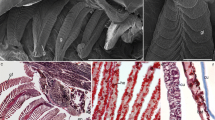
Abstract
In this paper we investigate by means of immunohistochemistry, the tissue distribution of constitutive cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A), from hatching until 30 days posthatching in developing Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri. For this purpose, a polyclonal (BN-1) antiserum developed against a conservative sequence of piscine CYP1A and a monoclonal (C10-7) antiserum directed against cod CYP1A were used on paraffin-embedded samples. From hatching onwards, distinct CYP1A immunoreactivity was distinctly observed in the following tissues and cells: envelope of oil droplets, matrix and syncytium of the yolk-sac, sinusoids, biliary epithelial cells and hepatocytes. In the digestive tract, buccopharyngeal, oesophageal, gastric and intestinal epithelia, as well as the cytoplasm and brush border of enterocytes were CYP1A-positive. Interestingly, gastric glands and melanin-plug present within lumen of the digestive system were strongly immunoreactive. Kidney (epithelia of renal tubules), gills (pillar and endothelial cells), skin (epithelial cells), muscle fibres of heart and eye (retina) were positive. In brain, we observed a strong CYP1A staining in the developing telencephalon and especially in olfactory system, as well as in those nerve fibres running ventrally toward the posterior brain. A strong CYP1A staining was observed in vascular endothelia of all organs/tissues, especially in the liver. In general, the intensity of CYP1A immunostaining increased during larval development, suggesting besides its known metabolic function (endogenous and/or exogenous), a possible participation of this heme-protein in control of cell division, regulation of growth and differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andersson T, Goksøyr A (1994) Distribution and induction of cytochrome P4501A1 in the rainbowtrout brain. Fish Physiol Biochem 13: 335–342.
Berndtson AK, Chen TT (1994) Two unique CYP1A genes are expressed in response to 3-methylcholanthrene treatment in rainbow trout. Arch Biochem Biophys 310: 187–195.
Binder RL, Lech JJ (1984) Xenobiotics in gametes of Lake Michigan lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) induce hepatic monooxygenase activity in their offspring. Fund Appl Toxicol 4: 1042–1054.
Binder RL, Stegeman JJ (1980) Induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activities in embryos of an estuarine fish. Biochem Pharmacol 29: 949–955.
Binder RL, Stegeman JJ (1983) Basal levels and induction of hepatic aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity during the embryonic period of development in brook trout. Biochem Pharmacol 32: 1324–1328.
Binder RL, Stegeman JJ (1984) Microsomal electron transport and xenobiotic monooxygenase activities during embryonic period of development in the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73: 432–443.
Binder RL, Stegeman JJ, Lech JJ (1985) Induction of cytochrome P-450-dependent monooxigenase systems in embryos and eleutheroembryos of the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Chem Biol Interactions 55: 185–202.
Buchmann A, Wannemacher R, Kulzer E, Buhler DR, Bock KW (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes LMC2 and LM4B (CYP1A1) in 2,3,7,8 Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxintreated zebrafish (Brachydanio ratio). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 123: 160–169.
Buddington RK, Christofferson JP (1985) Digestive and feeding characteristics of the chondrosteans. Environ Biol Fish 14: 31–41
Das M, Seth PIK, Mukhtar H (1981) NADPH-dependent inducible aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in rat brain mitochondria. Drug Metab Dispos 9: 69–70
Dettlaff TA, Ginsburg AS, Schmalhausen OI (1993) Sturgeon fishes. Developmental Biology and Aquaculture. Springer-Verlag. Berlin.
Dhawman A, Parmar D, Das M, Seth K (1990) Cytochrome P-450 dependent monooxygenase in neuronal and glial cells: Inducibility and specificity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 170: 441–447.
Elkus AA, Monosson E, McElroy AE, Stegeman JJ, Woltering DS (1999) Altered CYP1A expression in Fundulus heteroclitus adults and larvae: a sign of pollutant resistance? Aquatic Toxicology 45: 99–113.
Gawlicka A, Teh SJ, Hung SSO, Hinton DE, De La Noüe J (1995) Histological and histochemical changes in the digestive tract of white sturgeon larvae during ontogeny. Fish Physiol Biochem 14: 357–371.
Gisbert E (1999) Early development and allometric growth patterns in Siberian sturgeon and their ecological significance. J Fish Biol 54: 852–862.
Gisbert E, Sarasquete C (2000) Histochemical identification of the blackbrown pigment granules found in the alimentary canal of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri) during the lecitotrophic stage. Fish Physiol Biochem 22: 349–354.
Gisbert E, Rodriquez A, Williot P, Castello-Orvay F (1998) A histological study of the development of the digestive tract of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri) during early ontogeny. Aquaculture 167: 195–209.
