Abstract
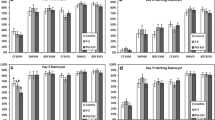
We studied the effects of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) on the development of parthenogenetic mouse embryos (CBA × C57BK/6)FF1. The parthenogenetic embryos were treated in vitro during the preimplantation period and, at the blastocyst stage, transplanted into the uterus of pseudopregnant females. The addition of FGF2 at an optimal dose (2.5 ng/ml) to the culture medium increased twofold the number of embryos developed in utero to the somite stages as compared to the control: 18 and 43%, respectively. The parthenogenetic embryos (18–21 somites), treated and nontreated with FGF2 during the preimplantation period, were explanted for further development in vitro and treated with IGF2 at 2.5 μg/ml. As a result, many more parthenogenetic embryos (> 87%) of both groups developed in vitro to the stage of 30 or more somites as compared to the control (59%). More than a half of FGF-2-treated parthenogenetic embryos developed to the stage of 40 and some of them, to the stage of 50 somites. The treatment of the parthenogenetic embryos with FGF2 alone at the preimplantation stages did not improve their development in vitro at the postimplantation stages. The results we obtained suggest that the treatment of parthenogenetic embryosin vitro with FGF2 during the preimplantation period increased twofold the number of somite embryos in utero, while their subsequent treatmentin vitro with IGF2 leads to a significant prolongation of their development, as compared to the control.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abramczuk, J., Solter, D., and Koprowski, H., The Beneficial Effect of EDTA on Development of Mouse One-Cell Embryos in Chemically Defined Medium, Devel. Biol., 1977, vol. 61, pp. 378-383.
Ambrosetti, D.C., Basilico, C., and Dailey, L., Synergistic Activation of the Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 Enhancer by Sox-2 and Oct-3 Depends on Protein-Protein Interactions Facilitated by a Specific Spatial Arrangement of Factor Binding Sites, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1997, vol. 17, pp. 6321-6329.
Baker, H., Liu, J.-P., Robertson, E.J., and Efstratiadis, A., Role of IGFs in Embryonic and Postnatal Growth, Cell, 1993, vol. 75, pp. 73-82.
Barlow, D.P., Stoger, B.G., Hartmann, B.G., et al., The Mouse Insulin-Like Growth Factor Type-2 Receptor Is Imprinted and Closely Linked to the Tme locus, Nature, 1991, vol. 349, pp. 84-87.
Basilico, C. and Moscatelli, D., The FGF Family of Growth Factors and Oncogenes, Adv. Cancer Res., 1992, vol. 59, pp. 115-165.
Burdsal, C.A., Flannery, M.L., and Pedersen, R.A., FGF-2 Alters the Fate of Mouse Epiblast from Ectoderm to Mesoderm in vitro, Devel. Biol., 1998, vol. 198, pp. 231-244.
Coulier, P., Pontarotti, P., Roubin, R., et al., Of Worms and Men: An Evolutionary Perspective on the Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) and FGF Receptor Families, J. Mol. Evol., 1997, vol. 44, pp. 43-56.
Crossley, P.M. and Martin, G.R., The Mouse Fgf-8 Gene Encodes a Family of Polypeptides and Is Expressed in Regions That Direct Outgrowth and Patterning in the Developing Embryo, Development, 1995, vol. 121, pp. 439-451.
DeChiara, T.M., Robertson, E.J., and Efstratiadis, A., Parental Imprinting of the Mouse Insulin-Like Growth Factor II gene, Cell, 1991, vol. 64, pp. 849-859.
Doherty, A.S., Mann, M.R.W., Tremblay, K.D., et al., Differential Effects of Culture on Imprinted H19 Expression in the Preimplantation Mouse Embryo, Biol. Reprod., 2000, vol. 62, pp. 1526-1535.
Dono, R., Texido, G., Dussel, R., et al., Impaired Cerebral Cortex H Development and Blood Pressure Regulation in FGF-2-Deficient Mice, EMBO J., 1998, vol. 17, pp. 4213-4225.
Dyban, A.P. and Khozhai, L.I., Parthenogenetic Development of Ovulated Murine Eggs Induced by Ethyl Alcohol, Byull. Eksperim. Biol. Med., 1980, vol. 139, pp. 487-489.
Engstrom, W., Shokrai, A., Otte, K., et al., Transcriptional Regulation and Biological Significance of the Insulin Like Growth Factor H Gene, Cell Prolif., 1998, vol. 31, pp. 173-189.
Feldman, B., Poueymirou, W., Papaioannou, V.E., et al., Requirement of FGF-4 for Postimplantation Mouse Development, Science, 1995, vol. 267, pp. 246-249.
