Abstract
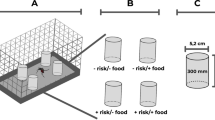
Dietary leaf litter chemistry is known to play an important ecotoxicological role in the plant–mosquito interaction in subalpine flooded areas surrounded by vegetation because of differential larvicidal effects of insoluble polyphenols formed during the leaf decaying process. This dietary interaction was investigated through comparative evaluation of the role of toxic/nontoxic leaf litter in both larval foraging and feeding behavior, by using different samples of decomposed alder leaf litter and larval Aedes aegypti as experimental references. Track analysis showed significant differences in larval foraging behavior in the absence or presence of leaf litter. Comparative alimentary preference investigations and further track analysis suggested that larvae are unable to detect leaf litter toxicity. These characteristics of the larval behavioral feeding pattern suggested that: (1) decomposed leaf litter may be involved as an important attractive food source in the habitat selection and evolutionary history of culicids, and (2) preingestive behavioral mechanisms appear to be minimally involved in the differential larval dietary adaptation to toxic leaf litter. These results may have interesting consequences for culicid biological control.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Appel, H. M. 1993.Phenolic compounds in ecological interactions: The importance of oxidation. J. Chem. Ecol.19:1521–1552.
Barbehenn, R. V. and Martin, M. M. 1994.Tannin sensitivity in larvae of Malacosoma disstria (Lepidoptera): Roles of the peritrophic envelope and midgut oxidation.J. Chem. Ecol. 20:1985–2001.
Berenbaum, M. R., Favret, C., and Schuler, M. 1996.On defining “key innovations” in an adaptive radiation: Cytochrome P 450 and Papilionidae.Am. Nat.148:S139–S155.
Bernays, E. A. and Chapman, R. F.1994.Host Plant Selection by Phytophagous Insects.Chapman and Hall, New York.
Bernays, E. A., Gonzalez, N., Angel, J., and Bright, K. L.1995.Food mixing by generalist grasshoppers: Plant secondary compounds structure the pattern of feeding.J. Insect Behav.8:161–180.
Bernays, E. A., Oppenheim, S., Chapman, R. F., Know, H., and Gould, F. 2000.Taste sensitivity of insect herbivores to deterrents is greater in specialists than in generalist: A behavioral test of the hypothesis with two closely related caterpillars.J. Chem. Ecol.26:547–563.
Brattsten, L. B.1992.Metabolic defense against plant allelochemicals, pp.145–242, inG. A. Rosenthal and M. R. Berenbaum (eds.). Herbivores: Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites. Academic Press, New York.
Chaton, P. F., Ravanel, P., Meyran, J. C., and Tissut, M.2001.The toxicological effects and bioaccumulation of fipronil in larvae of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti, in aqueous medium.Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 69:183–188.
Clements, A. N.1999. The Biology of Mosquitoes, Vol. 2. Chapman and Hall, London.
Cummins, K. W. and Klug, M. J. 1979. Feeding ecology of stream invertebrates.Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 10:147–172.
David, J. P., Rey, D., Pautou, M. P., and Meyran, J. C. 2000a.Differential toxicity of leaf litter to dipteran larvae of mosquito developmental sites.J. Invertebr. Pathol. 75:9–18.
David, J. P., Rey, D., Marigo, G., and Meyran, J. C.2000b. Larvicidal effect of a cell-wall fraction isolated from alder decaying leaves.J. Chem. Ecol.25:537–547.
David, J. P., Rey, D., Cuany, A., Amichot, M., and Meyran, J. C. 2000c.Comparative ability to detoxify alder leaf litter in field larval mosquito collections.Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 44:143–150.
David, J. P., Rey, D., Meyran, J. C., and Marigo, G.2001.Involvement of lignin like compounds in the toxicity of alder leaf litter against mosquito larvae.J. Chem. Ecol.27:161–174.
David, J. P., Rey, D., Cuany, A., Bride, J. M., and Meyran, J. C.2002. Toxicity of decomposed alder leaf litter in subalpine mosquito breeding sites.Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 21:62–66.
