Abstract
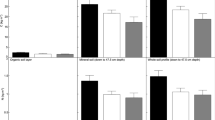
Stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies K.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) were investigated at the Höglwald research area, Southern Germany from 1985–1988 and from 1994–1997 in order to determine the effects of tree species on deposition and soil solution fluxes. The results were compared to 15 European case studies representing different deposition levels and site conditions. At the Höglwald site, which is characterised by a high nitrogen and a moderate sulphur load, throughfall deposition of nitrogen and sulphur compounds was about two-fold higher in spruce stands compared to beech stands. The differences in elemental input were clearly reflected in soil solution chemistry with a higher leaching of nitrate and sulphate in the spruce stands. The turnover of sulphur and nitrogen compounds induced a strong soil internal production of protons especially in the spruce stands. These results are in accordance with the other European case studies. Throughfall deposition and soil leaching of nitrogen and sulphur compounds was generally higher for spruce stands compared to beech stands. The species-related differences were mainly caused by dry deposition and were relatively small in remote areas. The consequences for the forest ecosystem itself and for the hydrosphere are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agren G I and Bosatta E 1988 Nitrogen saturation of terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 54, 185–197.
Agster G 1986 Ein-und Austrag sowie Umsatz gelöster Stoffe in den Einzugsgebieten des Schönbuchs. In Das Landschaftsökologische Projekt Schönbuch. Ed. G. Einele. pp 343–356. Verlag VCH, Weinheim.
Anderson A 1990 Untersuchungen über Ausmass und räumliche Variabilität des Bestandes niederschlages im forschungsprojekt Höglwald. Diplomarbeit Forstwissenschaftliche Fakultät München.
Assman E 1961 Waldertragskunde. BLV Verlag, München, Wien.
Berqkvist B and Folkeson L 1995 The influence of tree species an acid deposition, proton budgets and elemental fluxes in south Swedish forest ecosystems. Ecol Bull. 44, 90–99.
Bille-Hansen J and Hansen K (Eds.) 1999 “The Element Cycling Project”, 1985-1996. Studies of nutrient cycling in 3 conifer species and two deciduous on 3 forest districts. Ulborg, Lindet and Frederiksborg: The Research Series 1999. (In Danish with English abstract).
Binkley D and Giardina C 1998 Why trees affect soils in temperate and tropical forests: the warp and woof of tree/soil interactions. Biogeochemistry 42, 89–106.
Binkley D, Högberg P 1997 Does atmospheric deposition threaten Swedish forests? For. Ecol. Manage. 92, 119–152.
Bredemeier M, Matzner E and Ulrich B 1990 Internal and external proton loads to forest soils in Northern Germany. J. Environ. Qual. 19, 469–477.
Cronan C, Grigal DF 1995 Use of calcium/aluminium ratios as indicators of stress in forest ecosystems. J. Environ. Qual. 24, 209–226.
Ellenberg H 1996 Vegetation Mitteleuropas und der Alpen. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart. 5. Auflage.
Erkenberg A 1991 Schwefelausstattung europaïscher Waldböden unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Adsorptionskapazität für Sulfat. Dissertation Forstwissenschaftl., Fakultät Univ. München.
Fenn M E, Poth M A, Aber J D, Baron J S, Bormann B T, Johnson D W, Lemley D A, McNulty S G, Ryan D and Stottlemeyer R 1998. Nitrogen excess in North American ecosystems: Predisposing factors, ecosystem responses, and management strategies. Ecol. Appl. 8(3), 706–733.
Gasche R 1998 Ganzjährige Messungen zur Quantifizierung der NO/NO2-Flüsse in einem Stickstoff-übersättigtem Ökosystem (Höglwald) und die Identifizierung der an der N-Oxid-Emission beteiligten mikrobiellen Prozesse. Schriftenreihe des Fraunhofer-Instiutes für atmospärische Umweltforschung 51, Maraun-Verlag, Frankfurt/Main.
Gasche R and Papen H4999 A 3-year continuous record of nitrogen trace gas fluxes from untreated and limed soil of a N-saturated spruce and beech forest ecosystem in Germany. 2. NO and NO2 fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. 104(D15), 18505-18520.
Gundersen P, Emmett B A, Kjonaas O J, Koopmans C J and Tietmema A 1998 Impact of nitrogen deposition on nitrogen cycling in forests: a synthesis of NITREX data. For. J. Ecol. Manage. 101, 37–56.
Harrison R B, Johnson D W and Todd D E 1989 Sulfate adsorption and desorption reversibility in a variety of forest soils. J. Environ. Qual. 18, 419–426.
Hedin L O„ Armesto J J and Johnson A H 1995 Patterns of nutrient loss from unpolluted, old-growth temperate forests: Evaluation of the biogeochemical theory. Ecology 76(2), 493–509.
