Abstract
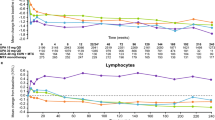
We assessed the correlations between some plasma markers of immune activation (soluble receptors of interleukin 2 (sIL2-R) and TNFαp75 (sTNFII-R) and usual markers of HIV infection in patients treated with protease-inhibitors (PI). Forty-six PI-naive HIV-1-infected adults were included in a 1-year prospective cohort from the initiation of a PI-containing regimen (M0). Measurements of CD4+cell count, plasma HIV-RNA, sIL2-R and sTNFII-R were performed at M0, M6, and M12. The evolution of sIL2-R from baseline to M12 was significantly different between immunological responders (IR) (CD4+count above 200/mm3 for subject having less than 200 CD4 +/mm3 at inclusion, or increase of at least 50 CD4+/mm3 for others) (58 UI/ml) and non-IR (+28 UI/ml) (P =0.01). The evolution of sTNFII-R between M0 and M12 was significantly different between virological responders (VR) (plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 500 copies/ml at M12) (−2.5 ng/ml) and non-VR (+0.2 ng/ml) (P =0.02). Our study shows significative correlations between the evolutions of soluble interleukin-2 and TNFR-II receptors and those of CD4+T-lymphocytes or HIV-RNA responses in patients under HAART.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hughes MD, Johnson VA, Hirsh MS, Bremer JW, Elbeik T, Erice A, Kuritzkes DR, Scott WA, Spector SA, Basgoz N, Fischl MA, D'Aquila RT: Monitoring plasma HIV-1 RNA levels in addition to CD4_lymphocyte count improves assessment of antiretroviral therapeutic response: ACTG Protocol Virology Substudy Team. Ann Intern Med 126:929–938, 1997
Mellors JW, Munoz A, Giorgi JV, Margolick JB, Tassoni CJ, Gupta P, Kingsley LA, Todd JA, Saah AJ, Detels R, Phair JP, Rinaldo CR Jr: Plasma viral load and CD4_lymphocytes as prognostic markers of HIV-1 infection. Ann Intern Med 126: 946–954, 1997
Fahey JL, Taylor JM, Detels R, Hofmann B, Melmed R, Nishanian P, Giorgi JV: The prognostic value of cellular and serologic markers in infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med 322:166–172, 1990
Godfried MH, van der Poll T, Weverling GJ, Mulder JW, Jansen J, van Deventer SJ, Sauerwein HP: Soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor as predictors of progression to AIDS in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Infect Dis169:739–745, 1994
Saves M, Morlat P, Chene G, Peuchant E, Pellegrin I, Bonnet F, Bernard N, Lacoste D, Salamon R, Beylot J: Prognostic value of immune activation in patients with advanced HIV disease treated by combination antiretroviral therapy. Clin Immunol 99:347–352, 2001
Fahey JL, Taylor JM, Manna B, Nishanian P, Aziz N, Giorgi JV, Detels R: Prognostic significance of plasma markers of immune activation, HIV viral load and CD4 T-cell measurements. AIDS 12:1581–1590, 1998
Matsuyama T, Kobayashi N, Yamamoto N: Cytokines and HIV infection: is AIDS a tumor necrosis factor disease? AIDS 5: 1405–1417, 1991
Noronha IL, Daniel V, Schimpf K, Opelz G: Soluble IL-2 receptor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in plasma of haemophilia patients infected with HIV. Clin Exp Immunol 87:287–292, 1992
Sulkowski MS, Chaisson RE, Karp CL, Moore RD, Margolick JB, Quinn TC: The effect of acute infectious illnesses on plasma human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 load and the expression of serologic markers of immune activation among HIVinfected adults. J Infect Dis 178:1642–1648, 1998
Sepkowitz KA: Effect of HAART on natural history of AIDSrelated opportunistic disorders. Lancet 351:228–230, 1998
Nokta M, Rossero R, Loesch K, Pollard RB: Kinetics of tumor necrosis factor alpha and soluble TNFRII in HIV-infected patients treated with a triple combination of stavudine, didanosine, and hydroxyurea. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 13:1633–1638, 1997