Eisenberg, J. N. S., Washburn, J. O., and Schreiber, S. J.2000.Generalist feeding behaviors of Aedes sierrensis larvae and their effects on protozoan populations.Ecology 81:921–935.
Gessner, M. O.1991.Differences in processsing dynamics of fresh and dried leaf litter in a stream ecosystem.Freshwater Biol.26:387–398.
Glendinning, J. I. and Slansky, F. 1995.Consumption of a toxic food by caterpillars increases with dietary exposure: Support for a role of induced detoxification enzymes.J. Comp. Physiol. A 176:337–345.
LÉONARD, P. M. and JULIANO, S. A. 1995.Effect of leaf litter and density on fitness and population performance of the hole mosquito Aedes triseriatus.Ecol. Entomol.20:125–136.
Merritt, R.W., Craig, D. A., Walker, E. D., Vanderploeg, H. A., and Wotton, R. S.1992a. Interfacial feeding behavior and particle flow patterns of Anopheles quadrimaculatus larvae (Diptera: Culicidae).J. Insect Behav.5:741–761.
Merritt, R.W., Dadd, R. H., and Walker, E.D.1992b. Feeding behavior, natural food, and nutritional relationships of larval mosquitoes.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 37:349–376.
Meyran, J. C., David, J. P., Rey, D., Cuany, A., Bride, J. M., and Amichot, M.2002. The biochemical basis of dietary polyphenols detoxification by subalpine aquatic detritivorous Arthropoda. Recent Res. Dev. Anal. Biochem. In press.
Olsson, B. and Klowden, M. J. 1998.Larval diet affect the alarm response of Aedes aegypti (L.) mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae).J. Insect Behav.11:593–596.
Pautou, G. and Girel, J. 2001.The floodplain forest of the French Upper Rhône river valley, pp. 147–167, in E. Klimo and H. Hager (eds.), The Floodplain Forests in Europe: Current Situation and Perspectives. Brill Academic Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands.
Rashed, S. S. and Mulla, M. S. 1989.Factors influencing ingestion of particulate materials by mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae).J. Med. Entomol.26:210–216. LEAF-LITTER FEEDING PATTERN IN MOSQUITO LARVAE 995
Rey, D., Long, A., Pautou, M. P., and Meyran, J. C.1998.Comparative histopathology of Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis on some dipteran larvae and Crustacea of aquatic hydrosystems. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 8:255–263.
Rey, D., Pautou, M. P., and Meyran, J. C. 1999a. Histopathological effects of tannins on the midgut epithelium of aquatic Diptera larvae.J. Invertebr. Pathol.73:173–181.
Rey, D., Cuany A., Pautou, M. P., and Meyran, J. C.1999b. Differential sensitivity of mosquito taxa against vegetable tannins.J. Chem. Ecol.25:537–548.
Rey, D., David, J. P., Martins, D., Pautou, M. P., Long, A., Marigo, G., and Meyran, J. C. 2000.Role of vegetable tannins in habitat selection among mosquito communities from the Alpine hydrosystems.C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Sci. Vie323:1–8.
Rey, D., DesprÉs, L., Schaffner, F., and Meyran, J. C.2001a. Mapping of resistance to vegetable polyphenols among Aedes taxa (Diptera, Culicidae) on a molecular phylogeny.Mol. Phyl. Evol. 19:317–325.
Rey, D., David, J. P., Besnard G., Jullien J. L., and Meyran, J. C.2001b. Comparative sensitivity of larval mosquitoes to vegetable phenolics versus conventional insecticides.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 98:361–367.
Steinly, B. A. and Berenbaum, M. R.1985.Histopathological effects of tannins on the midgut epithelium of Papilio polyxenes and Papilio glaucus. Entomol. Exp. Appl.39:3–9.
Widahl, L. E. 1992.Flow pattern around suspension-feeding mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culidae).Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 85:91–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, JP., Ferran, A., Gambier, J. et al. Taste Sensitivity of Detritivorous Mosquito Larvae to Decomposed Leaf Litter. J Chem Ecol 28, 983–995 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015257700992
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015257700992