Abstract
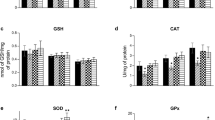
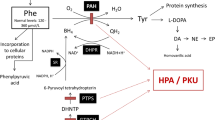
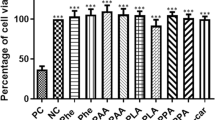
The mechanisms by which phenylalanine is toxic to the brain in phenylketonuria are not fully understood. Considering that brain glucose metabolism is reduced in these patients, our main objective was to determine pyruvate kinase activity in brain cortex of rats subjected to acute and chronic chemically induced hyperphenylalaninemia. The effect of alanine administration on the enzyme activity in the treated rats was also investigated. We also studied the in vitro effect of the two amino acids on pyruvate kinase activity in brain cortex of nontreated rats. The results indicated that phenylalanine inhibits pyruvate kinase in vitro and in vivo and that alanine prevents the inhibitory effect of phenylalanine on the enzyme activity. Considering the crucial role pyruvate kinase plays in glucose metabolism in brain, it is possible that inhibition of this enzyme activity may contribute to the brain damage characteristic of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Blascovics, M. E., Scheffler, G. E., and Hacks, S. 1974. Phenylalaninemia: Differential diagnosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 49:835-843.
Scriver, C. R. and Kaufman, S. 2001. Hyperphenylalaninemia: Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Pages 1667-1724, in Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S., and Valle, D. (eds): The Metabolic & Molecular Bases of Inherited Diseases, 8th ed., McGraw-Hill, New York.
Holtzman, N. A., Kronmal, R. A., van Doominck W., Azen C., and Koch, R. 1986. Effect of age at loss of dietary control on intellectual performance and behavior of children with phenylketonuria, New Engl. J. Med. 314:593-598.
Smith, I., Beasley M. G., and Ades, A. E. 1990. Intelligence and quality of dietary treatment in phenylketonuria. Arch. Dis. Child. 65:472-478.
Lou, H. C., Güttler F., Lykkelund C., and Niederwieser A. 1985. Decreased vigilance and neurotransmitter synthesis after discontinuation of dietary treatment of phenylketonuria in adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 144:17-29.
Clarke, J. T., Gates, R. T., Hogan, S. E., Barrett, M., and MacDonald, G. W. 1987. Neuropsychological studies on adolescents with phenylketonuria returned to phenylalanine-restricted diets. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 92:255-262.
Krause, W., Halminski, M., McDonald, L., Dembure, P., and Salvo, R. 1985. Biochemical and neuropsychological effects of elevated plasma phenylalanine in patients with treated phenylketonuria: A model for the study of phenylalanine and brain function in man. J. Clin. Invest. 75:40-48.
Weglage, J., Pietsch, M., Fünders, B., Koch, H. G., and Ullrich, K. 1995. Neurological findings in early treated phenylketonuria. Acta Pediatr. 84:411-415.
Cleary, M. A., Walter, J. H., Wraith, J. E., Jenkins, J. P., Alani, S. M., Tyler, K., and Whittle, D. 1994. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in phenylketonuria. Lancet 344:87-90.
Bick, U., Ullrich, K., Stöber, U., Möller, H., Schuierer, G., Ludolph, A. C., Oberwittler, C., Weglage, J., and Wendelm, U. 1993. White matter abnormalities in patients with treated hyperphenylalaninemia: Magnetic resonance relaxometry and proton spectroscopy findings. Eur. J. Pediatr. 152:1012-1020.
Erecinska, M., Nelson, D., Nissim, I., Daikhin, Y., and Yudkoff, M. 1994. Cerebral alanine transport and alanine aminotransferase reaction: Alanine as a source of glutamate. J. Neurochem. 62:1953-1964.
Balász, R. 1965. Control of glutamate metabolism: The effect of pyruvate. J. Neurochem. 12:63-67.
BaÑos, G., Daniel, P. M., and Pratt, O. E. 1978. The effect of age upon the entry of some amino acids into the brain and its incorporation into cerebral protein. Develop. Med. Child Neurol. 20:335-346.
Marsden, D., Barshop, B. A., Capistrano-Estrada, S., Rice, M., Prodanus, C., Sartoris, D., Wolff, J., Jones, K. L., Spector, S., and Nyhan, W. L. 1994. Anabolic effect of human hormone: Management of inherited disorders of catabolic pathways. Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 52:145-154.
Wyse, A. T. S., Bolognesi, G., Brusque, A. M., Wajner, M., and Wannmacher, C. M. D. 1995. Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the synaptic plasma membrane from the cerebral cortex of rats subjected to chemically induced phenylketonuria. Med. Sci. Res. 23:261-262.
