Abstract
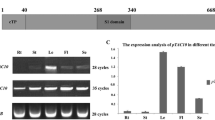
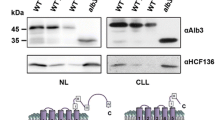
thi1 has been recently isolated fromArabidopsis thaliana and is probably involved in both thiamine biosynthesis and as protection of organellar DNA from damage. Studies of thiamine biosynthesis in plants suggests a plastid location for the pathway, which is in agreement with the predicted THI1 N-terminal chloroplastic transit peptide (TP). On the other hand, thiamine is synthesized in mitochondria in yeast cells. Interestingly, A. thaliana thi1 cDNA complements a yeast strain disrupted for the homologous gene. Analysis of THI1 amino acid sequence revealed the presence of a putative amphiphilic α-helix, which is typical for mitochondrial presequences, located downstream of the chloroplast transit peptide. To define the putative role of the two predicted targeting sequences in tandem, we produced two chimeric genes encompassing the chloroplastic THI1 TP and either 4 or 27 (including the putative mitochondrial presequence) N-terminal residues of the mature THI1, both linked to the reporter (gusA) gene. Analysis of GUS distribution in subcellular fractions of transgenic plants revealed that in the construct retaining only 4 residues of mature THI1, GUS was found in the chloroplastic fraction. Extension of the THI1 transit peptide to 27 residues of the mature protein allowed import and processing of GUS into both mitochondria and chloroplasts. Direct analysis by immunogold-labeling with an anti-THI1 polyclonal antibody identified THI1 in both organelles in Arabidopsis. We also provide evidence that the precursors of both organellar isoforms are encoded by a single nuclear transcript. Thus, THI1 is targeted simultaneously to mitochondria and chloroplasts by a post transcriptional mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addya, S., Anandatheerthavarada, H.K., Biswas, G., Bhagwat, S.V., Mullick, J. and Avadhani, N.G. 1997. Targeting of NH 2-terminal-processed microsomal protein to mitochondria: a novel pathway for the biogenesis of hepatic mitochondrial P450MT2. J. Cell Biol. 139: 589–599.
Akashi, K., Grandjean, O. and Small, I. 1998. Potential dual targeting of an Arabidopsis archaebacterial-like histidyl-tRNA synthase to mitochondria and chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 431: 39–44.
Barata, R.M., Chaparro, A., Chabregas, S.M., González, R., La-bate, C.A., Azevedo, R.A., Sarath, G., Lea, P.J. and Silva-Filho, M.C. 2000. Targeting of the soybean leghemoglobin to tobacco chloroplasts: effects on aerobic metabolism in transgenic plants. Plant Sci. 155: 193–202.
Belanger, F.C., Leustek T., Chu B. and Kriz, A.L. 1995. Evidence for the thiamine biosynthetic pathway in higher-plant plastids and its developmental regulation. Plant Mol. Biol. 29: 809–821.
Bhagwat, S.V., Biswas, G., Anandatheerthavarada, H.K., Addya, S, Pandak, W. and Avadhani, N.G. 1999. Dual targeting property of the N-terminal signal sequence of P4501A1. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 24014–24022.
Boutry, M., Nagy, F., Poulsen, C., Aoyagi, K. and Chua, N.-H. 1987. Targeting of bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase to mitochondria in transgenic plants. Nature 328: 340–342.
Brinck, S., Flügge, U.-I., Chaumont, F., Boutry, M., Emmermann, M., Schmitz, U., Becker, K. and Pfanner N. 1994. Preproteins of chloroplast envelope inner membrane contain targeting informa-tion for receptor-dependent import into fungal mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 16478–16485.
Bruce, B.D., Perry, S., Froehlich, J. and Keegstra, K. 1994. In vitro import of proteins into chloroplasts. In: S.B. Gelvin, and R.A. Schilperoort (Eds.) Plant Mol. Biol. Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Section J1, London, pp. 1–15.
Cartwright, P., Beilharz, T., Hansen, P., Garrett, J. and Lithgow, T. 1997. Mft52, an acid-bristle protein in the cytosol that delivers precursor proteins to yeast mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 5320–5325.
Chaumont, F., O'Riordan, V., and Boutry, M. 1990. Protein trans-port into mitochondria is conserved between plant and yeast species. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 16856–16862.
Chaumont, F., Silva-Filho, M.C., Thomas, D., Leterme, S. and Boutry, M. 1994. Truncated presequences of mitochondrial F 1-ATPas e β subunit from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia transport CAT and GUS proteins into mitochondria of transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol. 24: 631–641.