Gisbert E, Sarasquete C, Williot P, Castello-Orvay F (1999) Histochemistry of the development of the digestive system of Siberian sturgeon during early ontogeny. J Fish Biol 55: 596–616.
Goksøyr A, Solberg TS (1987) Cytochromes P-450 in fish larvae: immunochemical detection of responses to oil pollution. Sarsia 72: 405–407
Goksøyr A, Husoy AM (1998) Immunochemical approaches to studies of CYP1A localization and induction by xenobiotics in fish. Fish Ecotoxicol Basel: Birkhauser: 165–202.
Goksøyr A, Solberg TS, Serigstad B (1991) Immunochemical detection of cytochrome P4501A1 induction in cod larvae and juveniles exposed to a water soluble fraction of North Sea crude oil. Mar Pollut Bull 22: 122–127.
Gooneratne R, Miranda CL, Henderson MC, Buhler DR (1997) β-naphtoflavone induced CYP1A1 and CYP1A3 proteins in the liver of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Xenobiotica 27: 175–187.
Guiney PD, Smolowitz RM, Peterson RE, Stegeman JJ (1997) Correlation of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induction of Cytochrome P4501A in vascular endothelium with toxicity in early life stages of Lake trout. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 143: 256–273
Heilmann LJ, Sheen YY, Bigelow SW, Nebert DW (1988) Trout P4501A1: cDNA and deduced protein sequence, expression in liver and evolutionary significance. DNA 7: 379–387.
Henry TR, Spitsbergen JM, Hornung MW, Abnet CC, Peterson RE (1997) Early life stage toxicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 142: 56–68.
Husoy AM, Myers MS, Willis ML, Collier TK, Celander M, Goksøyr A (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of CYP1A and CYP3A-like isozymes in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.), a marine fish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 129: 294–308.
Iscan M, Reuhl K, Weiss B Maines MD (1990) Regional and subcellular distribution of cytochrome P-450 dependent drug metabolism in monkey brain. The olfactory bulb and the mitochondrial fraction have high levels of activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 169: 858–863.
Jacsik Z, Bihari N, Müller WEG, Zahn RK, Batel R (1998) Modulation of cytochrome P450 1A in sea bass liver by model substances and seawater extracts. Aquat Toxicol 40: 265–273.
Miller MR, Hinton DE, Blair JJ, Stegeman JJ (1988) Immunohistochemical localization of cytochrome P-450E in liver, gill and heart of scup (Stenotomus chrysops) and rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Mar Environ Res 24: 37–39.
Monod G, Boudry MA, Gillet C (1996) Biotransformation enzymes and their induction by β-naphthoflavone during embryo-larval development in salmonid species. Comp Biochem Physiol 114C: 45–50.
Nebert DW, Gonzalez FJ (1987) P450 genes. Structure, evolution and regulation. Ann Rev Biochem 56: 945–993.
Nebert DW, Nelson DR, Coon MJ, Estabrook RW, Feyereisen R, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Gonzalez F, Guengerich FP, Gunsalus IC, Jonson EF, Loper JC, Sato R, Watermanm MR, Waxman DJ (1991) The 450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene, mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol 10: 1–14.
Nelson DR, Koymans L, Kamataki T, Stegeman JJ, Feyereisen R, Waxman DJ, Waterman MR, Gotoh O, Coon MR, Estrabrook RW, Gunsalus IC, Nebert DW (1996) P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers and nomenclature. Pharmacog 6: 1–42.
Peters LD, Livingstone DR (1995) Studies of cytochrome P4501A in early life stages of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Mar Env Res 39: 5–9.
Peters LD, Porte C, Albaigés J, Livingstone DR(1994) 7-Ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) and antioxidant enzyme activities in larvae of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) from the north coast of Spain. Mar Pollut Bull 28: 299–304.
Peters LD, O'Hara SCM, Livingstone DR (1996) Benzo(a)pyrene metabolism and xenobiotic-stimulated reactive oxygen species generation by subcellular fraction of larvae of turbot, Scophthalmus maximum. L. Comp Biochem Physiol 114C: 221–227.
Reinecke M, Segner H (1998) Immunohistochemical localization of cytochrome P4501A in developing turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Mar Environ Res 46: 487–492.
Riebeiro L, Sarasquete C, Dinis MT (1999) Histological and histochemical characteristics during development of the Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis. Aquaculture 171: 291–306.
Sarasquete C, Segner H (2000) Cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in teleostean fishes. A review of immunohistochemical studies. Sci Tot Environ 247: 313–332.
Sarasquete C, Polo A, Yùfera M(1995) Histology and histochemistry of the development of the digestive system of larval gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata L. Aquaculture 130: 79–92.
Sarasquete C, Muñoz Cueto JA, Ortiz JB, Rodríguez-Gomez FJ, Dinis MT, Segner H (1999) Immunocytochemical distribution of cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in developing gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata. Histol Histopathol 14: 407–415.
