Abstract
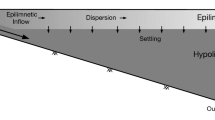
The characteristic feature of the physical structure of Lac Pavin is a distinct and permanent chemically induced density increase between about 60 and 70 m depth. This chemocline separates the seasonally mixed mixolimnion from the monimolimnion, which is characterized by elevated temperature and salinity as well as complete anoxia. Previously published box-models of the lake postulated substantial groundwater input at the lake bottom, and consequently a short water residence time in the monimolimnion and high fluxes of dissolved constituents across the chemocline. We present a new view of the physical structure and dynamics of Lac Pavin, which is based on the results of high-resolution CTD profiles, transient and geochemical tracers (tritium, CFCs, helium), and numerical modeling. The CTD profiles indicate the existence of a sublacustrine spring above rather than below the chemocline. A stability analysis of the water column suggests that vertical turbulent mixing in the chemocline is very weak. A numerical one-dimensional lake model is used to reconstruct the evolution of transient tracer distributions over the past 50 years. Model parameters such as vertical diffusivity and size of sublacustrine springs are constrained by comparison with observed tracer data. Whereas the presence of a significant water input to the monimolimnion can clearly be excluded, the input to the mixolimnion – both at the surface and from the indicated sublacustrine spring – cannot be accurately determined. The vertical turbulent diffusivity in the chemocline is well constrained to K ≈ 5×10-8 m2 s-1, about a factor of three below the molecular diffusivity for heat. Assuming thus purely molecular heat transport, the heat flow through the chemocline can be estimated to between 30 and 40 mW m-2. With respect to dissolved constituents, the very weak turbulent diffusive exchange is equivalent to a stagnant monimolimnion with a residence time of nearly 100 years. Based on these results and vertical concentration profiles of dissolved species, diffusive fluxes between monimolimnion and mixolimnion can be calculated. A large excess of helium with a 3He/4He ratio of (9.09 ± 0.01)×10-6 (6.57 R a) is present in the monimolimnion, clearly indicating a flux of magmatic gases into the monimolimnion. We calculate a flux of 1.0×10-12 mol m-2 s-1 for mantle helium and infer a flux of 1.2×10-7 mol m-2 s-1 (72 t year-1) for magmatic CO2. The monimolimnion appears to be in steady state with respect to these fluxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., 1994. Helium und Tritium als Tracer für physikalische Prozesse in Seen. Diss. ETH Nr. 10714, ETH Zürich, 272 pp.
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., R. Kipfer, M. Hofer, D. M. Imboden & H. Baur, 1996a. Density-driven exchange between the basins of Lake Lucerne (Switzerland) traced with the 3H–3He method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 707–721.
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., M. Hofer, R. Kipfer, D. Imboden & R. Wieler, 1999a. Accumulation of mantle gases in a permanently stratified volcanic Lake (Lac Pavin, France). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63: 3357–3372.
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., R. Kipfer, M. Hofer, D. M. Imboden, R. Wieler & P. Signer, 1996b. Quantification of gas fluxes from the subcontinental mantle: The example of Laacher See, a maar lake in Germany. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60: 31–41.
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., F. Peeters, U. Beyerle & R. Kipfer, 1999b. Interpretation of dissolved atmospheric noble gases in natural waters. Water Resour. Res. 35: 2779–2792.
Alvinerie, J., B. Dégot, P. Lévèque & M. Vigneaux, 1966. Activité en tritium et caractéristiques chimiques des eaux du lac Pavin. C. r. Acad. Sci. Paris 262 D: 846–849.
Beyerle, U., R. Kipfer, D. M. Imboden, H. Baur & T. Graf, 2000. A mass spectrometric system for the analysis of noble gases from water samples. Envir. Sci. Technol. 34: 2042–2050.
Bullister, J. L. & B.-S. Lee, 1995. Chlorofluorocarbon-11 removal in anoxic marine waters. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22: 1893–1896.
