Abstract
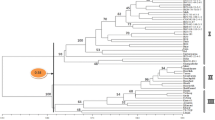
The use of bulked leaf samples from individual plants for amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis was evaluated as a tool for assessment of genetic diversity in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Bulking of leaf samples produced slightly simpler AFLP profiles compared to the combined profiles of individual plants from the same cultivar. Approximately 90% of bands which were present in individual plants were present in bulked samples of the same cultivar. The majority of those absent were rare bands, shared by less than 25% of individual plants. Replicate bulk samples gave almost identical banding patterns, demonstrating the robustness of the bulked AFLP technique. Cluster analysis of AFLP data derived from individual plants resulted in a phenogram similar to that produced from data derived from bulked samples of the same plants. AFLP analysis of bulked samples detected significant amounts of genetic variability among 52 cultivars and accessions with genetic similarity values ranging from 0.42 to 0.92. However, cluster analysis of AFLP data only partially reflected the geographic origin of cultivars and accessions and was not congruent with cluster analysis based on variation for morphophysiological characters. Bulked AFLP analysis provides a powerful tool for rapid assessment of genetic variability in white clover and may also be used for cultivar identification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwood, S.S., 1940. Genetics of cross-incompatibility among selfincompatible plants of Trifolium repens. J Am Soc Agron 32: 955–968.
Bachmann, K., 1994. Molecular markers in plant ecology. New Phytol 126: 403–418.
Beer, S.C., J. Goffreda, T.D. Phillips, J.P. Murphy & M.E. Sorrells, 1993. Assessment of genetic variation in Avena sterilis using morphological traits, isozymes and RFLPs. Crop Sci 33: 1386–1393.
Carnahan, H.L., 1960. A comparison of 1st and 2nd synthetic generation forage yields of ladino white clover in association with bromegrass. Agron J 52: 302.
Carnahan, H.L., H.D. Hill, A.A. Hanson & K.G. Brown, 1955. Inheritance and frequencies of leaf markings in white clover. J Hered 46: 109–114.
Chowdari, K.V., S.R. Venkatachalam, A.P. Davierwala, V.S. Gupta, P.K. Ranjekar & O.P. Govila, 1998. Hybrid performance and genetic distance as revealed by the (GATA)(4) microsatellite and RAPD markers in pearl millet. Theor Appl Genet 97: 163–169.
Crawford, D.J., E.J. Esselman, J.L. Windus & C.S. Pabin, 1998. Genetic variation in running buffalo clover (Trifolium stoloniferum - Fabaceae) using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers (RAPDs). Ann MO Bot Gard 85: 81–89.
Divaret, I., E. Margale & G. Thomas, 1999. RAPD markers on seed bulks efficiently assess the genetic diversity of a Brassica oleracea L. collection. Theor Appl Genet 98: 1029–1035.
Dulson, J., L.S. Kott & V.L. Ripley, 1998. Efficacy of bulked DNA samples for RAPD DNA fingerprinting of genetically complex Brassica napus cultivars. Euphytica 102: 65–70.
Excoffier, L., P.E. Smouse & J.M. Quattro, 1992. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131: 479–491.
Fernando, W.M.U., M.D. Hayward & M.J. Kearsey, 1997. Isozyme and quantitative traits polymorphisms in European provenances of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Euphytica 93: 263–269.
Fulton, T.M., J. Chunwongse & S.D. Tanskley, 1995. Microprep protocol for extraction of DNA from tomato and other herbaceous plants. Plant Molec Biol Rep 13: 207–209.
Gilbert, J.E., R.V. Lewis, M.J. Wilkinson & P.D.S. Caligari, 1999. Developing an appropriate strategy to assess genetic variability in plant germplasm collections. Theor Appl Genet 98: 1125–1131.
Golembiewski, R.C., T.K. Danneberger & P.M. Sweeney, 1997. Potential of RAPD markers for use in the identification of creeping bentgrass cultivars. Crop Sci 37: 212–214.
Gustine, D.L. & D.R. Huff, 1999. Genetic variation within and among white clover populations from managed permanent pastures of the northeastern USA. Crop Sci 39: 524–530.
Huff, D.R., 1997. RAPD characterisation of heterogeneous perennial ryegrass cultivars. Crop Sci 37: 557–564.
Jahufer, M.Z.Z., M. Cooper & L.A. Brien, 1994. Genotypic variation for stolen and other morphological attributes of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) populations and their influence on herbage yield in the summer rainfall region of New South Wales. Aust J Agric Res 45: 703–720.
Jones, C.J., K.J. Edwards, S. Castaglione, M.O. Winfield, F. Sala, C. Vandewiel, G. Bredemeijer, B. Vosman, M. Matthes, A. Daly, R. Brettschneider, P. Bettini, M. Buiatti, E. Maestri, A. Malcevschi, N. Marmiroli, R. Aert, G. Volckaert, J. Rueda, R. Linacero, A. Vazquez & A. Karp, 1997. Reproducibility testing of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers in plants by a network of European laboratories. Mol Breed 3: 381–390.
