Abstract
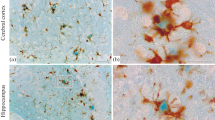
Post-mortem brain tissue was obtained from 28 patients with brain disorders, of which 15 had clinically diagnosed schizophrenia, 6 Alzheimer type dementia, 5 dementia with tangles and 2 cases of Down's syndrome. The controls were 22 cases from autopsies without brain disorders or with no known episodes of brain disorder. The tissues were stained for the detection of carbohydrate deposits in the hippocampal formation, using lectin, immunohistochemical and conventional staining methods. The staining revealed the existence of spherical deposits in the inner and middle molecular layers of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampal formation which contained fucose, galactose, N-acetyl galactosamine, N-acetyl glucosamine, sialic acid, mannose and chondroitin sulfate. The number of the deposits was higher in patients with brain disorder such as schizophrenia, Alzheimer type dementia, dementia with tangles or Down's syndrome, and in some aged individuals, in comparison to those in younger individuals. No deposits were detected in a few younger or aged individuals. Spherical deposits 3–10[emsp4 ]μm in diameter may be an immature form of the corpora amylacea, since they were similar in the histochemical characteristics with lectin, immunohistochemical and conventional staining methods. However, differing staining ability by hematoxylin, periodic acid Schiff's reagent and antibodies against the intracellular degraded proteins such as ubiquitin and tau-protein was observed. The antibodies against ubiquitin and tau-protein showed clear reactivity with the corpora amylacea and no reactivity with spherical deposits, indicating that the corpora amylacea has an intracellular origin and spherical deposits an extracellular matrix origin. The results obtained in this study indicate that not only neuronal degeneration but also unusual glycometabolism in neurons may disturb the neuronal function and cause brain disorders, and that spherical deposits may cause dysfunction of the neuronal network in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus which is closely linked with recognition and memory functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hakornori SI, Histochem J 24, 771–6 (1992).
Kobata A, Glycoconjugate J 15, 323–32 (1998).
Nishimura A, Sawada S, Ushiyama I, Yamamoto Y, Nakagawa T, Tanegashima A, Nishi K, Forensic Sci Int 113(1–3), 265–9 (2000).
Ito N, Nishi K, Nakajima Y, Okamura Y, Hirota T, Histochemistry 92, 307–12 (1989).
Ito N, Nishi K, Kawahara S, Okamura Y, Hirota T, Rand S, Fechner G, Brinkmann B, Histochemical J 22, 604–14 (1990).
Yamamoto Y, Li Y, Huang K, Ohkubo I, Nishi K, Forensic Sci Int 113(1–3), 143–6 (2000).
Sawada S, Nishimura A, Ushiyama I, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto Y, Nishi K, Forensic Pathology 6, 46–54 (2000) (in Japanese).
Tanegashima A, Nishi K, Fukunaga T, Rand S, Brinkmann B, Glycoconjugate J 13, 537–45 (1996).
Nishi K, Fukunaga T, Yamamoto Y, Yamada Y, Kane M, Tanegashima A, Rand S, Brinkmann B, Int J Legal Med 105, 75–80 (1992).
Cisse S, Perry G, Lacoste-Royal G, Cabana T, Gauvrean D, Acta Neuropathol 85, 233–40 (1993).
Allendoerfer KL, Magnani JL, Patterson PH, Mol Cell Neurosci 6(4), 381–95 (1995).
Wiederschain GYA, Koul O, Aucoin JM, Smith FI, McClur RH, Glycoconjugate J 15, 379–88 (1998).
Suzuki A, Protein, Nucleic Acid and Enzyme 43, 2631–9 (1998).
Fukuda M, Seikagaku 72, 269–83 (2000) (in Japanese).
Nagayana Y, Seitai no kagaku 50, 548–54 (1999) (in Japanese).
Hopfer RL, Johnson SW, Masserini M, Giuliani A, Alhadeff JA, Biochem J 266, 491–6 (1990).
Margolis RK, Margolis RU, Experimentia 49, 429–46 (1993).
Lorente NR, J Psychol Neurol 46, 113–177 (1934).
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH, Nat Med 4(11), 1313–7 (1998).
Bliss TVP, Lomo T, J Physiol (London) 232, 331–56 (1973).
Hill C, Keks N, Roberts S, Opeski K, Dean B, Am J Psychiatry 153, 533–7 (1996).
Grace AA, Brain Res Rev 31, 330–41 (2000).
Wang JZ, Grundeke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Nature Med 2, 871–5 (1996).
Snow AD, Sekiguchi RT, Nochin D, Kakaria RN, Kimata K, Am J Pathol 144, 337–47 (1994).
Mann DMA, Bonshek RE, Marcyniuk B, Stoddart RW, Torgerson E, Neurosci Lett 85, 277–82 (1988).
Shinghrao SK, Neal JW, Newman GR, Neuropathol App Neurobiol 19, 269–76 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimura, A., Ikemoto, K., Satoh, K. et al. The carbohydrate deposits detected by histochemical methods in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampal formation of patients with schizophrenia, Down's syndrome and dementia, and aged person. Glycoconj J 17, 815–822 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010996911581
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010996911581