Busenberg, E., E. P. Weeks, L. N. Plummer & R. C. Bartholomay, 1993. Age dating ground water by use of chlorofluorocarbons (CCl3F and CCl2F2), and distribution of chlorofluorocarbons in the unsaturated zone, Snake River plain aquifer, Idaho National Engineering Laboratory, Idaho. USGS Water Resources Investigations Report Nr. 93–4054, United States Geological Survey.
Camus, G., G. Michard, P. Olive, P. Boivin, P. Desgranges, D. Jézéquel, M. Meybeck, J.-C. Peyrus, J.-M. Vinson, E. Viollier & J. Kornprobst, 1993. Risques d'éruption gazeuse carbonique en Auvergne. Bull. Soc. Géol. France 164: 767–781.
Chen, C. T. & F. J. Millero, 1986. Precise thermodynamic properties for natural waters covering only the limnological range. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 657–662.
Clark, J. F. & G. B. Hudson, 2001. Quantifying the flux of hydrothermal fluids into Mono Lake by use of helium isotopes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 46: 189–196.
Clark, J. F., P. Schlosser, R. Wanninkhof, H. J. Simpson, W. S. F. Schuster & D. T. Ho, 1995. Gas transfer velocities for SF6 and 3He in a small pond at low wind speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22: 93–96.
Clarke, W. B., W. J. Jenkins & Z. Top, 1976. Determination of tritium by mass spectrometric measurement of 3He. Int. J. appl. Radiat. Isotopes 27: 515–522.
Delebecque, A., 1898. Les lacs français. Chamerot & Renouard, Paris, 436 pp.
Dunai, T. J. & H. Baur, 1995. Helium, neon, and argon systematics of the European subcontiental mantle: Implications for its geochemical evolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59: 2767–2783.
Elkins, J. W., T. M. Thompson, T. H. Swanson, J. H. Butler, B. D. Hall, S. O. Cummings, D. A. Fisher & A. G. Raffo, 1993. Decrease in the growth rates of atmospheric chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12. Nature 364: 780–783.
Glangeaud, P., 1916. Le cratère-lac du Pavin et le volcan de Montchalm. C. r. Acad. Sci. Paris 162: 428–430.
Hofer, M. & D. M. Imboden, 1998. Simultaneous determination of CFC-11, CFC-12, N2 and Ar in water. Anal. Chem. 70: 724–729.
Hohmann, R., R. Kipfer, F. Peeters, G. Piepke, D. M. Imboden & M. N. Shimaraev, 1997. Processes of deep water renewal in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 841–855.
IAEA, 1992. Statistical treatment of data on environmental isotopes in precipitation. Technical Reports Series Nr. 331, IAEA, Vienna, 781 pp.
IAEA/WMO, 2001. Global network of isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP database. http://isohis.iaea.org.
Imboden, D. M. & A. Wüest, 1995. Mixing mechanisms in lakes. In Lerman, A., D. M. Imboden & J. R. Gat (eds), Physics and Chemistry of Lakes. Springer, Berlin: 83–138.
Imboden, D. M., R. F. Weiss, H. Craig, R. L. Michel & C. R. Goldman, 1977. Lake Tahoe geochemical study. 1. Lake chemistry and tritium mixing study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 1039–1051.
Imboden, D. M., U. Lemmin, T. Joller, K. H. Fischer & W. Weiss, 1981. Lake mixing and trophic state. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol. 21: 115–119.
Imboden, D. M., U. Lemmin, T. Joller & M. Schurter, 1983. Mixing processes in lakes: Mechanisms and ecological relevance. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 45: 11–44.
Khalil, M. A. K. & R. A. Rasmussen, 1989. The potential of soils as a sink of chlorofluorocarbons and other man-made chlorocarbons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 16: 679–682.
Kipfer, R., W. Aeschbach-Hertig, H. Baur, M. Hofer, D. M. Imboden & P. Signer, 1994. Injection of mantle type helium into Lake Van (Turkey): The clue for quantifying deep water renewal. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 125: 357–370.
Kipfer, R., W. Aeschbach-Hertig, F. Peeters & M. Stute, 2002. Noble gases in lakes and ground waters. In Porcelli, D., C. Ballentine & R. Wieler (eds), Noble Gases in Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 47: 615–700.