Froesch, E. R., Schmid, Chr., Schwander, J., and Zapf, J., Actions of Insulin-Like Growth Factors, Ann. Rev. Physiol., 1985, vol. 47, pp. 443-467.
Gospodarowicz, D., Localisation of a Fibroblast Growth Factor and Its Effect Alone and with Hydrocortisone on 3T3 Cell Growth, Nature, 1974, vol. 249, pp. 123-127.
Haub, O. and Goldfarb, M., Expression of the Fibroblast Growth Factor-5 Gene in the Mouse Embryo, Development, 1991, vol. 112, pp. 397-406.
Hébert, J.M., Rosenquist, T., Götz, J., and Martin, G.R., FGF5 as a Regulator of the Hair Growth Cycle: Evidence from Targeted and Spontaneous Mutations, Cell, 1994, vol. 78, pp. 1017-1025.
Hoshikawa, M., Ohbayashi, N., Yonamine, A., et al., Structure and Expression of a Novel Fibroblast Growth Factor, fgf-17, Preferentially Expressed in the Embryonic Brain, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1998, vol. 244, pp. 187-191.
Hunter, E.S., Balkan, W., and Sadler, T.W., Improved Growth and Development of Presomite Mouse Embryos in Whole Embryo Culture, J. Exp. Zool., 1988, vol. 245, pp. 264-269.
Kaufman, M.H., The Chromosome Complement of Single Pronuclear Haploid Mouse Embryos, Following Activation by Ethanol Treatment, J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1982, vol. 71, pp. 139-154.
Keresztes, M. and Boonstra, J., Import(ance) of Growth Factors in(to) the Nucleus, J. Cell Biol., 1999, vol. 145, pp. 421-424.
Kono, T., Obata, Y., Yoshimizu, T., et al., Epigenetic Modi-fications during Oocyte Growth Correlates with Extended Parthenogenetic Development in the Mouse, Nat. Genet., 1996, vol. 13, pp. 91-94.
Konyukhov, B.V. and Isaev, D.A., Use of Chimeric Mice for Studying the Effects of Genomic Imprinting, Ontogenes, 2000, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 360-367.
Konyukhov, B.V. and Platonov, E.S., Genomic Imprinting in Mammals, Genetika, 2001, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 5-17.
Latham, K.E., Doherty, A.S., Scott, C.D., and Schultz, R.M., Igf2r and Igf2 Gene Expression in Androgenetic, Gynogenetic and Parthenogenetic Preimplantation Mouse Embryos: Absence of Regulation by Genomic Imprinting, Genes Dev., 1994, vol. 8, pp. 290-299.
Lerchner, W. and Barlow, D.P., Paternal Repression of the Imprinted Mouse Igf2r Locus Occurs during Implantation and Is Stable in All Tissues of the Postimplantation Mouse Embryo, Mech. Dev., 1997, vol. 1, pp. 141-149.
Lovicu, F.J. and Overbeek, P.A., Overlapping Effects of Different Members of the FGF Family on Lens Fiber Differentiation in Transgenic Mice, Development, 1998, vol. 125, pp. 3365-3377.
Mansour, S.L., Goddard, J.M., and Capecchi, M.R., Mice Homozygous for a Targeted Disruption of the Proto-Oncogene int-2 Have Developmental Defects in the Tail and Inner Ear, Development, 1993, vol. 117, pp. 13-28.
Mason, I., The Ins and Outs of Fibroblast Growth Factors, Cell, 1994, vol. 78, pp. 547-552.
McGrath, J. and Solter, D., Completion of Mouse Embryogenesis Requires both the Maternal and Paternal Genomes, Cell, 1984, vol. 7, pp. 179-183.
Moscatelli, D. and Quarto, N., Transformation of NIH 3T3 Cells Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor or the hst/K-fgf Oncogene Causes Down Regulation of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor: Reversal of Morphological Transformation and Restoration of Receptor Number by Suramin, J. Cell Biol., 1989, vol. 109, pp. 2519-2527.
Moses, A.C., Nissley, S.P., Short, P.A., et al., Increased Levels of Multiplication-Stimulating Activity, an Insulin-Like Growth Factor in Fetal Rat Serum, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1980, vol. 77, pp. 3649-3653.
New, D.A.T. and Cockroft, D.L., A Rotating Bottle Culture Method with Continuous Replacement of the Gas Phase, Experientia, 1979, vol. 35, pp. 138-139.
Newman-Smith, E.D. and Werb, Z., Stem Cell Defects in Parthenogenetic Preimplantation Embryos, Development, 1995, vol. 121, pp. 2069-2077.
