Abstract
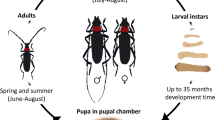
The South American tree Solanum mauritianum is a major environmental weed in the high-rainfall regions of South Africa and has been targeted for biological control. Potential agents included five species of the genus Platyphora, which were imported from South America in 1994. Platyphora species associated with Solanaceae reputedly have very specific habitat requirements and host plant preferences in the field. Despite this, host-specificity tests on one species, Platyphora semiviridis, revealed a broad physiological host range. Although laboratory tests showed that P. semiviridis is confined to Solanum species and cannot survive on solanaceous crops outside that genus, it developed on potato and cultivated eggplant (aubergine) as well as on 10 native South African Solanum species. With few exceptions, there were no consistent differences in survival and duration of development on these compared with S. mauritianum. Furthermore, at least six of these non-target species, including potato and eggplant, supported breeding colonies of the beetles in cages. During choice tests in both small and larger cages, P. semiviridis avoided potato but did not consistently discriminate between S. mauritianum, eggplant and six native solanums for larviposition. Despite these findings, P. semiviridis has never been recorded on either potato or eggplant in South America, where it was only observed to feed on S. mauritianum. Although there are several reasons why P. semiviridis is unlikely to attack non-target Solanum species in the field, it will not be released in South Africa because there are other imported agents which have displayed narrower physiological host ranges and which may be more effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annecke, D.P. and V.C. Moran, 1982. Insects and Mites of Cultivated Plants in South Africa. Butterworths, Durban.
Balciunas, J.K., D.W. Burrows and M.F. Purcell, 1996. Comparison of the physiological and realized host-ranges of a biological control agent from Australia for the control of the aquatic weed, Hydrilla verticillata. Biol. Contr. 7: 148-158.
Cullen, J.M., 1990. Current problems in host-specificity screening. In: E.S. Delfosse (ed), Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, March 6- 11, 1988, Italy, Instituto Sperimentale per la Patologia VegetaleMinistero dell'Agricoltura e delle Foreste, Rome, Italy. pp. 27-36.
D'Arcy, W.G., 1972. Solanaceae studies II: typification of subdivisions of Solanum. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.59: 262-278.
Hill, M.P. and P.E. Hulley, 1995. Biology and host range of Gratiana spadicea(Klug, 1829) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Cassidinae), a potential biological control agent for the weed Solanum sisymbriifoliumLamarck (Solanaceae) in South Africa. Biol. Contr.5: 345-352.
Hoffmann, J.H., 1995. Biological control of weeds: the way forward, a South African perspective. In: C.H. Stirton (ed), British Crop Protection Council Proceedings No. 64: Weeds in a Changing World, November 20, 1995, British Crop Protection Council, Farnham, UK. pp. 77-89.
Jaeger, P-M.L. and F.N. Hepper, 1986. A review of the genus Solanumin Africa. In: W.G. D'Arcy (ed), Solanaceae: biology and systematics. Columbia University Press, New York. pp. 41-45.
Jolivet, P.H. and T.J. Hawkeswood, 1995. Host-plants of Chrysomelidae of the world: an essay about the relationships between the leaf-beetles and their food-plants. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden.
Julien, M.H., 1992. Biological control of weeds: a world catalogue of agents and their target weeds(third edition). C.A.B. International, Wallingford.
Lorenzi, H., 1991. Plantas Daninhas do Brasil: terrestres, aquáticas, parasitas, tóxicas e medicinais (Segunda Edição). Editora Plantarum, Nova Odessa.
Maw, M.G., 1976. Biology of the tortoise beetle Cassida hemisphaerica(Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) a possible biological control agent for Bladder Campion Silene cucubalus(Caryophyllaceae) in Canada. Can. Entomol. 108: 945-954.
McFadyen, R.E.C., 1998. Biological control of weeds. Annu. Rev. Entomol.43: 369-393.
Medeiros, L. and J. Vasconcellos-Neto, 1994. Host plants and seasonal abundance patterns of some Brazilian Chrysomelidae. In: P.H. Jolivet, M.L. Cox and E. Petitpierre (eds), Novel aspects of the biology of Chrysomelidae, Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands. pp. 185-189.
