Abstract
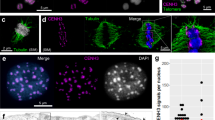
The location of centromeres and telomeres was studied in human and mouse lymphocyte nuclei (G0) employing 3D-FISH, confocal microscopy, and quantitative image analysis. In both human and murine lymphocytes, most centromeres were found in clusters at the nuclear periphery. The distribution of telomere clusters, however, differed: in mouse nuclei, most clusters were detected at the nuclear periphery, while, in human nuclei, most clusters were located in the nuclear interior. In human cell nuclei we further studied the nuclear location of individual centromeres and their respective chromosome territories (CTs) for chromosomes 1, 11, 12, 15, 17, 18, 20, and X. We found a peripheral location of both centromeres and CTs for 1, 11, 12, 18, X. A mostly interior nuclear location was observed for CTs 17 and 20 and the CTs of the NOR-bearing acrocentric 15 but the corresponding centromeres were still positioned in the nuclear periphery. Autosomal centromeres, as well as the centromere of the active X, were typically located at the periphery of the respective CTs. In contrast, in about half of the inactive X-CTs, the centromere was located in the territory interior. While the centromere of the active X often participated in the formation of centromere clusters, such a participation was never observed for the centromere of the inactive X.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abranches R, Beven AF, Aragon-Alcaide L, Shaw PJ (1998). Transcription sites are not correlated with chromosome territories in wheat nuclei. J Cell Biol 143: 5-12.
Alcobia I, Dilao R, Parreira L (2000) Spatial associations of centromeres in the nuclei of hematopoietic cells: evidence for cell-type-specific organizational patterns [published erratum appears in Blood 2000 Aug 1;96(3): 987]. Blood 95: 1608-1615.
Avner P, Heard E (2001) X-chromosome inactivation: counting, choice and initiation. Nat Rev Genet 2: 59-67.
Barr ML, Bertram EG (1949) A morphological distinction between neurones of the male and female, and the behaviour of the nucleolar satellite during accelerated nucleoprotein synthesis. Nature 163: 676-677.
Baxter J, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG (2002) Nuclear organ-isation and gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14: 372-376.
Bolzer A, Craig JM, Cremer T, Speicher MR (1999) A complete set of repeat-depleted, PCR-amplifiable, human chromosome-specific painting probes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 84: 233-240.
Boyle S, Gilchrist S, Bridger JM, Mahy NL, Ellis JA, Bickmore WA (2001) The spatial organization of human chromosomes within the nuclei of normal and emerin-mutant cells. Hum Mol Genet 10: 211-219.
Brown KE, Guest SS, Smale ST, Hahm K, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG (1997) Association of transcriptionally silent genes with Ikaros complexes at centromeric heterochromatin. Cell 91: 845-854.
Brown KE, Baxter J, Graf D, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG (1999) Dynamic repositioning of genes in the nucleus of lymphocytes preparing for cell division. Mol Cell 3: 207-217.
Carvalho C, Pereira HM, Ferreira J et al. (2001) Chromosomal G-dark bands determine the spatial organization of centromeric heterochromatin in the nucleus. Mol Biol Cell 12: 3563-3572.
Chevret E, Volpi EV, Sheer D (2000) Mini review: form and function in the human interphase chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 90: 13-21.
Choo, AKH (1997) The Centromere. Oxford, New York, Tokyo: Oxford University Press, pp 304.
Cooke, HJ, Hindley J (1979) Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 6: 3177-3197.
Craig JM, Kraus J, Cremer T (1997) Removal of repetitive sequences from FISH probes using PCR-assisted affinity chromatography. Hum Genet 100: 472-476.
Cremer T, Cremer C (2001) Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat Rev Genet 2: 292-301.
Cremer T, Kreth G, Koester H (2000) Chromosome territories, interchromatin domain compartment, and nuclear matrix: an integrated view of the functional nuclear architecture. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 10: 179-212.
Cremer M, von Hase J, Volm T et al. (2001) Non-random radial higher-order chromatin arrangements in nuclei of diploid human cells. Chromosome Res 9: 541-567.
Croft JA, Bridger JM, Boyle S, Perry P, Teague P, Bickmore WA (1999) Differences in the localization and morphology of chromosomes in the human nucleus. J Cell Biol 145: 1119-1131.
Dietzel S, Jauch A, Kienle D et al. (1998a) Separate and variably shaped chromosome arm domains are disclosed by chromosome arm painting in human cell nuclei. Chromosome Res 6: 25-33.
