Abstract
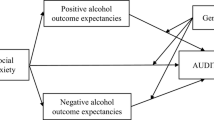
Previous research has found a positive relationship between social anxiety disorder and alcoholism, and that certain alcohol outcome expectancies are related to drinking behaviors. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among drinking behaviors and alcohol expectancies in treatment-seeking individuals diagnosed with social anxiety disorder or dysthymia, as well as normal controls. No significant differences were found across the 3 groups in alcohol consumption. As expected, socially anxious participants had higher social assertiveness expectancies than both participants with dysthymia and normal controls. Participants with social anxiety disorder had greater tension reduction and global positive change expectancies than the normal controls, but did not differ from participants with dysthymia. Additionally, the increased social assertiveness, tension reduction, and positive change expectancies were found to predict amount of drinking per month for socially anxious participants. Implications for understanding the relationship between social anxiety disorder and alcoholism are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (1985). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed., revised). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Amies, P. L., Gelder, M. G., & Shaw, P. M. (1983). Social phobia: A comparative clinical study. British Journal of Psychiatry, 142, 174–179.
Beck, A. T., Ward, C. H., Mendelson, M., Mock, J., & Erbaugh, J. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 4, 561–571.
Brown, S. A., Goldman, M. S., Inn, A., & Anderson, L. R. (1980). Expectations of reinforcement by alcohol: Their domain and relation to drinking patterns. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48, 419–426.
Brown, S. A., & Munson. (1987). Extroversion, anxiety, and the perceived effects of alcohol. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 48, 272–276.
Bruch, M. A., Heimberg, R. G., Harvey, C. H., McCann, M., Mahone, M., & Slavkin, S. (1992). Shyness, alcohol expectancies, and alcohol use: Discovery of a suppressor effect. Journal of Research in Personality, 23, 137–149.
Burke, R. S., & Stephens, R. S. (1997). The effect of anxious affect on drinking self-efficacy in college students. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 11, 65–75.
Burke, R. S., & Stephens, R. S. (1999). Social anxiety and drinking in college students: A social cognitive theory analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 19(5), 513–530.
Chambless, D. L., Cherney, J., Caputo, G. C., & Rheinstein, B. J. G. (1987). Anxiety disorders and alcoholism: A study with inpatient alcoholics. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 1, 29–40.
Darkes, J., & Goldman, M. S. (1993). Expectancy challenge and drinking reduction: Experimental evidence for a mediational process. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61(2), 344–353.
Davidson, J. R. T., Hughes, D. L., George, L. K., & Blazer, D. G. (1993). The epidemiology of social phobia: Findings from the Duke Epidemiological Catchment Area Study. Psychological Medicine, 23, 709–718.
DiNardo, P. A., & Barlow, D. H. (1988). Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule—Revised (ADIS-R). Albany, NY: Center for Stress and Anxiety Disorders, University at Albany, State University of New York.
Fromme, K., Stroot, E., & Kaplan, D. (1993). Comprehensive effects of alcohol: Development and psychometric assessment of a new expectancy questionnaire. Psychological Assessment, 5(1), 19–26.
Hittner, J. B. (1995). Factorial validity and equivalency of the alcohol expectancy questionnaire tensionreduction subscale across gender and drinking frequency. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51(4), 563–577.
Holle, C., Heimberg, R. G., Sweet, R. A., & Holt, C. S. (1995). Alcohol and caffeine use by social phobics: An initial inquiry into drinking patterns and behavior. Behavior Research and Therapy, 33(5), 561–566.
Johnson, P. B., & Gurin, G. (1994). Negative affect, alcohol expectancies and alcohol-related problems. Addiction, 89, 581–586.
Jones-Madsen, L., Silvia-Young, L., & Richman, C. K. (1995). Increased awareness and self-challenge of alcohol expectancies. Substance Abuse, 16(2), 77–85.
Kessler, R. C., McGonagle, K. A., Zhao, S., Nelson, C. B., Hughes, M., Eshleman, S., et al. (1994). Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R Psychiatric disorders in the United States. Archives of General Psychiatry, 51, 8–19.
Kushner, M. G., Abrams, K., & Borchardt, C. (2000). The relationship between anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorders: A review of major perspectives and findings. Clinical Psychology Review, 20(2), 149–171.
Kushner, M. G., Sher, K. J., & Beitman, B. D. (1990). The relation between alcohol problems and the anxiety disorders. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 147(6), 685–695.
Leigh, B. C. (1989). In search of the seven dwarves: Issues of measurement and meaning in alcohol expectancy research. Psychological Bulletin, 105(3), 361–373.
Leary, M. R. (1983). A brief version of the Fear of Negative Evaluation Scale. Personality and Social Psychological Bulletin, 9, 371–375.
Liebowitz, M. R., Gorman, J. M., Fyer, A. J., & Klein, D. F. (1985). Social phobia: Review of a neglected anxiety disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 42, 729–736.
Lydiard, R. B., Brady, K., Ballenger, J. C., Howell, E. F., & Malcolm, R. (1992). Anxiety and mood disorders in hospitalized alcoholic individuals. The American Journal on Addictions, 1(4), 325–331.
Mullaney, J. A., & Trippett, C. J. (1979). Alcohol dependence and phobias: Clinical description and relevance. British Journal of Psychiatry, 135, 563–573.
O'Hare, T. M. (1990). Alcohol expectancies and social anxiety in male and female undergraduates. Addictive Behaviors, 15, 561–566.
Regier, D. A., Farmer, M. E., Rae, D. S., Locke, B. Z., Keith, S. J., Judd, L. L., et al. (1990). Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse. Journal of the American Medical Association, 264(19), 2511–2518.
Sanderson, W. C., DiNardo, P. A., Rapee, R. M., & Barlow, D. H. (1990). Syndrome comorbidity in patients with a DSM-III-R anxiety disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99(3), 308–312.
Smith, G. T., Goldman, M. S., Greenbaum, P. E., & Christiansen, B. D. (1995). Expectancy for social facilitation from drinking: The divergent paths of high expectancy and low expectancy adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 32–40.
Sobell & Sobell (1992). Timeline follow-back: A technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In R. Litten & J. Allen (Eds.)., Measuring alcohol consumption (pp. 41–72). Humana: New Jersey.
Spitzer,R. L., Williams, J.B., Gibbon, M., & First, M.B. (1989). Structured clinical interview for DSM-III-R (9/1/89 revision). New York Biometrics Institute. Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Tran, G. Q., Haaga, D. A. F., & Chambless, D. L. (1997). Expecting that alcohol use will reduce social anxiety moderates the relation between social anxiety and alcohol consumption. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 21(5), 535–553.
Van Ameringen, M., Mancini, C., Styan, G., & Donison, D. (1991). Relationship of social phobia with other psychiatric illness. Journal of Affective Disorders, 21, 93–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ham, L.S., Hope, D.A., White, C.S. et al. Alcohol Expectancies and Drinking Behavior in Adults with Social Anxiety Disorder and Dysthymia. Cognitive Therapy and Research 26, 275–288 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014582005745
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014582005745