Joyce, T.A., M.T. Abberton, T.P.T. Michaelson-Yeates & J.W. Forster, 1999. Relationships between genetic distance measured by RAPD-PCR and heterosis in inbred lines of white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Euphytica 107: 159–165.
Kidwell, K.K., E.T. Bingham, D.R. Woodfield & T.C. Osborn, 1994. Relationships among genetic distance, forage yield and heterozygosity in isogenic diploid and tetraploid alfalfa populations. Theor Appl Genet 89: 323–328.
Kölliker, R., F.J. Stadelmann, B. Reidy & J. Nösberger, 1999. Genetic variability of forage grass cultivars: A comparison of Festuca pratensis Huds., Lolium perenne L. and Dactylis glomerata L. Euphytica 106: 261–270.
Kongkiatngam, P., M.J. Waterway, B.E. Coulman & M.G. Fortin, 1996. Genetic variation among cultivars of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) detected by RAPD markers amplified from bulk genomic DNA. Euphytica 89: 355–361.
Kongkiatngam, P., M.J. Waterway, M.G. Fortin & B.E. Coulman, 1995. Genetic variation within and between two cultivars of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) - Comparisons of morphological, isozyme, and RAPD markers. Euphytica 84: 237–246.
Kraft, T. & T. Sall, 1999. An evaluation of the use of pooled samples in studies of genetic variation. Heredity 82: 488–494.
Lee, C.K., H.A. Eagles, N.M. McFarlane & K.B. Kelly, 1993. Genetic variation within white clover (Trifolium repens L.) populations from North-Central Victoria. Aust J Exp Agric 33: 333–336.
Michelmore, R.W., I. Paran & R.V. Kesseli, 1991. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9828–9832.
Moreno-Gonzalez, J. & J.I. Cubero, 1993. Selection strategies and choice of breeding materials. In: M.D. Hayward, N.O. Bosemark & I. Romagosa (Eds.), Plant Breeding: Principles and Prospects, pp. 281–313. Chapman & Hall, London.
Mytton, L.R., 1975. Plant genotype x rhizobium strain interaction in white clover. Ann Appl Biol 80: 103–107.
Nei, M. & W.H. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 5269–5273.
Pejic, I., P. Ajmone-Marsan, M. Morgante, V. Kozumplick, P. Castiglioni, G. Taramino & M. Motto, 1998. Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs, and AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 97: 1248–1255.
Rafalski, J.A., J.M. Vogel, M. Morgante, W. Powell, C. Andre & S.V. Tingey, 1996. Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In: B. Birren & E. Lai (Eds.), Non-Mammalian Genomic Analysis: A Practical Guide, pp. 75–135. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego.
Rohlf, F.J., 1993. NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System. Exter Publishers, Setauket, NY.
Sambrook, J., E.F. Fritsch & T. Maniatis, 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, New York.
Staub, J.E., F.C. Serquen & M. Gupta, 1996. Genetic markers, map construction, and their application in plant breeding. Hortscience 31: 729–741.
Sweeney, P.M. & T.K. Danneberger, 1995. RAPD characterization of Poa annua L. populations in golf course greens and fairways. Crop Sci 35: 1676–1680.
Tohme, J., D.O. Gonzalez, S. Beebe & M.C. Duque, 1996. AFLP analysis of gene pools of a wild bean core collection. Crop Sci 36: 1375–1384.
Turkington, R., M.A. Cahn, A. Vardy & J.L. Harper, 1979. The growth, distribution, and neighbor-relationships of Trifolium repens in a permanent pasture. III. The establishment and growth of Trifolium repens in natural and perturbed sites. J Ecol 67: 231–243.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans, T. Vandelee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman, M. Kuiper & M. Zabeau, 1995. AFLP - a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Williams, W.M., 1987. Genetics and breeding. In: M.J. Baker & W.M. Williams (Eds.), White Clover, pp. 343–419. CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon.
Woodfield, D.R. & J.R. Caradus, 1990. Estimates of heritability for, and relationship between root and shoot characters of white clover. II. Regression progeny on mid parent. Euphytica 46: 211–215.
Xu, W.W., D.A. Sleper & G.F. Krause, 1991. Genetic diversity of tall fescue germplasm based on RFLPs. Crop Sci 34: 246–252.
Yu, K.F. & K.P. Pauls, 1993. Rapid estimation of genetic relatedness among heterogeneous populations of alfalfa by random amplification of bulked genomic DNA samples. Theor Appl Genet 86: 788–794.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kölliker, R., Jones, E., Jahufer, M. et al. Bulked AFLP analysis for the assessment of genetic diversity in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Euphytica 121, 305–315 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012048103585
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012048103585