Abstract
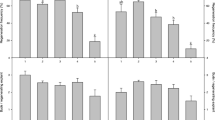
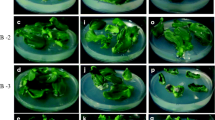
Efficient protocols have been developed to induce adventitious shoots in different types of explants of Campanula carpatica Jacq. More than five shoots per explant developed on hypocotyls of 5-week-old seedlings after 2 weeks of culture. Hypocotyls produced twice as many shoots as the cotyledons. TDZ proved to be about 6 times more efficient than BA. NAA had to be added to the regeneration medium to obtain the optimal balance of auxin and cytokinin to induce shoot regeneration. Significant differences were noted between different growth regulator concentrations in their effects on shoot organogenesis. BA induced double the number of callus clumps as TDZ. Incubation of explants in the dark produced about 6 shoots per explant while those in the light produced about 2 shoots per explant. Explants derived from 5-week-old seedlings were five times more regenerative compared to those derived from 15-week-old seedlings. Explants from cv. White Uniform were more organogenic than those from cv. Blue Clip. Root segments were also found to form shoots when treated with CPPU.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandt K (1992) Micropropagation of Campanula isophylla Moretti. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 29: 31–36
Brandt K (1994) Variation among and within clones in formation of roots and shoots during micropropagation of Campanula isophylla. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 39: 63–68
Bergmann BA & Stomp AM (1994) Effect of genotype on in vitro adventitious shoot formation in Pinus radiata and correlations between pairs of phenotypic traits during in vitro shoot development. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 39: 185–194
Christy CC (1997). Transgenic crop plants using Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation. In: Doran PM (ed) Hairy Root Culture and Applications (pp 99–111). Harwood Academic Publishers, Netherlands
Colinjn-Hooymans CM, Hakket JC, Jansen J & Custers JBM (1994) Competence for regeneration of cucumber cotyledons is restricted to specific developmental stages. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 39: 211–217
Gronroos L, Kubat B, Von Arnold S & Elliasson L (1989) Cytokinin contents in shoot cultures of four Salix clones. J. Plant Physiol. 153: 150–154
Luping Q, Polashock J & Nicholi V (2000) A highly efficient in vitro cranberry regeneration system using leaf explants. HortScience 35: 948–952
Millan-Mendoza B & Graham J (1999) Organogenesis and micropropagation in red raspberry using forchlorfenuron (CPPU). J. Hort. Sci. Biotech. 74: 219–223
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Staba JE (1969) Plant tissue culture as a technique for the phytochemist. Recent Adv. Phytochem. 2: 80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sriskandarajah, S., Frello, S. & Serek, M. Induction of adventitious shoots in vitro in Campanula carpatica. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 67, 295–298 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012786818689
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012786818689