Abstract
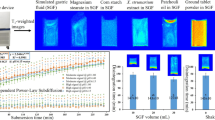
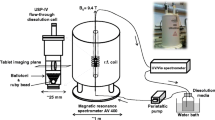
An NMR imaging method was developed to estimate the rate of water movement in slow-release capsule matrices of pseudoephedrine HC1 and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC). Test capsules were first placed in a USP method 2 (paddles, 50 rpm) dissolution apparatus. Each plug was removed from the dissolution medium at predetermined times, blotted dry, and placed within the magnetic field of a General Electric 400-MHz wide-bore NMR spectrometer equipped with a microimaging accessory. Images were recorded along the transverse plane of each plug. The water penetration rate was determined by comparison of the cut and weighed contour plots of the images acquired. After 1 hr, the plugs tamped to 200 N exhibited water penetration to the center, while only 45% of the drug was released. The percentage dry matrix was fitted to the lost equation to obtain a diffusion coefficient of 4.15 × 10−6 cm2/sec. NMR imaging is set forth as an important and practicable technique to investigate drug formulations. In the HPC matrix system of this study, the NMR imaging results convincingly revealed the rate of hydration front penetration not to be a rate-limiting step in the drug release process.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. Higuchi. Mechanism of sustained action medications. J. Pharm. Sci. 52:1145–1147 (1963).
E. Doelker. Water swollen cellulose derivatives in pharmacy. In N. A. Peppas (ed.), Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy, Vol. 2, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1987, p. 117.
D. R. Paul and S. K. McSpaden. Diffusional release of a solute from a polymer matrix. J. Membr. Sci. 1:33–47 (1976).
P. I. Lee. Diffusional release of a solute from a polymeric matrix-approximate analytical solution. J. Membr. Sci. 7:255 (1980).
W. R. Good. Diffusion of water-soluble drugs from initially dry hydrogels. In R. J. Kostenik (ed.), Polymeric Delivery Systems, Gordon and Beach, New York, 1976, p. 139.
J. T. Carstensen, M. Bamba, F. Puiseiux, and J. P. Marty. Release mechanisms in gel-forming sustained release preparations. Int. J. Pharm. 2:307–315 (1979).
F. W. Wehrli, J. R. McFall, G. H. Glover, and N. Grigsby. The dependence of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) image contrast on intrinsic and pulse sequence timing parameters. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2:3–16 (1984).
W. P. Rothwell, D. R. Holecek, and J. A. Kershew. NMR imaging: Study of fluid absorption by polymer composites. J. Polym. Sci. 22:241–247 (1984).
T. H. Mareci, S. Donstrup, and A. Rigamonti. NMR imaging and relaxation study of polymer swelling and chain dynamics. J. Mol. Liq. 38:185–206 (1988).
L. A. Weisenberg and J. L. Koenig. NMR imaging of diffusion processes in polymers. Macromolecules 23:2445–2453 (1990).
M. Ashraf. Ph.D. thesis, School of Pharmacy, University of Maryland, Baltimore (1993).
W. A. Edelstein, J. M. S. Hutchinson, G. Johnson, and T. Redpath. Spin-warp NMR imaging and applications to human whole-body imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 25:751 (1980).
W. Jost. Diffusion in Solids, Liquids, and Gases, Academic Press, New York, 1952, pp. 45–47.
C. Pitkin and J. T. Carstensen. Moisture content of granulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 62:1215–1216 (1973).
L. J. Lynch. Water relaxation in heterogeneous and biological systems. In J. S. Cohen (ed.), Magnetic Resonance in Biology, Vol. 2, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1983, pp. 248–304.
S. J. Desai, P. Singh, A. P. Simonelli, and W. I. Higuchi. Investigation of factors influencing release of solid drug dispersed in inert matrices, III. J. Pharm. Sci. 55:1230–1234 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, M., luorno, V.L., Coffin-Beach, D. et al. A Novel Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Imaging Method for Measuring the Water Front Penetration Rate in Hydrophilic Polymer Matrix Capsule Plugs and Its Role in Drug Release. Pharm Res 11, 733–737 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018988615712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018988615712