Wyse, A. T. S., Wajner, M., and Wannmacher, C. M. D. 1998. Kinetics of alanine reversal on the inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity by phenylalanine and phenyllactate in the synaptic plasma membrane from the cerebral cortex of rats. Med. Sci. Res. 26:141-143.
Wyse, A. T. S., Noriler, M. E., Borges, L. F., Floriano, P. J., Silva, C. G., Wajner, M., and Wannmacher, C. M. D. 1999. Alanine prevents the decrease of Na+, K+-ATPase activity in experimental phenylketonuria. Metab. Brain Dis. 14:95-101.
De Freitas, M. S., de Mattos, A. G., Camargo, M. M., Wannmacher, C. M. D., and Pessoa-Pureur, R. 1995. Effect of phenylalanine and α-methylphenylalanine on in vitro incorporation of 32P into cytoskeletal cerebral proteins. Neurochem. Int. 26:381-385.
De Freitas, M. S., Mattos-Dutra, A., Schroder, N., Wannmacher, C. M. D., and Pessoa-Pureur, R. 1997. Effect of hyperphenylalaninemia chemically induced on in vitro incorporation of 32P into cytoskeletal proteins from cerebral cortex of developing rats. Exper. Neurol. 143:188-195.
Carreras, A. L. R., Mattos-Dutra, A., Meirelles, R., Rocha, B. B., Wannmacher, C. M. D., and Pessoa-Pureur, R. 2000. Phenylalanine inhibition of the phosphorylation of cytoskeletal proteins from cerebral cortex of young rats is prevented by alanine. Eur. J. Clin. Invest, 30:536-542.
Weber, G. 1969. Inhibition of human brain pyruvate kinase and hexokinase by phenylalanine and phenylpiruvate: Possible relevance to phenylketonuric brain damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 63:1365-1369.
Chainy, G. B. N. and Kanungo, M. S. 1978. Induction and properties of pyruvate kinase of the cerebral hemisphere of rats of various ages. J. Neurochem. 30:419-427.
Rodrigues, N. R., Wannmacher, C. M. D., Dutra-Filho, C. S., Pires, R. F., Fagan, P. R., and Wajner, M. 1990. Effect of phenylalanine, p-chlorophenylalanine and α-methylphenylalanine on glucose uptake in vitro by the brain of young rats. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 18:419.
Hasselbach, S., Knudsen, G. M., Toft, P. B., Hogh, P., Tedeschi, E., Holm, S., Videbaek, C., Henriksen, O., Lou, H. C., and Paulson, O. B. 1996. Cerebral glucose metabolism is decreased in white matter changes in patients with phenylketonuria. Pediatr. Res. 40:21-24.
Cespedes, C., Thoene, J. G., Lower, K., and Christensen, H. N. 1989. Evidence of inhibition of exodus of small neutral amino acids from non-brain tissues in hyperphenylalaninemic rats. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 12:166-180.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265-275.
Leong, S. F., Lai, J. C. K., Lim, L., and Clark, J. B. 1981. Energy-metabolising enzymes in brain regions of adult and aging rats. J. Neurochem. 37:1548-1556.
Möller, H., Weglage, J., Wiedermann, D., Vermathen, P., Bick, U., and Ullrich, K. 1997. Kinetics of phenylalanine transport at the human blood-brain barrier investigated in vivo. Brain Res. 778:329-337.
Avison, M. J., Herschkowitz, N., Novotny, E. J., Petroff, O. A. C., Rothman, D. L., Colombo, J. P., Bachmann, C., Shulamn, R. G., and Princhard, J. W. 1990. Proton NMR observation of phenylalanine and an aromatic metabolite in the rabbit brain in vivo. Pediatr. Res. 27:566-570.
Clark, J. B., Bates, T. E., Cullingford, T., and Land, J. M. 1993. Development of enzymes of energy metabolism in the neonatal mammalian brain. Dev. Neurosci. 15:174-180.
Dobbing J. and Sands, J. 1979. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum. Dev. 3:79-84.
Girard, J., Ferre, P., Pegorier, J. P., and Duce, P. H. 1992. Adaptations of glucose and fatty acid metabolism during perinatal period and suckling-weaning transition. Physiol. Rev. 72:507-562.
Himwich, H. E. 1951. Brain metabolism and cerebral disorders, Willians and Wilkins Baltimore.
Beal, M. F. 2000. Energetics in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci. 23:298-304.
Schinder, A. F., Olson, E. C., Spitzer, N. C., and Montal, M. 1996. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a primary event in glutamate neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 16:6125-6133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feksa, L.R., Cornelio, A.R., Rech, V.C. et al. Alanine Prevents the Reduction of Pyruvate Kinase Activity in Brain Cortex of Rats Subjected to Chemically Induced Hyperphenylalaninemia. Neurochem Res 27, 947–952 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020351800882
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020351800882