Dietzel S, Eils R, Satzler K et al. (1998b) Evidence against a looped structure of the inactive human X-chromosome territory. Exp Cell Res 240: 187-196.
Dietzel S, Schiebel K, Little G et al. (1999). The 3D positioning of ANT2 and ANT3 genes within female X chromosome territories correlates with gene activity [In Process Citation]. Exp Cell Res 252: 363-375.
Dong F, Jiang J (1998) Non-Rabl patterns of centromere and telomere distribution in the interphase nuclei of plant cells. Chromosome Res 6: 551-558.
Dundr M, Misteli T (2001) Functional architecture in the cell nucleus. Biochem J 356: 297-310.
Eils R, Dietzel S, Bertin E et al. (1996) Three-dimensional reconstruction of painted human interphase chromosomes: active and inactive X chromosome territories have similar volumes but differ in shape and surface structure. J Cell Biol 135: 1427-1440.
Falk M, Lukasova E, Kozubek S, Kozubek M (2002) Topography of genetic elements of X-chromosome relative to the cell nucleus and to the chromosome X territory determined for human lymphocytes. Gene 292: 13-24.
Ferguson M, Ward DC (1992) Cell cycle dependent chromosomalmovement in pre-mitotic human T-lymphocyte nuclei. Chromosoma 101: 557-565.
Fransz P, De Jong JH, Lysak M, Castiglione MR, Schubert I (2002) Interphase chromosomes in Arabidopsis are organized as well defined chromocenters from which euchromatin loops emanate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 14584-14589.
Garagna S, Zuccotti M, Capanna E, Redi CA (2002) High-resolution organization of mouse telomeric and pericentromeric DNA. Cytogenet Genome Res 96: 125-129.
Haaf T, Schmid M (1991) Chromosome topology in mammalian interphase nuclei. Exp Cell Res 192: 325-332.
Hulspas R, Houtsmuller AB, Krijtenburg PJ, Bauman JG, Nanninga N (1994) The nuclear position of pericentromeric DNA of chromosome 11 appears to be random in G0 and non-random in G1 human lymphocytes. Chromosoma 103: 286-292.
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST (1991) Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucl Acids Res 19: 4780.
Kipling D, Cooke HJ (1990) Hypervariable ultra-long telomeres in mice. Nature 347: 400-402.
Kipling D, Ackford HE, Taylor BA, Cooke HJ (1991) Mouse minor satellite DNA genetically maps to the centromere and is physically linked to the proximal telomere. Genomics 11: 235-241.
Kozubek S, Lukasova E, Jirsova P et al. (2002) 3D Structure of the human genome: order in randomness. Chromosoma 111: 321-331.
Kurz A, Lampel S, Nickolenko JE et al. (1996) Active and inactive genes localize preferentially in the periphery of chromosome territories. J Cell Biol 135: 1195-1205.
Leitch AR (2000) Higher levels of organization in the interphase nucleus of cycling and differentiated cells. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64: 138-152.
Lyon MF (1961) Gene action in the X chromosome of the mouse. Nature 190: 372.
Mahy NL, Perry PE, Gilchrist S, Baldock RA, Bickmore WA (2002a) Spatial organization of active and inactive genes and noncoding DNA within chromosome territories. J Cell Biol 157: 579-589.
Mahy NL, Perry PE, Bickmore WA (2002b). Gene density and transcription influence the localization of chromatin outside of chromosome territories detectable by FISH. J Cell Biol 159: 753-763.
Manuelidis L (1984) Different central nervous system cell types display distinct and nonrandom arrangements of satellite DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 3123-3127.
Martens UM, Brass V, Engelhardt M et al. (2000) Measurement of telomere length in haematopoietic cells using in situ hybridization techniques. Biochem Soc Trans 28: 245-250.
Mitchell AR, Gosden JR, Miller DA (1985) A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma 92: 369-377.
Nagele RG, Velasco AQ, Anderson WJ et al. (2001) Telomere associations in interphase nuclei: possible role in maintenance of interphase chromosome topology. J Cell Sci 114: 377-388.
Nogami M, Kohda A, Taguchi H, Nakao M, Ikemura T, Okumura K (2000) Relative locations of the centromere and imprinted SNRPN gene within chromosome 15 territories during the cell cycle in HL60 cells. J Cell Sci 113 (Pt 12): 2157-2165.