Heil K 1996 Wasserhaushalt und Stoffumsatz in fichten-(Picea abies (L) Karst) und Buchenökosystemen (Fagus sylvatica L.) der höheren Lagen des Bayer. Waldes. PhD thesis, Univ. München.
Hofmann C, Forster H and Rehfuess K-E 1994 Bodenkundliche und hydrologische Untersuchungen in den Hochlagen des Bayerisehen Waldes-Ein Beitrag zur Aufklärung der montanen Vergilbung von Fichtenbeständen. Forstliche Forschungsberichte München. p. 139.
Hösl G 1986 Stoffeintrag und Sickerwasserqualität in Fichten-und Buchenbeständen. Diplomarbeit Forstwissenschaffliche Fakultät, Univ. München.
Huber C 1998 Untersuchungen zur Ammoniakimmission und zum Stoffhaushalt auf ungekalkten und neugekalkten Fláchen in einem stickstoffüberstättigten Fichtenökosystem (Höglwald). PhD thesis, Univ. München.
Ibrom A 1993 Die Deposition und die Pflanzenauswaschung (Leaching) von Pflanzennährstoffen in einem Fichtenbestand im Solling. Berichte d. Forschungszentrums Waldökosystem, Reihe A, Bd. 105.
Kreutzer K 1981 Die Stoffbefrachtung des Sickerwassers in Waldbeständen. Mitteilgn. Deutsch. Bodenkundl. Gesellsch. 32 273–286.
Kreutzer K 1986 Untersuchungen über den Einflußvon Standort und Bestockung auf den Nitrataustrag ausWaldböden. Berichte. XIII Congress Int. Bodenkundl. Gesellsch., Band II, pp 63–64.
Kreutzer K 1992 The impact of forest management practices on the soil acidification in established forests. Air Pollution Report 13 of the European Community EG, Brussels. pp 75-90.
Kreutzer K 1993 Changes in the role of nitrogen in Central European forests. In pp 82–96. Forest Decline in the Atlantic and Pacific region. Eds. R F Huettl and D Mueller-Dombois. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg.
Kreutzer K 1994a Folgerungen aus der Höglwaldforschung. AFZ 14, 769–774.
Kreutzer K 1994b The influence of catchment processes in forests on the recovery in fresh waters. In Acidification of Freshwater Ecosystems: Implications for the Future. Eds. C E W Steinberg and R F Wright. pp 325-344. John Wileys & Sons Ltd.
Kreutzer K & Bittersohl J 1986 Stoffauswaschung aus Fichtenkronen (Picea abies (L) Karst.) durch saure Beregnung. Forstw. Centralbl. 105, 357–363.
Kreuzer K, Deschu E and Hösl G 1986 Vergleichende Untersuchungen über den Einflußvon Fichte (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) und Buche (Fagus sylvatica L.) auf die Sickerwasserqualität. Fowissenschaftliches Centralblatt 105, 364–371.
Kreutzer K and Weis T 1998 The Höglwald field experiments-aims, concept and basic data. Plant Soil 199(1), 1–10.
Lochmann V and Mares V 1995 Air pollutant fallout in forest ecosystems of the Orlicke Mountains and its effect on chemical composition of precipitation, soil, and stream water and on soil development. Communicationes Instituti Forestalis Behemicae 18, Forestry and Game Management Research Institute Jiloviste-Staradny, CR.
Lovett GM 1992 Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of nitrogen. In Atmospheric Deposition and Forest Nutrient Cycling. Eds. D W Johnson and S E Lindberg. pp 152–165. Ecological Studies 91, Springer Verlag, New York.
Lovett G M and Lindberg S E 1993 Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of nitrogen in forests. Can. J. For Res. 23, 1603–1616.
Manderscheid B and Matzner E 1995 Spatial and temporal variation of soil solution chemistry a ion fluxes through the soil in a mature Norway spruce stand. Biogeochemistry 30, 99–114.
Matzner E 1988 Der Stoffumsatz zweier Waldökosysteme im Solling. Ber. des Forschungszentrums Waldökosyst. d. Univ. Göttingen, Reihe A, Bd. 41.
Matzner E and Meiwes K J 1994 Long-term development of element fluxes with bulk precipitation and throughfall in two German forests. Environ. Qual. 23, 162–166.
Miles J 1985 The pedogentic effects of different species and vegetation types and the implications of successions. J. Soil Sci. 36, 571–584.
Mischerlich G 1981 Wald, Wachstum, Umwelt, Band I. Sauerländer's Verlag, Frankfurt. 144 p.
Nadelhoffer K J, Aber J D and Melillo J M 1983 Leaf-Litter production and soil organic matter dynamics along a nitrogenavailability gradient in southern Wisconsin (USA). Can. J. For. Res. 13, 12–21.
Nihlgard B 1970 Precipitation, its chemical composition and effect on soil water in a beech and a spruce forest in South Sweden. Oikos 21, 208–217.
