Abstract
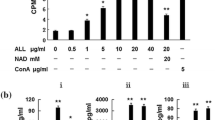
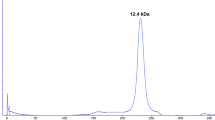
Korean mugwort herb is a preparation of dried leaves from Artemisia species and has been used as a traditional medicine in Asia. An oligosaccharide fraction, AVF3, purified from the preparation promoted survival of the mouse thymocytes in culture. A mouse gene array study suggests that the AVF3 may modulate Fas/FasL dependent apoptotic cell death and thus has influence on the survival of the thymocytes in culture. RT-PCR analysis confirmed the down-regulation of the Fas gene by the AVF3 treatment, supporting that the AVF3 modulated thymocyte death by suppressing the Fas gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barve SS, Kelkar SV, Gobejishvilli L, Joshi-Barve S, McClain CJ (2002) Mechanisms of alcohol-mediated CD4+ T lymphocyte death: relevance to HIV and HCV pathogenesis. Front. Biosci. 7: 1689–1696.
Dai Z, Arakelov A, Wagener M, Konieczny BT, Lakkis FG (1999) The role of the common cytokine receptor gamma-chain in regulating IL-2-dependent, activation-induced CD8+ T cell death. J. Immunol. 163: 3131–3137.
Hahm KB, Kim JH, You BM, Kim YS, Cho SW, Yim H, Ahn BO, Kim WB (1998) Induction of apoptosis with an extract of Artemisia asiatica attenuates the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas 17: 153–157.
Hwang JS, Chung HK, Bae EK, Lee AY, Ji HJ, Park DW, Jung HJ, Cho CW, Choi HJ, Lee DS, Lee KR, Youn HJ (2003) The polysaccharide fraction AIP1 from Artemisia iwayomogi suppresses apoptotic death of the mouse spleen cells in culture. Arch. Pharm. Res. 26: 294–300.
Kawamura T, Azuma M, Kayagaki N, Shimada S, Yagita H, Okumura K (2000) Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis of murine Langerhans cells. J. Dermatol. Sci. 22: 96–101.
Kim KH, Seong BL (2003) Pro-apoptotic function of HBV X protein is mediated by interaction with c-FLIP and enhancement of death-inducing signal. EMBO J. 22: 2104–2116.
Kroemer G, Bosca L, Zamzami N, Merchetti P, Hortelano S, Martinez AC (1997) Detection of apoptosis and apoptosis-associated alterations. In: Lefkovits I. Immunology Methods Manual. San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 1111–1125.
Middlebrook AJ, Martina C, Chang Y, Lukas RJ, DeLuca D (2002) Effects of nicotine exposure on T cell development in fetal thymus organ culture: arrest of T cell maturation. J. Immunol. 169: 2915–2124.
Miura Y, Misawa N, Kawano Y, Okada H, Inagaki Y, Yamamoto N, Ito M, Yagita H, Okumura K, Mizusawa H, Koyanagi Y (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand induces neuronal death in a murine model of HIV central nervous system infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100: 2777–2782.
Novelli F, Di Pierro F, Francia di Celle P, Bertini S, Affaticati P, Garotta G, Forni G (1994) Environmental signals influencing expression of the IFN-gamma receptor on human T cells control whether IFN-gamma promotes proliferation or apoptosis. J. Immunol. 152: 496–504.
Taylor K (1995) A modification of the phenol sulfuric acid method of total sugar determination. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 53: 207–214.
Zeytun A, McKallip RJ, Fisher M, Camacho I, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS (2002) Analysis of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-pdioxin-induced gene expression profile in vivo using pathwayspecific cDNA arrays. Toxicology 178: 241–260.
Zhao M, Cribbs DH, Anderson AJ, Cummings BJ, Su JH, Wasserman AJ, Cotman CW (2003) The induction of the TNFalpha death domain signaling pathway in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurochem. Res. 28: 307–318.
Zhou H, Perkins SL, Tripp S, Hussong JW, Coffin CM (2002) Expression of apoptosis-related antigens, Fas, bcl-2, and p53, and Mib-1 proliferation index in the hypoplastic thymus of DiGeorge syndrome. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 5: 465–471.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyung Chung, H., Kyong Bae, E., Jung Ji, H. et al. An oligosaccharide fraction from Korean mugwort herb suppresses death of the mouse thymocytes in culture by down-regulating the Fas death receptor gene. Biotechnology Letters 25, 1549–1553 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025482516404
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025482516404