Kling, G. W., M. A. Clark, H. R. Compton, J. D. Devine, W. C. Evans, A. M. Humphrey, E. J. Koenigsberg, J. P. Lockwood, M. L. Tuttle & G. N. Wagner, 1987. The 1986 Lake Nyos gas disaster in Cameroon, West Africa. Science 236: 169–175.
Krause, W. J., 1980. Tritium-Bilanzierung kleiner Einzugsgebiete in der Eifel, Teil I – Wasserbilanz. Dtsche Gewässerkundl. Mitt.24: 2–14.
Kuhn, W., 1977. Berechnung der Temperatur und Verdunstung alpiner Seen auf klimatologisch-thermodynamischer Grundlage. Arbeitsberichte der Schweizerischen Meteorologischen Zentralanstalt Nr. 70, Schweizerische Meteorologische Zentralanstalt, Zürich, 33 pp.
Li, Y.-H., 1973. Vertical eddy diffusion coefficient in Lake Zürich. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 35: 1–7.
Lovley, D. R. & J. C. Woodward, 1992. Consumption of freons CFC-11 and CFC-12 by anaerobic sediments and soils. Envir. Sci. Technol. 26: 925–929.
Maloszewski, P. & A. Zuber, 1982. Determining the turnover time of groundwater systems with the aid of environmental tracers, I. Models and their applicability. J. Hydrol. 57: 207–231.
Martin, J.-M., 1985. The Pavin Crater Lake. In Stumm, W. (ed.), Chemical Processes in Lakes. John Wiley & Sons, New York: 169–188.
Meybeck, M., J. M. Martin & P. Olive, 1975. Géochimie des eaux et des sédiments de quelques lacs volcaniques du Massif Central français. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 1150–1164.
Michard, G., E. Viollier, D. Jézéquel & G. Sarazin, 1994. Geochemical study of a crater lake: Pavin Lake, France – Identification, location and quantification of the chemical reactions in the lake. Chem. Geol. 115: 103–115.
Montzka, S. A., J. H. Butler, R. C. Myers, T. M. Thompson, T. H. Swanson, A. D. Clarke, L. T. Lock & J. W. Elkins, 1996. Decline in the tropospheric abundance of halogen from halocarbons: Implications for stratospheric ozone depletion. Science 272: 1318–1322.
Oliver, B. M., H. Farrar IV & M. M. Bretscher, 1987. Tritium halflife measured by helium-3 growth. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 38: 959–965.
Olivier, L., 1952. Sur la présence en été, dans le lac Pavin, d'une couche dépourvue d'oxygéne, vers 70 m de profondeur. C. r. Acad. Sci. Paris 234: 743–745.
Oster, H., C. Sonntag & K. O. Münnich, 1996. Groundwater age dating with chlorofluorocarbons. Water Resour. Res. 32: 2989–3001.
Peeters, F., G. Piepke, R. Kipfer, R. Hohmann & D. M. Imboden, 1996. Description of stability and neutrally buoyant transport in freshwater lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 1711–1724.
Peeters, F., R. Kipfer, R. Hohmann, M. Hofer, D. M. Imboden, G. G. Kodenev & T. Khozder, 1997a. Modelling transport rates in Lake Baikal: gas exchange and deep water renewal. Envir. Sci. Technol. 31: 2973–2982.
Peeters, F., G. Piepke & M. Gloor, 1997b. A diffusion model for the development of a boundary layer in lakes. Aquat. Sci. 59: 95–114.
Peeters, F., R. Kipfer, D. Achermann, M. Hofer, W. Aeschbach-Hertig, U. Beyerle, D. M. Imboden, K. Rozanski & K. Fröhlich, 2000. Analysis of deep-water exchange in the Caspian Sea based on environmental tracers. Deep-Sea Res. I 47: 621–654.
Pelletier, J.-P., 1968. Un lac meromictique, le Pavin (Auvergne). Annales de la Station Biol. Besse-en-Chandesse 3: 147–170.
Reichert, P., 1994. AQUASIM – a tool for simulation and data analysis of aquatic systems. Wat. Sci. Tech. 30: 21–30.