Segner H, Storch V, Reinecke M, Kloas W (1994) The development of functional digestive and metabolic organs in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Mar Biol 119: 471–486.
Segner H, González de Canales ML, Sarasquete C (1998) Avances en Ecotoxicología Marina. Los citocromos P450 (CYP1A) como biomarcadores de la contaminación por compuestos xenobióticos y ensayos de citotoxicidad con líneas celulares de peces. In: Muñoz-Cueto JA, Miguel Mancera J, Piñuela C, Sarasquete C, eds. Estado Actual y Perspectivas en Acuicultura. Histofisiologίa, Histopatologίa y Biotoxicologίa. Servicio de Publicaciones. Universidad de Cádiz, pp. 71–94.
Smolowitz RM, Hahn ME, Stegeman JJ (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of cytochrome P450IA1 induced by 3,34′,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl and by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in liver and extrahepatic tissues of the teleost Stenotomus chrysops (scup). Drug Metab Dispos 19: 113–123
Spitsbergen J, Walker KM, Olson JR, Peterson RE (1991) Pathologic lesions in early life stages of lake trout, Salvelinus namaycush, exposed to 2,3,7,8, tertachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin as fertilized eggs. Aquat Toxicol 19: 42–73.
Stahl RG, Kocan RM (1986) Influence of age on patterns of uptake and excretion of policyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rainbow trout embryo. In: Poston TM, Pudrí R, eds. Aquatic Toxicology and Environmental Fate, 9. ASTM STP 921, American Society for Testing and Materials, pp. 287–303. Philadelphia, PA.
Stegeman JJ, Hahn ME (1994) Biochemistry and molecular biology of monooxygenases: current perspectives on forms, functions, and regulation of cytochrome P450 in aquatic species. In: Malins DC, Ostrander GK, eds. Boca Raton: Aquatic Publishers, pp. 87–203.
Stegeman JJ, Smolowitz RM, Hahn ME (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of environmentally induced cytochrome P4501A1 in multiple organs of the marine teleost Stenotomus chrysops (scup). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 110: 486–504
Van Veld PA, Vetter RD, Lee RF, Patton JS (1987) Dietary fat inhibits the intestinal metabolism of the carcinogen benzo[a]pyrene in fish. J Lipid Res 28: 810–817.
Van Veld PA, Vogelbein WK, Cochran MK, Goksøyr A, Stegeman JJ (1997) Route-specific cellular expression of cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in fish (Fundulus heteroclirus) following exposure to aqueous and dietary benzo[a]pyrene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 142: 348–359.
Vieira L (2000) Histologia e histoquímica do tubo digestivo e organos anexos de pos-larvas e juvenis do Solea senegalensis (Kaup 1858) alimentados com diferentes dietas. Relatorio de estagio do curso de Licenciatura em Biolog´?a Marinha e Pescas. Univ do Algarbe Faro Portugal, 97 pp.
Vigano L, Arillo A, Bagnasco M, Bennicelli C, Melodia F (1993) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in uninduced and induced rainbow trout: effects of diets and food deprivation. Comp Biochem Physiol 104C: 51–55.
Vigano L, Arillo A, De Flora S, Lazorchak J (1995) Evaluation of microsomal and cytosolic biomarkers in a seven-day larval trout sediment toxicity test. Aquat Toxicol 31: 189–202.
Walker MK, Cook PM, Batterman AR, Butterworth BC, Berini C, Libal JJ, Hulnagle LC, Peterson RE (1994) Translocation of 2,3,7,8,-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin from adult female lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) to oocytes: effects on early life stage development and sac fry survival. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51: 1410–1419
Walther B, Guersi-Egea JF, Minn A, Siest G (1986) Subcellular distribution of cytochrome P450 in the brain. Brain Res 375: 338–344.
Walther B, Guersi-Egea JF, Jayosi Z, Minn A, Siest G (1987) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity in rat brain subcellular fraction. Neurosci Lett 76: 58–62.
Williot P, Brun R, Rouault T, Rooryck O (1991) Management of female spawners of Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri Brandt: first results. In: Williot P, ed. Acipenser. Actes du Colloque Bordeaux: Cemagref, pp. 365–379.
Wisk JD, Cooper KR (1992) Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzop-dioxin and benzo(a)pyrene hydroxylase activity in embryos of the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Arch Toxicol 66: 245–249
Zabel EW, Cook PR, Peterson RE (1995) Toxic equivalency factors of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran and biphenyl congeners based on early life stage mortality in rainbow trout, Oncorynchus mykiss. Aquat Toxicol 31: 315–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarasquete, C., Ortiz, J.B. & Gisbert, E. Immunohistochemical Distribution of Cytochrome P4501A in Larvae and Fingerlings of the Siberian Sturgeon, Acipenser baeri. Histochem J 33, 101–110 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017900314779
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017900314779