Abstract
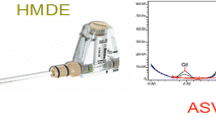
The technique of differential pulse polarography is shown here to be applicable to the monitoring directly the biosorption of metal ions from solution by live bacteria from mixed metal solutions. Biosorption of Cd(II), Zn(II) and Ni(II) by P. cepacia was followed using data obtained at the potential which is characteristic of the metal ion in the absence and presence of cells. Hepes buffer (pH 7.4, 50 mM) was used as a supporting electrolyte in the polarographic chamber and metal ion peaks in the presence of cells of lower amplitude were obtained due to metal-binding by the cells. Well defined polarographic peaks were obtained in experiments involving mixtures of metal ions of Cd(II)-Zn(II), Cu(II)-Zn(II), Cu(II)-Cd(II) and Cd(II)-Ni(II). Biosorption of Cd(II), Zn(II) increased with solution pH. The method was also tested as a rapid technique for assessing removal of metal ions by live bacteria and the ability of the polarographic technique in measuring biosorption of metal ions from mixed metal solutions is demonstrated. Cu(II) was preferentially bound and removal of metals was in the order Cu(II) > Ni(II) > Zn(II), Cd(II) by intact cells of P. cepacia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agraz R., Vanderwal A. and Vanleeuwen H.P. 1994. Voltammetric study of the interaction of cadmium with bacterial cells. Bioelec. Bioener. 34: 53–59.
Beveridge T.J. and Doyle R.J. 1989. Metal Ions and Bacteria. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Beveridge T.J., Hughes M.N., Lee H., Leung K.T., Poole R.K., Savvaidis I. et al. 1997. Metal-microbe interactions: contemporary approaches. Adv Microb Physiol. 38: 178–243.
Bridge T.A.M., White C. and Gadd G.M. 1999. Exracellular metal-binding activity of the sulphate-reducing bacterium Desulfococcus multivorans. Microbiology 145: 2987–2995.
Dunn G.M. and Bull A.T. 1983. Bioaccumulation of copper by a defined community of activated-sludge bacteria. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17: 30–34.
Ehrlich H.L. 1997. Microbes and metals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 48: 687–692.
Escheverria J.C., Morera M.T., Mazkiaran C. and Garrido J.J. 1998. Competitive sorption of heavy metal by soils. Isotherms and fractional factorial experiments. Environ. Pollution 101: 275–284.
Florence T.M. 1992. Trace element speciation by anodic stripping voltammetry. Analyst 117: 551–553.
Gadd G.M. and White C. 1993. Microbial treatment of metal pollution-a-working biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 11: 353–359.
Gibson J.F., Poole R.K., Hughes M.N. and Rees J.F. 1986. Ruthenium nitrosyl complexes-toxicity to Escherichia coli and yeasts and biosorption by marine-bacteria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 15: 519–528.
Goncalves M.de.L.S., Sigg L., Reutlinger M. and Stumm W. 1987. Metal ion binding by biological surfaces. Voltammetric assessment in the presence of bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 60: 105–120.
Hughes M.N. and Poole R.K. 1989. Metals and Micro-organisms. Chapman and Hall, London.
Laddaga R.A. and Silver S. 1985. Cadmium biosorption in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 162: 1100–1105.
Nobar A.M. 1988. Studies on microbes isolated from metal-polluted environments, Ph.D, University of London.
Parker D.L., Mihalick J.E., Plude J.L., Plude M.J., Clark T.P., Egan L. et al. 2000. Sorption of metals by extracellular polymers from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa f. flos-aquae strain C3-40. J. Appl. Phycol. 12: 219–224.
Poole R.K. and Gadd G.M. 1989. Metal-Microbe Interactions. IRL Press, Oxford.
Pradham S. and Rai L.C. 2001. Biotechnological potential of Microcystis sp. in Cu, Zn and Cd biosorption from single and multimetallic systems. Biometals 14: 67–74.
De Rome L. and Gadd G.M. 1987. Measurement of copper biosorption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a Cu+2 selective electrode. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 43: 283–287.
De Rome L. and Gadd G.M. 1991. Use of pelleted and immobilized yeast and fungal biomass for heavy-metal and radionuclide deterrecovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. 7: 97–104.
Savvaidis I., Nobar A., Hughes M.N. and Poole R.K. 1990. Displacement of surface-bound cationic dyes: a method for the rapid and semi-quantitative assay of metal binding to microbial cell surfaces. J. Microbiol. Meth. 11: 95–106.
Savvaidis I., Hughes M.N. and Poole R.K. 1992. Differential pulse polarography: a method of directly measuring biosorption of metal ions by live bacteria without separation of biomass and medium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 92: 181–186.
Smith W.L. and Gadd G.M. 2000. Reduction and precipitation of chromate by mixed culture sulphate-reducing bacterial biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88: 983–991.
Webster E.A., Murphy A.J., Chudek J.A. and Gadd G.M. 1997. Metabolism-independent binding of toxic metals by Ulva lactuca: cadmium binds to oxygen-containing groups, as determined by NMR. Biometals. 10: 105–117.
White C. and Gadd G.M. 1995. Determination of metals and metal fluxes in algae and fungi. Sci. Total Environ. 176: 107–115.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savvaidis, I., Hughes, M.N. & Poole, R.K. Differential pulse polarography: a method for the direct study of biosorption of metal ions by live bacteria from mixed metal solutions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 84, 99–107 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025489915704
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025489915704