Chow, K.S., Singh, D.P., Roper, J.M and Smith, A.G. 1997. A single precursor protein for ferrochelatase-I from Arabidopsis is imported in vitro into both chloroplasts and mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 27565–27571.
Claros, M.G. and Vincens, P. 1997. Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur. J. Biochem. 241: 779–786.
Creissen, G., Reynolds, H., Xue, Y. and Mullineaux, P. 1995. Simul-taneous targeting of pea glutathione reductase and of a bacterial fusion protein to chloroplasts and mitochondria in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 8: 167–175.
Cunillera, N., Boronat, A. and Ferrer, A. 1997. The Arabidopsis thaliana FPS1 gene generates a novel mRNA that encodes a mitochondrial farnesyl-diphosphate synthase isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 15381–15388.
Danpure, C. 1995. How can the products of a single gene be localized to more than one intracellular compartiment? Trends Cell Biol. 5: 230–238.
Dreses-Werringloer, U., Fischer, K., Wachter, E., Link, T.A. and Flügge, U.-I. 1991. cDNA sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the precursor of the 37-kDa inner envelope membrane polypeptide from spinach chloroplasts. Its transit peptide contains an amphiphilic alpha-helix as the only detectable structural element. Eur. J. Biochem. 195: 361–368.
Flügge, U.-I., Fischer, K., Gross, A., Sebald, W., Lottspeich, F. and Eckerskorn, C. 1989. The triose phosphate-3-phosphoglycerate-phosphate translocator from spinach chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of full-length cDNA clone and import of the in vitro synthesized precursor protein into chloroplasts. EMBO J. 8 39–46
Franzén, L.G., Rochaix, J.D. and von Heijne, G. 1990. Chloroplast transit peptides from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii share features with both mitochondrial and higher plant chloroplast presequences. FEBS Lett. 260: 165–168.
Frohman, M.A., Dush, M.K. and Martin, G.R. 1988. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 8998–9002.
Glaser E., Sjöling, S., Tanudji, M. and Whelan, J. 1998. Mitochondrial protein import in plants. Signals, sorting, targeting, processing and regulation. Plant Mol. Biol. 38: 311–338.
Hachiya N., Alam R., Sakasegawa Y., Sakaguchi M., Mihara K and Omura T. 1993. A mitochondrial import factor purified from rat liver cytosol is an ATP-dependent conformational modulator for precursor proteins. EMBO J. 12: 1579–1586.
Höfgen, R. and Willmitzer, L. 1988. Storage competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucl. Acids Res. 16: 9877.
Huang, J., Hack, E., Thornburg, R.W. and Myers, A.M. 1990. A yeast mitochondrial leader peptide functions in vivo as a dual targeting signal for both chloroplast and mitochondria. Plant Cell 2: 1249–1260.
Hurt, E.C., Soltanifar, N., Goldschmidt-Clermont, M., Rochaix, J.-D. and Schatz, G. 1986. The cleavable pre-sequence of an imported chloroplast protein directs attached polypeptides into yeast mitochondria. EMBO J. 5: 1343–1350.
Jefferson, R.A., Kavanagh, T.A. and Bevan, MW. 1987. GUS fu-sions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 6: 3901–3907.
Joshi, C.P. 1987. An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucl. Acids Res. 15: 6643–6653.
Keegstra, K., Olsen, L.J. and Theg, S.M. 1989. Chloroplastic precursors and their transport across the envelope membranes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 40: 471–501.
Kim, Y.S., Nosaka, K., Downs, D.M., Kwak, J.M., Park, D., Chung, I.K. and Nam, H.G. 1998. A Brassica cDNA clone encoding a bi-functional hydroxymethylpyrimidine kinase/thiamin-phosphate pyrophosphorylase involved in thiamin biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 37: 955–966.
Knight, J.S. and Gray, J.C. 1994. Expression of genes encoding the tobacco chloroplast phosphate translocator is not light-regulated and is repressed by sucrose. Mol. Gen. Genet. 242: 586–594.
Lee, J.H. and Schöffl, F. 1997. GUS activity staining - a powerful tool in plant molecular biology. In: S.B. Gelvin and R.A. Schilperoort (Eds.) Plant Mol. Biol. Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Section C5, London, pp. 1–10.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L. and Randall, R.L. 1951. Protein mensurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
Machado, C.R., Costa de Oliveira, R.L., Boiteux, S., Praekelt, U.M., Meacock, P.A. and Menck, C.F.M. 1996. Thi1, a thi-amine biosynthetic gene in Arabidopsis thaliana, complements bacterial defects in DNA repair. Plant Mol. Biol. 31: 585–593.
