Abstract
Background: Approximately 60% of meningiomas are associated with perilesional brain oedema. Several aspects have been evaluated in order to understand the pathophysiological mechanisms of oedema (age, sex of the patient, size and location of the tumour, histotype, grading), although at present they have yet to be completely clarified. We focused on pial blood supply, microvascular density (MVD) and angiogenic growth factors (i.e. vascular endothelial growth factor – VEGF) in order to evaluate their putative role in the development of brain oedema.
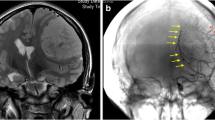
Methods: We retrospectively studied 55 patients with intracranial meningiomas. Computerized tomography (CT) and angiographic studies were obtained in all cases. The angiograms provided an accurate differentiation between pial and dural blood supply, concomitantly with its semi-quantitative evaluation. The location and the volume of oedema, in relation to the meningioma surface, was evaluated using CT scans, as an oedema index (E/I). We also determined the expression of VEGF and MVD using standard immunohistochemical methods.
Results: Thirty-two out of 55 meningiomas presented peritumoural oedema, with an angiographic blush ranging from 2 to 4; VEGF protein was expressed in 27 out of 32 cases, independent of grade or histotype of tumours. In all patients, MVD ranged from 4 to 33.3 vessels (median value: 10.6).
A significant relationship was found between the expression of VEGF and MVD (p = 0.0003) and between VEGF and E/I (p = 0.0023).
Moreover, the E/I ratio was related to the blush (p = 0.0005). A significant association was also present between VEGF expression and pial blush (p = 0.0001).
Conclusion: Our data confirm the central role of VEGF and pial blood supply in the pathogenesis of peritumoural oedema and support the hypothesis that the development of oedema in meningioma is vasogenic in type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitzer M, Wockel L, Luft AR, Wakhloo AK, Petersen D, Opitz H, Sievert T, Ernemann U, Voigt K: The importance of pial blood supply to the development of pertumoural brain oedema in meningiomas. J Neurosurg 87: 368–373, 1997
Lobato RD, Alday R, Gomez PA, Rivas JJ, Dominguez J, Cabrera A, Madero S, Ayerbe J: Brain oedema in patients with intracranial meningioma. Correlation between clinical, radiological and histological factors and the presence and intensity of oedema. Acta Neurochir 138: 485–493, 1996
Abe T, Black PM, Ojemann RG, Hedley-White ET: Cerebral oedema in intracranial meningiomas: evidence for local and diffuse patterns and factors associated with its occurrence. Surg Neurol 42: 471–475, 1994
Bitzer M, Nagele T, Geist-Barth B, Klose U, Gronewaller E, Morgalla M, Heiss E, Voigt K: Role of hydrodynamic processes in the pathogenesis of peritumoural brain oedema in meningiomas. J Neurosurg 93: 594–604, 2000
Nishikawa R, Cheng SY, Nagashima R, Huang HJ, Cavanee WK, Matsutani M: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human brain tumours. Acta Neuropathol 96: 753–762, 1998
Goldman CK, Bharara S, Palmer CA, Vitek J, Tsai JC, Weiss HL, Gillespie GY: Brain oedema in meningiomas is associated with increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Neurosurgery 40: 1269–1277, 1997
Kalkanis SN, Carroll RS, Zhang J, Zamani AA, Black PM: Correlation of vascular endothelial growth factor messenger RNA expression with peritumoural vasogenic cerebral oedema in meningiomas. J Neurosurg 85: 1095–1101, 1996
Yoshioka H, Hama S, Taniguchi E, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Kurisu K: Peritumoural brain oedema associated with meningioma: influence of vascular endothelilal factor expression and vascular blood supply. Cancer 85: 936–944, 1999
Tsai JC, Hsiao YY, Teng LJ, Shun CT, Goldman CK, Kao MC: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human meningioma cells. J Formos Med Assoc 98: 111–117, 1999
Benzel EC, Gelder FB: Correlation between sex hormone binding and peritumoural oedema in intracranial meningiomas. Neurosurgery 23: 169–174, 1988
Parenti G, Cocciaro A, Ferdighini P, Boni G, Lutzemberger L, Lenzi B, Castagna M, Cristofani R, Pellegrino D: I recettori della somatostatina nei meningiomi cerebrali. XLVII Congresso della Societ`a Italiana di Neurochirurgia, Trieste 11–14 ottobre, 1998
Assimakopoulou M, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Maraziotis T, Papadakis N, Varakis I: Microvessel density in brain tumours. Anticancer Res 17: 4747–4753, 1997
Ferrara N: The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pathological angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36: 127–137, 1995
Fontanini G, Vignati S, Boldrini L, Chin`e S, Silvestri V, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Angeletti CA, Bevilacqua G: Vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with neovascularization and influences progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 3: 861–865, 1997
Takahashi Y, Mai M, Kitadai Y, Bucana C, Cleary KR, Ellis LM: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 55: 3964–3968, 1995
Takahashi Y, Cleary KR, Mai M, Kitadai Y, Bucana C, Ellis LM: Significance of vessel count and vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor (KDR) in intestinal type gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2: 1679–1684, 1996
Izycka-Swieszewska E, Rzepko R, Borowska-Lehman J, Baranowska E, Warzocha D: Recurrent meningiomas-the immunohistochemical analysis of angiogenesis and cellular proliferation. Preliminary study. Folia Neuropathol 37: 179–184, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pistolesi, S., Fontanini, G., Camacci, T. et al. Meningioma-associated Brain Oedema: The Role of Angiogenic Factors and Pial Blood Supply. J Neurooncol 60, 159–164 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020624119944
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020624119944