Parada L, Misteli T (2002) Chromosome positioning in the interphase nucleus. Trends Cell Biol 12: 425-432.
Pardue ML, Gall JG (1970) Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science 168: 1356-1358.
Rawlins DJ, Shaw PJ (1990) Localization of ribosomal and telomeric DNA sequences in intact plant nuclei by in-situ hybridization and three-dimensional optical microscopy. J Microsc 157 (Pt 1): 83-89.
Schubeler D, Lorincz MC, Cimbora DM et al. (2000) Genomic targeting of methylated DNA: influence of methylation on transcription, replication, chromatin structure, and histone acetylation. Mol Cell Biol 20: 9103-9112.
Skalnikova M, Kozubek S, Lukasova E et al. (2000) Spatial arrangement of genes, centromeres and chromosomes in human blood cell nuclei and its changes during the cell cycle, differentiation and after irradiation. Chromosome Res 8: 487-499.
Solovei I, Cavallo A, Schermelleh L et al. (2002a) Spatial preservation of nuclear chromatin architecture during three-dimensional fluorescence in situ hybridization (3D-FISH). Exp Cell Res 276: 10-23.
Solovei I, Walter J, Cremer M, Habermann F, Schermelleh L, Cremer T (2002b) FISH on Three-dimensionally Preserved Nuclei. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp 119-157.
Solovei I, Schermelleh L, Düring K et al. (2003). Differences in centromere positioning during cell cycle and at G0 in four types of human cells. (In preparation).
Sullivan GJ, Bridger JM, Cuthbert AP, Newbold RF, Bickmore WA, McStay B (2001) Human acrocentric chromosomes with transcriptionally silent nucleolar organizer regions associate with nucleoli. Embo J 20: 2867-2874.
Tanabe H, Muller S, Neusser M et al. (2002a) Evolutionary conservation of chromosome territory arrangements in cell nuclei from higher primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 4424-4429.
Tanabe H, Habermann FA, Solovei I, Cremer M, Cremer T (2002b) Non-random radial arrangements of interphase chromosome territories: evolutionary considerations and functional implications. Mutat Res 504: 37-45.
Volpi EV, Chevret E, Jones T et al. (2000) Large-scale chromatin organization of the major histocompatibility complex and other regions of human chromosome 6 and its response to interferon in interphase nuclei. J Cell Sci 113 (Pt 9): 1565-1576.
Vourc'h C, Taruscio D, Boyle AL, Ward DC (1993) Cell cycle-dependent distribution of telomeres, centromeres, and chromosome-specific subsatellite domains in the interphase nucleus of mouse lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res 205: 142-151.
Wachtler F, Hopman AH, Wiegant J, Schwarzacher HG (1986) On the position of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in interphase nuclei. Studies with a new, non-autoradiographic in situ hybridization method. Exp Cell Res 167: 227-240.
Walter J, Schermelleh L, Cremer M, Tashiro S, Cremer T (2003) Chromosome order in HeLa cells changes during mitosis and early G1, but is stably maintained during subsequent interphase stages. J Cell Biol 160: 685-697.
Weimer R, Haaf T, Kruger J, Poot M, Schmid M (1992) Characterization of centromere arrangements and test for random distribution in G0, G1, S, G2, G1, and early S′ phase in human lymphocytes. Hum Genet 88: 673-682.
Willard HF, Smith KD, Sutherland J (1983) Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucl Acids Res 11: 2017-2033.
Williams RR, Broad S, Sheer D, Ragoussis J (2002) Subchromosomal positioning of the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) in keratinocyte and lymphoblast interphase nuclei. Exp Cell Res 272: 163-175.
Zijlmans JM, Martens UM, Poon SS et al. (1997) Telomeres in the mouse have large inter-chromosomal variations in the number of T2AG3 repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 7423-7428.
Zink D, Bornfleth H, Visser A, Cremer C, Cremer T (1999) Organization of early and late replicating DNA in human chromosome territories. Exp Cell Res 247: 176-188.
Zirbel RM, Mathieu UR, Kurz A, Cremer T, Lichter P (1993) Evidence for a nuclear compartment of transcription and splicing located at chromosome domain boundaries. Chromosome Res 1: 93-106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weierich, C., Brero, A., Stein, S. et al. Three-dimensional arrangements of centromeres and telomeres in nuclei of human and murine lymphocytes. Chromosome Res 11, 485–502 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025016828544
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025016828544