Machado, C.R., Praekelt, U.M., Costa de Oliveira, R.L., Barbosa, A.C.C., Byrne, K.L., Meacock, P.A. and Menck, C.F.M. 1997. Dual role for the yeast THI4 gene in thiamine biosynthesis and DNA damage tolerance. J. Mol. Biol. 273: 114–121.
May, T. and Soll, J. 2000. 14-3-3 proteins form a guidance complex with chloroplast precursor proteins in plants. Plant Cell 12: 53–63.
Menand B., Marechal-Drouard L., Sakamoto W., Dietrich A. and Wintz H. 1998. A single gene of chloroplast origin codes for mitochondrial and chloroplastic methionyl-tRNA synthetase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 11014–11019.
Mireau, H., Lancelin, D. and Small, I.D. 1996. The same Arabidopsis gene encodes both cytosolic and mitochondrial alanyl-tRNA synthetases. Plant Cell 8: 1027–1039.
Murakami K., Tanase S., Morino Y. and Mori M. 1992. Presequence binding factor-dependent and-independent import of proteins into mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 13119–13122.
Neupert, W. 1997. Protein import into mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66: 863–917.
Pfaller, R., Pfanner, N. and Neupert, W. 1989. Mitochondrial protein import. bypass of proteinaceous surface receptors can occur with low specificity and efficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 34–39.
Praekelt, U., Byrne, K.L. and Meacock, P.A. 1994. Regulation of THI4 (MOL1), a thiamine-biosynthetic gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 10: 481–490.
Rogers S.G., Horsch R.B. and Fraley R.T. 1986. Gene-transfer in plants-production of transformed plants using Ti-plasmid vectors. Methods Enzymol. 118: 627–640.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Schmidt, G.W., Devillers-Thiery, A., Desrusseaux, H., Blobel, G.F. and Chua, N.-H. 1979. Biosynthetic pathways of two polypeptide subunits of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex. J. Cell Biol. 83: 615–622.
Schmitz, U. and Lonsdale, D.M. 1989. A yeast mitochondrial prese-quence functions as a signal for targeting to plant mitochondria in vivo. Plant Cell 1: 783–791.
Sharp, P.A., Berk, A.J. and Berget, S.M. 1980. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 65: 750–768.
Silva-Filho, M.C. 1999. Translocation of a reporter protein into mitochondria is mediated by a chloroplast transit peptide and follows a normal route. J. Plant Physiol. 151: 51–54.
Silva-Filho, M.C., Chaumont, F., Leterme, S. and Boutry M. 1996. Mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting sequences in tandem modify protein import specificity in plant organelles. Plant Mol. Biol. 30: 769–780.
Silva-Filho, M.C., Wieërs M.-C., Flügge, U.-I., Chaumont, F. and Boutry, M. 1997. Different in vitro and in vivo targeting properties of the transit peptide of a chloroplast envelope inne membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 15264–15269.
Small, I., Wintz, H., Akashi, K. and Mireau, H. 1998. Two birds with one stone: genes that encode products targeted to two or more compartments. Plant Mol. Biol. 38: 265–277.
Soll, J., and Tien, R. 1998. Protein translocation into and across the chloroplast envelope membranes. Plant Mol. Biol. 38: 191–207.
von Heijne, G. and Nishikawa, K. 1989. Chloroplast transit peptides. The perfect random coil? FEBS Lett. 278: 1–3.
von Heijne, G., Steppuhn, J. and Herrmann, R.G. 1989. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 180: 535–545.
Waegemann K. and Soll J. 1996. Phosphorylation of the transit sequence of chloroplast precursor proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 6545–6554.
Willey, D.L., Fischer, K., Wachter, E., Link, T.A. and Flügge, U.-I. 1991. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of the phos-phate translocator from pea chloroplasts and its comparison to the spinach phosphate translocator. Planta 183: 451–461.
Wimmer, B., Lottspeich, F., Van Der Klei, I., Veenhuis, M. and Gietl, C. 1997. The glyoxysomal and plastid molecular chaperones (70-kDa heat shock protein) of watermelon cotyledons are encoded by a single gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 13624–13629.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chabregas, S.M., Luche, D.D., Farias, L.P. et al. Dual targeting properties of the N-terminal signal sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana THI1 protein to mitochondria and chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 46, 639–650 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011628510711
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011628510711