Nihlgard B 1985 The ammonium hypothesis-an additional explanation to the forest dieback in Europe. Ambio 14, 2–8.
Papen H and Butterbach-Bahl K 1999 A 3-year continuous record of nitrogen trace gas fluxes from untreated and limed soil of a N-saturated spruce and beech forest ecosystem in Germany. 1. N2O emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 104(D15), 18487–18503.
Prietzel J and Kölling C 1999 Ein einfaches Routineverfahren zur Beurteilung der Remobilisierungspotentials in Waldböden für Sulphat-Schwefel aus atmosphärischen Eintragen. Forstwissenschaftliches Centralblatt 118, im Druck.
Ragsdale H C, Lindberg S E, Lovett G M and Schaefer D A 1992 Atmospheric deposition and through fall fluxes of base cations. In Atmospheric Deposition and Forest Nutrient Cycling. Eds. D W Johnson and S E Lindberg. Ecol. Studies 91, 193-243.
Ranger J and Nys C 1994 The effect of spruce (Picea abies Karst) on soil development: an analytical and experimental approach. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 45, 193–204.
Rehfuess K-E 1990 Waldböden. Entwicklung. Eigenshaften und Nutzung. Verlag Paul Parey, Hamburg und Berlin.
Rennenberg H, Kreutzer K, Papen H and Weber P 1998 Consequences of high nitrogen loads of nitrogen for spruce (Picea abies L.) and beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests. New Phytol. 139, 71–86.
Rosenberg, W 1999 Auswirkungen einer Dolomit-Kalkung auf den Humus eines Fichtenwaldes (Höglwald-Projekt). Dissertation, Forest Faculty, University of Munich.)
Rothe A 1997 Influence of tree species composition on rooting patterns, hydrology, elemental turnover and growth in a mixed spruce-beech stand in Southern Germany (Höglwald). PhD thesis, University of Munich, Forstliche Forschungsberichte München. Bd 163. (In German with English summary).
Rothe A, Brand S and Hurler R 1999 Waldbewirtschaftung und Nitratbelastung des Grundwassers am Beispiel des Eurasburger Forstes. AFZ 10, 531–533.
Schierl R 1989 Bestimmmung des Komplexierungsgrades von Al, Fe und Mn in Bodenlösungen durch Kationenaustausch. Vom Wasser 73, 161–165.
Schütt P, Schick H-J and Stimm B 1991 Lexikon der Forstbotanik. Ecomed, Landsberg, Germany. 881 pp.
Simonicic P 1996 The response of the forest ecosystem to the influence of acid depositions, with emphasis on the study of nutrition conditions for spruce (Picea abies (L) Karst.) and beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) in the area affected by the Sostanj thermal power plant. PhD thesis, Ljubljana, Biotechnical Faculty, Forestry Department. p. 155. (In Slovene with English summary).
Spieker H, Mielikainen K, Köhl M and Skovsgaard J P (Eds.) 1996 Growth trends in European forests. European Forest Institute Research Report No. 5. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Stone E 1975 Effects of species on nutrient cycles and soil change. Phil. Trans. R. Soc., London (B) 271, 149–162
Svedrup H and Warfinge P 1995 Critical loads of acidity for Swedish forest ecosystems. Ecol. Bull. 44, 75–89.
Ten-Harkel M J 1997 The effects of particle-size distribution and chloride depletion of sea-salt aerosols on estimating atmospheric deposition at a coastal site. Atmos. Environ. 31(3), 417–427.
Ulrich B 1983 Interaction of forest canopies with atmospheric constituents: alkali and earth alkali cations and chloride. In Effects of Accumulation of Air pollutants in Frest Ecosystems. D. Reidel Publishing.
Weis W, Kitzbichler J, Kreuzter K and Rothe A 2001 Water balance in spruce and beech stands-Modelling and results. Plant Soil, submitted.
Wiedemann E 1942 Der gleichaltrige Buchen-Fichten-Mischbestand. Mitt. Forstwirt. Forstwiss. 13, 1–81.
Wilpert v K, Kohler M and Zirlewagen D (1996) Die Differenzierung des Stofthaushalts von Waldoekosystemen durch die waldbauliche Behandlung auf einem Gneisstandort des Mittleren Schwarzwaldes. Mitt. FVA Baden-Wuerttemberg 197, 94 S.
Wittich W 1933 Untersuchungen in Nordwestdeutschland über den Einflußder Holzart auf den biologischen Zustand des Bodens. Mitt. aus der Forstwissenschaft. 4, 115–158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothe, A., Huber, C., Kreutzer, K. et al. Deposition and soil leaching in stands of Norway spruce and European Beech: Results from the Höglwald research in comparison with other European case studies. Plant and Soil 240, 33–45 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015846906956
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015846906956