsymbiont. J. Environ. Qual. 25, 1032–1040.
Iyengar S S, Martens D C and Miller W P 1981 Distribution and plant availability of soil zinc fraction. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 45, 735–739.
Jing J and Logan T J 1992 Effects of sewage sludge cadmium concentration on chemical extractability and plant uptake. J. Environ. Qual. 21, 73–81.
King L D 1988 Effect of selected soil properties on cadmium content of tobacco. J. Environ. Qual. 17, 251–255.
Logan T J and Chaney R L 1987 Nonlinear rate response and relative crop uptake of sludge cadmium for land application of sludge risk assessment. In Proc. 6th Int. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment. Eds S E Lindberg and T C Hutchinson. pp 387–388. CEP Consultants, Edinburgh, Scotland.
Logan T J, Lindsay B J, Goins L E and Ryan J A 1997 Field assessment of sludge metal bioavailability to crops: sludge rate response. J. Environ. Qual. 26, 534–550.
Lorenz S E, Hamon R E and McGrath S P 1994a. Differences between soil solutions obtained from rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soils by water displacement and soil centrifugation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 45, 431–438.
Lorenz S E, Hamon R E, McGrath S P, Holm P E and Christensen T H 1994b Applications of fertilizer cations affect cadmium and zinc concentrations in soil solutions and uptake by plants. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 45, 159–165.
Lorenz S E, Hamon R E, Holm P E, Domingues H C, Sequiera E M, McGrath S P and Christensen T H 1997 Cadmium and zinc in plants and soil solutions from contaminated soils. Plant Soil 189, 21–31.
Luo Y M and Christie P 1998 Bioavailability of copper and zinc in soils treated with alkaline stabilized sewage sludges. J. Environ. Qual. 27, 335–342.
Mahler R J, Bingham F T, and Page A L 1978 Cadmium-enriched sewage sludge applications to acid and calcareous soils: effect on yield and cadmium uptake by lettuce and chard. J. Environ. Qual. 7, 274–281.
Marschner H and Römheld V 1983 In vivo measurement of rootinduced pH changes at the soil-root interface: effect of plant species and nitrogen source. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. Bodenk. 111, 241–251.
McBride M B 1995 Toxic metal accumulation from agricultural use of sludge: are USEPA regulations protective? J. Environ. Qual. 24, 5–18.
McGrath S P 1984 Metal concentrations in sludges and soil from a long-term field trial. J. Agric. Sci. 103, 25–35.
Sanders J R 1982 The effects of pH upon the copper and cupric ion concentrations in soil solutions. J. Soil Sci. 33, 679–689.
Smith S R 1996 Agricultural Recycling of Sewage Sludge and the Environment. CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK.
Street J J, Sabey B R and Lindsay W L 1978 Influence of pH, phosphorus, cadmium, sewage sludge, and incubation time on the solubility and plant uptake of cadmium. J. Environ. Qual. 7, 286–290.
Van der Zaal B J, Neuteboom L W, Pinas J E, Chardonnens A N, Schat H, Verkleij J A C and Hooykaas P J J 1999 Overexpression of a novel Arabidopsis gene related to putative zinc-transporter genes from animals can lead to enhanced zinc resistance and accumulation. Plant Physiol. 119, 1047–1055.
Veltrup W 1978 Characteristics of zinc uptake by barley roots. Physiol. Plant. 42, 190–194.
Williams C H, and David D J 1977 Some effects of the distribution of cadmium and phosphate in the root zone on the cadmium content of plants. Aust. J. Soil Res. 15, 59–68.
Zhao F J, Dunham S J and McGrath S P 1997 Lessons to be learned about soil-plant metal transfers from the 50-year sewage sludge experiment at Woburn, UK. In Extended Abstracts of the 4th International Conference on the Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, University of California, Berkeley, USA, 23–26 June 1997, pp 693–694.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamon, R., Holm, P., Lorenz, S. et al. Metal uptake by plants from sludge-amended soils: caution is required in the plateau interpretation. Plant and Soil 216, 53–64 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004780720809
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004780720809