Chougnet C, Fowke KR, Mueller BU, Smith S, Zuckerman J, Jankelevitch S, Steinberg SM, Luban N, Pizzo PA, Shearer GM: Protease inhibitor and triple-drug therapy: Cellular immune parameters are not restored in pediatric AIDS patients after 6 months of treatment. AIDS 12:2397–2406, 1998
Aukrust P, Muller F, Lien E, Nordoy I, Liabakk NB, Kvale D, Espevik T, Froland SS: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) system levels in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients during highly active antiretroviral therapy: Persistent TNF activation is associ-ated with virologic and immunologic treatment failure. J Infect Dis 179:74–82, 1999
Merrill JE, Koyanagi Y, Chen IS: Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-A" can be induced from mononuclear phagocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by binding to the CD4 receptor. J Virol 63:4404–4408, 1989
Westendorp MO, Shatrov VA, Schulze-Osthoff K, Frank R, Kraft M, Los M, Krammer PH, Droge W, Lehmann V: HIV-1 Tat potentiates TNF-induced NF-kappa B activation and cytotoxicity by altering the cellular redox state. EMBO J 14:546–554, 1995
Duh EJ, Maury WJ, Folks TM, Fauci AS, Rabson AB: Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5974–5978, 1989
Matsuyama T, Hamamoto Y, Soma G, Mizuno D, Yamamoto N, Kobayashi N: Cytocidal effect of tumor necrosis factor on cells chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): Enhancement of HIV replication. J Virol 63:2504–2509, 1989
Stein DS, Lyles RH, Graham NM, Tassoni CJ, Margolick JB, Phair JP, Rinaldo C, Detels R, Saah A, Bilello J: Predicting clinical progression or death in subjects with early-stage human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: A comparative analysis of quantification of HIV RNA, soluble tumor necrosis factor type II receptors, neopterin, and beta2-microglobulin. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. J Infect Dis 176:1161–1167, 1997
La Maestra L, Zaninoni A, Marriott JB, Lazzarin A, Dalgleish AG, Barcellini W: The thalidomide analogue CC-3052 inhibits HIV-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) expression in acutely and chronically infected cells in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol 119:123–129, 2000
Moreira AL, Corral LG, Ye W, Johnson B, Stirling D, Muller GW, Freedman VH, Kaplan G: Thalidomide and thalidomide analogs reduce HIV type 1 replication in human macrophages in vitro. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 13:857–863, 1997
Jacobson JM, Greenspan JS, Spritzler J, Ketter N, Fahey JL, Jackson JB, Fox L, Chernoff M, Wu AW, MacPhail LA, Vasquez GJ, Wohl DA: Thalidomide for the treatment of oral aphthous ulcers in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases AIDS Clinical Trials Group. N Engl J Med 336:1487–1493, 1997
Salazar-Gonzalez JF, Martinez-Maza O, Nishanian P, Aziz N, Shen LP, Grosser S, Taylor J, Detels R, Fahey JL: Increased immune activation precedes the inflection point of CD4 T cells and the increased serum virus load in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis 178:423–430, 1998
Ortiz GM, Nixon DF, Trkola A, Binley J, Jin X, Bonhoeffer S, Kuebler PJ, Donahoe SM, Demoitie MA, Kakimoto WM, Ketas T, Clas B, Heymann JJ, Zhang L, Cao Y, Hurley A, Moore JP, Ho DD, Markowitz M: HIV-1-specific immune responses in subjects who temporaly contain virus replication after discontinuation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Invest 104:R13–18, 1999
Kaufmann D, Pantaleo G, Sudre P, Telenti A: CD4-cell count in HIV-1-infected individuals remaining viraemic with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Lancet 351:723–724, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonnet, F., Savès, M., Morlat, P. et al. Correlations of Soluble Interleukin-2 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Type II Receptors with Immunologic and Virologic Responses Under HAART. J Clin Immunol 22, 75–82 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014475618504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014475618504