Nielsen, L.L., Werb, Z., and Pedersen, R.A., Induction of cfos Transcripts in Early Postimplantation Mouse Embryos by TGF-α, EGF, PDGF, and FGF, Mol. Reprod. Dev., 1991, vol. 29, pp. 227-237.
Niswander, L. and Martin, G.M., Fgf-4 Expression during Gastrulation, Myogenesis, Limb and Tooth Development in the Mouse, Development, 1992, vol. 114, pp. 755-768.
Obata, Y., Kaneko-Ishino, T., Koide, T., et al., Disruption of Primary Imprinting during Oocyte Growth Leads to the Modified Expression of Imprinted Genes during Embryogenesis, Development, 1998, vol. 125, pp. 1553-1560.
Penkov, L.I. and Platonov E.S., Effects of Fibroblastic Growth Factors (FGF-2 and FGF-4) on Development of Parthenogenetic Mouse Embryos, Ontogenes, 1999, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 448-452.
Penkov, L.I., Platonov, E.S., and New, D.A.T., Prolonged Development of Normal and Parthenogenetic Postimplantation Mouse Embryos in vitro, Int. J. Dev. Biol., 1995, vol. 39, pp. 985-999.
Penkov, L.I., Platonov, E.S., Mironova, O.V., and Konyukhov, B.V., Effects of 5-Azacytidine on the Development of Parthenogenetic Mouse Embryos, Devel. Growth Differ., 1996, vol. 38, pp. 263-270.
Rappolee, D.A., Brenner, C.A., and Schultz, R., Developmental Expression of PDGF, TGF-α, and TGF-α-Genes in Preimplantation Mouse Embrvos, Science, 1988, vol. 241, pp. 1823-1825.
Rappolee, D.A., Sturm, K.S., and Schultz, G.A., et al., The Expression of Growth Factor Ligands and Receptors in Preimplantation Mouse Embryos, Early Embryo Development and Paracrine Relationships, Heyner, S. and Wileys, L.M., Eds., New York: Wiley-Liss, 1990, pp. 11-25.
Rappolee, D.A., Sturm, K.S., Behrendtsen, O., et al., Insulin-Like Growth Factor II Acts through an Endogenous Growth Pathway Regulated by Imprinting in Early Mouse Embryos, Genes Devel., 1992, vol. 6, pp. 939-952.
Robertson, E.J., Insulin-Like Growth Factors, Imprinting and Embryonic Growth Control, Semin. Devel. Biol., 1995, vol. 6, pp. 293-299.
Sadler, T.W. and New, D.A.T., Culture of Mouse Embryos during Neurulation, J. Embrvol. Exp. Morphol., 1981, vol. 66, pp. 109-116.
Sasaki, H., Ferguson-Smith, A.C., Shum, A.S.W., et al., Temporal and Spatial Regulation of H19 Imprinting in Early Embryogenesis, Development, 1995, vol. 121, pp. 4195-4202.
Slack, J.M.W., Darlington, E.G., Heath, J.K., and Godsave, S.F., Mesoderm Induction in Early Xenopus Embryos by Heparin-Binding Growth Factors, Nature, 1987, vol. 326, pp. 197-200.
Steele, C.E. and New, D.A.T., Serum Variants Causing the Formation of Double Hearts and Other Abnormalities in Explanted Rat Embryos, J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 1974, vol. 31, pp. 707-719.
Surani, M.A.H. and Barton, S.C., Development of Gynogenetic Eggs in the Mouse: Implication for Parthenogenetic Embryos, Science, 1983, vol. 222, pp. 1034-1036.
Surani, M.A.H., Barton, S.C., and Norris, M.L., Development of Reconstituted Mouse Eggs Suggests Imprinting of the Genome during Gametogenesis, Nature, 1984, vol. 308, pp. 548-550.
Wilkinson, D.G., Peters, G., Dickson, C., and McMahon, A.P., Expression of the FGF-Related Proto-Oncogene int-2 during Gastrulation and Neurulation in the Mouse, EMBO J., 1988, vol. 7, pp. 691-695.
Yamaguchi, T.P. and Rossant, J., Fibroblast Growth Factors in Mammalian Development, Curr. Biol., 1995, vol. 5, pp. 485-491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platonov, E.S., Penkov, L. & New, D.A.T. Effects of Growth Factors FGF2 and IGF2 on the Development of Parthenogenetic Mouse Embryos in utero and in vitro. Russian Journal of Developmental Biology 33, 52–58 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013877113325
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013877113325