Abstract
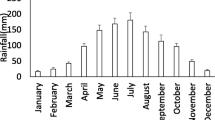
The benthic macroinvertebrate community (BMC) of Lake Tecuitlapa Sur, central Mexico, was monitored to determine the structure of the community (i.e. species composition, richness, abundance and biomass), throughout an annual cycle. Tecuitlapa Sur is shallow, seasonally-astatic, warm, mesosaline, and soda-alkaline. The physical, chemical and biological variables were determined monthly for a yearly cycle. Tecuitlapa Sur displayed a seasonal patterns of dilution (June–August) and concentration (September–November) phases. Salinity and pH were the most important parameters explaining environmental variance. The BMC consisted of two species: Culicoides occidentalis sonorensis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) and Tanypus Apelopia sp. (Diptera: Chironomidae). C. occidentalis was the most important species both numerically and in biomass (≥95%). Annual density (mean ± sd) of C. occidentalis (1 141 082 ± 2 765 879 ind. m−2, n = 120) was notably higher than other reported for other saline water bodies. However, the mean annual density of T. Apelopia (6782 ± 8310 ind. m−2, n = 120) was similar to other saline lakes. Seasonal abundance and biomass dynamics of the BMC showed an increasing trend until October (T. Apelopia) and November (C. occidentalis), when massive emergence occurred, just before the lake dried out. Contrary to most temporal waters, Tecuitlapa Sur did not show taxonomic or trophic succession. C. occidentalis, a transient detritivore, dominated over T. Apelopia, a resident predator during the wet period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcocer, J., 1995. Análisis holístico de la comunidad de macroinvertebrados bentónicos litorales de seis lagos-cráter con un gradiente de salinidad. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Facultad de Ciencias. México: 106 pp.
Alcocer, J. & U. T. Hammer, 1998. Saline lake ecosystems of Mexico. Aquat. Ecosystems Health and Management 1: 291–315.
Alcocer, J., A. Lugo, E. Escobar & M. Sánchez, 1997. The macrobenthic fauna of a former perennial and now episodically filled Mexican saline lake. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 5: 1–14.
Alcocer, J., E. Escobar, A. Lugo & L. A. Oseguera, 1999. Benthos of a perennially-astatic, saline, soda lake in Mexico. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 8: 113–126.
Bayly, I. A. E. & W. D. Williams, 1973. Inland Waters and their Ecology. Longman, Melbourne: 314 pp.
Boulton, A. J. & M. A. Brock, 1999. Australian Freshwater Ecology. Processes and Management. Cooperative Research Center for Freshwater Ecology, Australia: 300 pp.
Colburn, E. A., 1988. Factors influencing species diversity in saline waters of Death Valley, U.S.A. Hydrobiologia 158: 215–226.
Dejoux, C., 1993. Benthic macroinvertebrates of some saline lakes of the Sud Lipez region, Bolivia. Hydrobiologia 267: 257–267.
García, E., 1988. Modificaciones al Sistema de Clasificación Climática de Köppen. E. García, México: 217 pp.
Hammer, U. T., J. S. Sheard & J. Kranabetter, 1990. Distribution and abundance of littoral benthic fauna in Canadian prairie saline lakes. Hydrobiologia 197: 173–192.
Hayford, B. L., J. E. Sublette & S. J. Hermann, 1995. Distribution of chironomids (Diptera: Chironomidae) and ceratopogonids (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) along a Colorado thermal spring effluent. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 68: 77–92.
Herbst, D. B., 1988. Comparative population ecology of Ephydra hians Say (Diptera: Ephydridae) at Mono Lake (California) and Abert Lake (Oregon). Hydrobiologia 158: 145–166.
Linley, J. R. & G. M. Adams, 1972. Ecology and behavior of immature Culicoides melleus (Coq.) (Dipt., Ceratopogonidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 62: 113–127.
Linley, J. R., F. D. S. Evans & H. T. Evans, 1970. Seasonal emergence of Culicoides furens (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) at Vero Beach, Florida. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 5: 1332–1339.
Margalef, R., 1983. Limnología. Omega, Barcelona: 1010 pp.
McCafferty, W. P., 1981. Aquatic Entomology. Science Books International, Boston: 448 pp.
Moorhead, D. L., D. L. Hall & M. R. Willig, 1998. Succession of macroinvertebrates in playas of the Southern High Plains, U.S.A. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 17: 430–442.
Schneider, D. W. & T. M. Frost, 1996. Habitat duration and community structure in temporary ponds. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 15: 64–86.
Stahl, J. B., 1986. A six-year study of abundance and voltinism of Chironomidae (Diptera) in an Illinois cooling reservoir. Hydrobiologia 134: 67–79.
Timms, B. V., 1982. A study of the benthic communities of twenty lakes in South Island, New Zealand. Freshwat. Biol. 12: 123–138.
Timms, B. V., 1983. A study of benthic communities in some shallow saline lakes of western Victoria, Australia. Hydrobiologia 105: 165–177.
Vilaclara, G., M. Chávez, A. Lugo, H. González & M. Gaytán, 1993. Comparative description of crater-lakes basic chemistry in Puebla state, Mexico. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 25: 435–440.
Wiggins, G. B., R. J. Mackay & I. M. Smith, 1980. Evolutionary and ecological strategies of animals in annual temporary pools. Arch. Hydrobiol., Supple. 58: 97–206.
Wilbur, H. M., 1987. Regulation of structure in complex systems: experimental temporary pond communities. Ecology 68: 1437–1452.
Williams, D. D., 1987. The Ecology of Temporary Waters. Croom Helm, London: 205 pp.
Williams, D. D., 1996. Environmental constraints in temporary fresh waters and their consequences for the insect fauna. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 15: 634–650.
Williams, W. D. & M. J. Kokkinn, 1988. The biogeographical affinities of the fauna in episodically filled salt lakes: a study of Lake Eyre South, Australia. Hydrobiologia 158: 227–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcocer, J., Escobar, E.G., Lugo, A. et al. Benthos of a seasonally-astatic, saline, soda lake in Mexico. Hydrobiologia 466, 291–297 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014573920414
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014573920414