Abstract
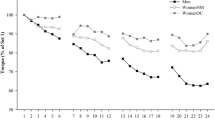
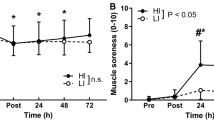
This study tested the hypothesis that estrogen levels of women influences the development of a muscle-tissue damage (creatine kinase, CK) marker and delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) following eccentric exercise. Seventeen oral contraceptive (OC) users and ten eumenorrheic (EU) subjects completed a 30-min downhill run at ∼60% VO2max. The OC completed the exercise during the midluteal phase (day 22.9 ± 1.5; high estrogen) while the EU did their exercise in the midfollicular phase (day 9.6 ± 4.4; low estrogen) of the menstrual cycle, respectively. The CK activity and DOMS were assessed preexercise, immediately postexcercise, 24, 48, and 72 h postexercise. ANOVA results indicated that there was a significant increase in CK activity in response to the downhill run (p< 0.001), and the interaction of group x time was significantly different (p< 0.01). The OC group had lower CK at 72 h postexercise than did the EU group. Preexercise estrogen levels correlated with the overall mean CK (r= –0.43. p< 0.05) and 72 h (r= –0.38, p < 0.05) responses, respectively. Exercise caused an increase in DOMS in both groups (p< 0.001); but, no significant interaction was observed. These findings suggest that elevated estrogen levels have a protective effect on muscle tissue following eccentric exercise. The mechanism of this protective effect is unclear, but it may be related to the antioxidant characteristics and membrane stability properties associated with estrogen and its derivatives.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Amelink, G.J., Koot, R.W., Erich, W.B., Van Gijn, J., and Bar, P.R., Sex-Linked Variation in Creatine Kinase Release and Its Dependence on Estradiol, Can Be Demonstrated in In Vitro Rat Skeletal Muscle Preparation, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1990, vol. 138, no. 2, pp. 115-124.
Bär, P.R., Amelink, G.J., Oldenburg, B., and Blankenstein, M.A., Prevention of Exercise-Induced Muscle Membrane Damage by Oestradiol, Life Sci., 1988, vol. 42, pp. 2677-2681.
Buckley-Bleiler, R., Maughan, R.J., Clarkson, P.M., Bleiler, T.L., and Whiting, P.H., Serum Creatine Kinase Activity after Isometric Exercise in Premenopausal and Postmenopausal Women, Exp. Aging Res., 1989, vol. 15, nos. 3-4, pp. 195-198.
Byrnes, W.C. and Clarkson, P.M., Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness Following Repeated Bouts of Downhill Running, J. Appl. Physol., 1985, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 710-715.
Byrnes, W.C. and Clarkson, P.M., Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness and Training, Clinics in Sports Medicine, 1986, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 605-614.
Clarkson, P.M. and Ebbeling, C., Investigation of Serum Creatine Kinase Variability after Muscle-Damaging Exercise, Clin. Sci., 1988, vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 257-261.
Clarkson, P.M., Byrnes, W.C., McCormick, K.M., Turcotte, L.P., and White, J.S., Muscle Soreness and Serum Creatine Kinase activity Following Isometric, Eccentric and Concentric Exercise, Int. J. Sports Med., 1986, vol. 7, pp. 152-155.
Freiden, J., Sjorstrom, M., and Ekblom, B., A Morphological Study of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness, Experimentia, 1981, vol. 37, pp. 506-507.
Hortobagyi, T. and Denahan, T., Variability in Creatine Kinase: Methodology, Exercise and Clinically Related Factors, Int. J. Sports Med., 1989, vol. 10, pp. 69-80.
Jackson, A.S. and Pollock, M.L., Practical Assessment of Body Composition, The Physician & Sports Medicine, 1985, vol. 13, pp. 76-90.
Kagan, V., Spirichev, V., Serbinova, E., Witt, E., Erin, A., and Packer, L., The Significance of Vitamin E and Free Radicals in Physical Exercise, Wolinsky, I. and Hickson, J., Eds., Nutrition in Exercise and Sport 2nd ed, Boca Raton, CRC Press, 1994, pp. 185-213.
Koot, R.W., Amelink, G.J., Blankenstein, M.A., and Bar, P.R., Tamoxifen and Estrogen Both Protect the Rat Muscle against Physiological Damage, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1991, vol. 40, nos. 4-6, pp. 689-695.
Kose, K., Dogan, P., and Ozesmi, C., Contraceptive Steroids Increase Erythroc-Lipid Peroxidation in Female Rats, Contraception, 1993, vol. 47, pp. 421-425.
Nakano, M., Sugloka, K., Naito, I., Susumu, T., and Niki, E., Novel and Potent Biological Antioxidants on Membrane Phospholipid Peroxidation: 2-Hydroxy Estrone and 2-Hydroxy Estradiol, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1987, vol. 142, pp. 919-924.
O'Grady, M., Hackney, A.C., Steinberg, K., and Schneider, K., Diclofenac Sodium Reduces Exercise Induced Injury in Human Skeletal Muscle, Med. Sci. Sports Exercise., 2000, vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 1191-1196.
Shumate, J., Brooke, M., Carroll, J., and Davis, J., Increased Serum Creatine Kinase after Exercise: A Sex Linked Phenomenon, Neurology, 1979, vol. 29, pp. 902-904.
Thompson, H.S., Hyatt, J.P., DeSouza, M.J., and Clarkson, P.M., The Effects of Oral Contraceptives on Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness Following Exercise, Contraception, 1997, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 59-65.
Tiidus, P.M., Can Estrogen Diminish Exercise Induced Muscle Damage? Can. J. Appl. Physiol., 1995, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 26-38.
Tiidus, P.M. and Bombardier, E., Oestrogen Attenuates Postexercise Myeloperoxidase Activity in Skeletal Muscle of Male Rats, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1999, vol. 166, no. 2, pp. 85-90.
Tiidus, P.M., Holden, D., Bombardier, E., and Zajchowski, S., Estrogen Influences Postexercise Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle Neutrophil Infiltration. The American College of Sports Medicine Meeting, Indianapolis, Indiana, 2000.
Van der Meulen, J., Kuipers, H., and Drukker, J., Relationship between Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Enzyme Release in Rats, J. Appl. Physiol., 1991, vol. 71, pp. 999-1004.
Wiseman, H., Quinn, P., and Halliwell, B., Tamoxifen and Related Compounds Decrease Membrane Fluidity in Liposomes, FEBS Lett., 1993, vol. 330, pp. 53-56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, A., Dobridge, J. & Hackney, A.C. Influence of Estrogen on Markers of Muscle Tissue Damage Following Eccentric Exercise. Human Physiology 27, 626–630 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012395831685
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012395831685