Medeiros, L., D.N. Ferro and A. Mafra-Neto, 1996. Association of chrysomelid beetles with solanaceous plants in the south of Brazil. In: P.H. Jolivet and M.L. Cox (eds), Chrysomelidae biology, Vol. 2: Ecological studies. SPB Academic Publishing, Amsterdam. pp. 339-363.
Neser, S., H.G. Zimmermann, H.E. Erb and J.H. Hoffmann, 1990. Progress and prospects for the biological control of two Solanumweeds in South Africa. In: E.S. Delfosse (ed), Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds,March 6- 11, 1988, Italy, Instituto Sperimentale per la Patologia VegetaleMinistero dell'Agricoltura e delle Foreste, Rome, Italy. pp. 371-381.
Olckers, T., 1996. Improved prospects for biological control of three solanum weeds in South Africa. In: V.C. Moran and J.H. Hoffmann (eds), Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, January 19-26, 1996, University of Cape Town, South Africa. pp. 307-312.
Olckers, T. and P.E. Hulley, 1989. Insect herbivore diversity of the exotic weed Solanum mauritianumScop. and three other Solanumspecies in the eastern Cape. J. Ent. Soc. Sth. Afr.52: 81-93.
Olckers, T. and P.E. Hulley, 1991. Impoverished insect herbivore faunas on the exotic bugweed Solanum mauritianumScop. relative to indigenous Solanumspecies in Natal/KwaZulu and the Transkei. J. Ent. Soc. Sth. Afr.54: 39-50.
Olckers, T. and P.E. Hulley, 1994. Resolving ambiguous results of host-specificity tests: the case of two Leptinotarsaspecies (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) for biological control of Solanum elaeagnifoliumCavanilles (Solanaceae) in South Africa. Afr. Ent.2: 137-144.
Olckers, T. and H.G. Zimmermann, 1991. Biological control of silverleaf nightshade, Solanum elaeagnifolium, and bugweed, Solanum mauritianum(Solanaceae) in South Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ.37: 137-155.
Olckers, T., H.G. Zimmermann and J.H. Hoffmann, 1995. Interpreting ambiguous results of host-specificity tests in biological control of weeds: assessment of two Leptinotarsaspecies (Chrysomelidae) for the control of Solanum elaeagnifolium(Solanaceae) in South Africa. Biol. Contr.5: 336-344.
Roe, K.E., 1972. A revision of Solanumsect. Brevantherum(Solanaceae). Brittonia24: 239- 278.
Schroder, R.F.W., B. Puttler, S.S. Izhevsky and D. Gandolfo. 1994. Viviparity and larval development of Platyphora quadrisignata(Germar) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Brazil. Coleopt. Bull. 48: 237-243.
Silva, A.G.d'A., C.R. Gonçalves, D.M. Galvão, A.J.L. Gonçalves, J. Gomes, M.D. Silva and L. de Simoni, 1968. Quarto Catálogo dos Insetos que Vivem nas Plantas do Brasil seus Parasitos e Predatores, Parte 2-1 Tomo, Insetos, Hospedeiros e Inimigos Naturais.Ministério da Agricultura, Departemento de Defesa e Inspeção Agropecuária, Rio de Janeiro.
Teixeira, E.P. and S.A. Casari-Chen, 1992. Description of larvae and pupae of Stichotaenia conviva(Stål, 1858) and S. fasciatomaculata(Stål, 1857), with biological notes on the species (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae, Chrysomelinae). Revta bras. Ent.36: 779-786.
Wells, M.J., A.A. Balsinhas, H. Joffe, V.M. Engelbrecht, G. Harding and C.H. Stirton, 1986. A catalogue of problem plants in South Africa. Mem. Bot. Surv. S. Afr. No. 53. Botanical Research Institute, Department of Agriculture and Water Supply, Pretoria, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olckers, T. Biology and host range of Platyphora semiviridis, a leaf beetle evaluated as a potential biological control agent for Solanum mauritianum in South Africa. BioControl 43, 225–239 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009912011121
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009912011121