Abstract
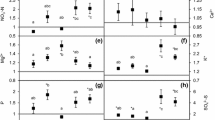
Although Artemisia ordosica Krasch. and Sabina vulgaris Ant. are the dominant shrub species in the Mu-us desert ecosystem, they differ in their botanical traits. We investigated the spatial patterns of soil properties using geostatistical analysis to examine the effect of plant species on these spatial patterns. Comparison among three microsite types (under A. ordosica, under S. vulgaris, and the opening between vegetation) showed that A. ordosica generally had less effect than S. vulgaris on local soil properties. The long life-span, prostrate life-form, and evergreen leaf-habit of S. vulgaris may lead to a higher accumulation of organic and fine materials under S. vulgaris. The range of spatial autocorrelation found in the mass of organic matter on the soil surface was smaller than that of the coverage of S. vulgaris (11.5 m) which corresponded to the canopy patch size of this species, and was longer than the canopy patch size of A. ordosica. The ranges of total C and N, and pH (11.7–15.6 m) were similar to that of S. vulgaris. The range of available P (106.3 m) was comparable to that of the coverage of A. ordosica (86.2 m) considered to be the scale of the distribution of this species. The ranges of silt+clay and exchangeable K, Ca, and Mg (31.0–46.7 m) were not related to plant presence, and were similar to that of topography (43.1 m).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R 1990 Nutrient use efficiency in evergreen and deciduous species from heathlands. Oecologia 84, 391–397.
Boettcher S E and Kalisz P J 1990 Single-tree influence on soil properties in the mountains of eastern Kentucky. Ecology 71, 1365–1372.
Burke I C 1989 Control of nitrogen mineralization in a sagebrush steppe landscape. Ecology 70, 1115–1126.
Burke I C, Reiners W A and Schimel D S 1989 Organic matter turnover in a sagebrush steppe landscape. Biogeochemistry 7, 11–31.
Charley J L and West N E 1975 Plant-induced soil chemical patterns in some shrub-dominated semi-desert ecosystems of Utah. J. Ecol. 63, 945–963.
Chen J and Stark J M 2000 Plant species effects and carbon and nitrogen cycling in a sagebrush-crested wheatgrass soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 47–57.
Commissione Redactorum Florae Intramongolicac 1985 Flora Intramongolica 1. Typis Intramongolicae Pupularis, Huhhot, China. 294 p.
Commissione Redactorum Florae Iintramongolicae 1993 Flora Intramongolica 4. Typis Intramongolicae Pupularis, Huhhot, China. 907 p.
Commissione Redactorum Florae Intramongolicae 1994 Flora Intramongolica 5. Typis Intramongolicae Pupularis, Huhhot, China. 634 p.
Coppinger K D, Reiners W A, Burke I C and Olson R K 1991 Net erosion on a sagebrush steppe landscape as determined by cesium-137 distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 55, 254–258.
Elkins N Z, Sabol G V, Ward T J and Whitford WG 1986 The influence of subterranean termites on the hydrological characteristics of a Chihuahuan desert ecosystem. Oecologia 68, 521–528.
Garner W and Steinberger Y 1989 A proposed mechanism for the formation of ‘fertile islands’ in the desert ecosystem. J. Arid Environ. 16, 257–262.
Gee G W and Bauder J W 1986 Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1. Ed. A Mute. pp 383–411. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI.
Goovaerts P 1998 Geostatistical tools for characterizing the spatial variability of microbiological and physico-chemical soil properties. Biol. Fertil. Soils 27, 315–334.
Hirose T and Tateno M 1984 Soil nitrogen patterns induced by colonization of Polygonum cuspidatum on Mt. Fuji. Oecologia 61, 218–223.
Hook P B, Burke I C and Lauenroth WK 1991 Heterogeneity of soil and plant N and C associated with individual plants and openings in North American shortgrass steppe. Plant Soil 138, 247–256.
Imhoff S, da Silva A P and Tormena C A 2000 Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties in areas under elephant-grass short-duration grazing system. Plant Soil 219, 161–168.
Isaaks E H and Srivastava R M 1989 Applied Geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York, USA. 561 p.
Jackson R B and Caldwell M M 1993 The scale of nutrient heterogeneity around individual plants and its quantification with geostatistics. Ecology 74, 612–614.
Jenny H 1980 The Soil Resource: Origin and Behavior. Springer, New York, USA. 377 p.
Kelly R H and Burke I C 1997 Heterogeneity of soil organic matter following death of individual plants in shortgrass steppe. Ecology 78, 1256–1261.
Kobayashi T 1990 Origin and land classification of the Mu us shadi desert in China. J. Jap. Soc. Reveget. Tech. 15, 43–57 (in Japanese).
Kobayashi T, Liao R and Li S 1995 Ecophysiological behavior of Artemisia ordosica on the process of sand dune fixation. Ecol. Res. 10, 339–349.
Matson P 1990 Plant-soil interactions in primary succession at Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Oecologia 85, 241–246.
Olsen S R and Sommers L E 1982 Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Eds. A L Page, R H Miller and D R Keeney. pp 403–430. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI.
Padien D J and Lajtha K 1992 Plant spatial pattern and nutrient distiibution in pinyon-juniper woodlands along an elevational gradient in northern New Mexico. Int. J. Plant Sci. 153, 425–433.
Rice W R 1989 Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 43, 223–225.
Robertson G P 1987 Geostatistics in ecology: interpolating with known variance. Ecology 68, 744–748.
Robertson G P 1998 GS+: Geostatistics for the Environmental Sciences. Gamma Design Software, Plainwell, MI, USA. 152 p.
Robertson G P, Huston M A, Evans F C and Tiedje J M 1988 Spatial variability in a successional plant community: patterns of nitrogen availability. Ecology 69, 1517-1524.
Rossi R E, Mulla D J, Journel A G and Franz E H 1992 Geostatistical tools for modeling and interpreting ecological spatial dependence. Ecol. Monogr. 62, 277–314.
Schimel D, Stillwell M A and Woodmansee R G 1985 Biogeochemistry of C, N, and P in a soil catena of the shortgrass steppe. Ecology 66, 276–282.
Schlesinger W H and Pilmanis A M 1998 Plant-soil interactions in deserts. Biogeochemistry 42, 169–187.
Schlesinger W H, Reynolds J F, Cunningham G L, Huenneke L F, Jarrell W M, Virginia R A and Whitford W G 1990 Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science 247, 1043–1048.
Schlesinger W H, Raikes J A, Hartley A E and Cross A F 1996 On the spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology 77, 364–374.
SPSS 1999 SPSS Base 10.0J for Windows. SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL. 484 p.
Vinton M A and Burke I C 1995 Interactions between individual plant species and soil nutrient status in shortgrass steppe. Ecology 76, 1116–1133.
Yamanaka N, Wang L and Yoshikawa K 1998 Seed production and seed bank of Sabina vulgaris Ant. in the Mu-us desert, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Jpn. Soc. Reveget. Tech. 23, 211–219 (in Japanese with English summary).
Yoshikawa K and Li S 1989 Stand structure of S. vulgaris in the Mu-us desert, China. In Proceedings of 1989 International Symposium for Japan and China Joint Research. pp 83–87. Inner Mongolian Research Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirobe, M., Ohte, N., Karasawa, N. et al. Plant species effect on the spatial patterns of soil properties in the Mu-us desert ecosystem, Inner Mongolia, China. Plant and Soil 234, 195–205 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017943030924
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017943030924