Restituito, F., 1987. Consequences of redox conditions on the distribution of cations in a meromictic oligotrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 144: 63–75.
Rozanski, K., R. Gonfiantini & L. Araguas-Araguas, 1991. Tritium in the global atmosphere: Distribution patterns and recent trends. J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 17: S523–S536.
Schmid, M., 1997. Physikalische und chemische Prozesse im Lac Pavin: Ursachen und Folgen der stabilen Schichtung eines vulkanischen Kratersees. Diploma thesis, ETH Zürich, 93 pp.
Shapiro, S. D., P. Schlosser, W. M. Smethie & M. Stute, 1997. The use of 3H and tritiogenic 3He to determine CFC degradation and vertical mixing rates in Framvaren Fjord, Norway. Mar. Chem. 59: 141–157.
Torgersen, T., Z. Top, W.B. Clarke, W. J. Jenkins & W. S. Broecker, 1977. A new method for physical limnology – tritium-helium-3 ages – results for Lakes Erie, Huron and Ontario. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 181–193.
Upstill-Goddard, R. C., A. J. Watson, P. S. Liss & M. I. Liddicoat, 1990. Gas transfer velocities in lakes measured with SF6. Tellus 42B: 364–377.
Van Senden, D. C., R. Portielje, A. Borer, H. Ambühl & D. M. Imboden, 1990. Vertical exchange due to horizontal density gradients in lakes; the case of Lake Lucerne. Aquat. Sci. 52: 381–398.
Viollier, E., D. Jézéquel, G. Michard, M. Pèpe, G. Sarazin & P. Albéric, 1995. Geochemical study of a crater lake (Pavin Lake, France): Trace-element behaviour in the monimolimnion. Chem. Geol. 125: 61–72.
Viollier, E., G. Michard, D. Jézéquel, M. Pèpe & G. Sarazin, 1997.Geochemical study of a crater lake: Lake Pavin, Puy de Dôme, France. Constraints afforded by the particulate matter distribution in the element cycling within the lake. Chem. Geol. 142: 225–241.
Wanninkhof, R., 1992. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 97: 7373–7382.
Wanninkhof, R., J. Ledwell & J. Crusius, 1990. Gas transfer velocities on lakes measured with sulfur hexafluoride. In Wilhelms, S.C. & J. S. Gulliver (eds), Air–Water Mass Transfer. Amer. Soc. Civil Eng., New York: 441–458.
Warner, M. J. & R. F. Weiss, 1985. Solubilities of chlorofluorocarbons 11 and 12 in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res. 32: 1485–1497.
Weiss, R. F., 1971. Solubility of helium and neon in water and seawater. J. Chem. Eng. Data 16: 235–241.
Weiss, R. F., E. C. Carmack & V. M. Koropalov, 1991. Deep-water renewal and biological production in Lake Baikal. Nature 349: 665–669.
Weiss, W., J. Bullacher & W. Roether, 1979. Evidence of pulsed discharges of tritium from nuclear energy installations in Central European precipitation. In Behaviour of tritium in the environment (San Francisco, 16–20 October, 1978), IAEA, Vienna: 17–30.
Welander, P., 1968. Theoretical forms for the vertical exchange coefficients in a stratified fluid with application to lakes and seas. Geophys. Gothoburg. 1: 1–27.
Wüest, A., W. Aeschbach-Hertig, H. Baur, M. Hofer, R. Kipfer & M. Schurter, 1992. Density structure and tritium-helium age of deep hypolimnetic water in the northern basin of Lake Lugano. Aquat. Sci. 54: 205–218.
Wüest, A., G. Piepke & J. D. Halfman, 1996. Combined effects of dissolved solids and temperature on the density stratification of Lake Malawi. In Johnson, T. C. & E. O. Odada (eds), The Limnology, Climatology and Paleoclimatology of the East African Lakes, Gordon & Breach, Toronto: 183–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., Hofer, M., Schmid, M. et al. The physical structure and dynamics of a deep, meromictic crater lake (Lac Pavin, France). Hydrobiologia 487, 111–136 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022942226198
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022942226198